The electrical construction industry involves the design, installation, and maintenance of electrical systems and infrastructure in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. It comprises various professionals, like engineers, electricians, contractors, and project managers who work together to deliver quality electrical services. GAO RFID Inc., a global top 10 RFID leader based in New York and Toronto, has deployed several RFID, BLE, and IoT projects in the electrical construction industry to enhance safety, productivity, and efficiency.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for the Electrical Construction
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antennas, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including the electrical construction industry.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with important functions such as temperature, humidity, vibration, and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for all kinds of industries, including the electrical construction industry.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including the electrical construction industry:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, and wristbands for various industries, including the electrical construction industry:
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications), and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including the electrical construction industry:
- High Frequency 13.56 MHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 134 kHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 125 kHz Passive RFID Readers
HF, NFC, and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, and wristbands for various industries, including the electrical construction industry:
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers, Digital I/O adapters and relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules suitable for use in the electrical construction industry:
UHF 860-960 MHz RFID modules:
13.56 MHz high-frequency RFID modules:
125 kHz low-frequency RFID modules:
The RFID systems provided by GAO are highly popular among clients in the electrical construction industry for various purposes:
Personnel or worker tracking system:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
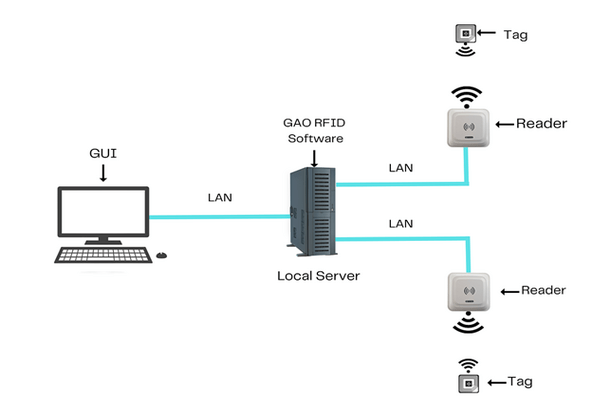
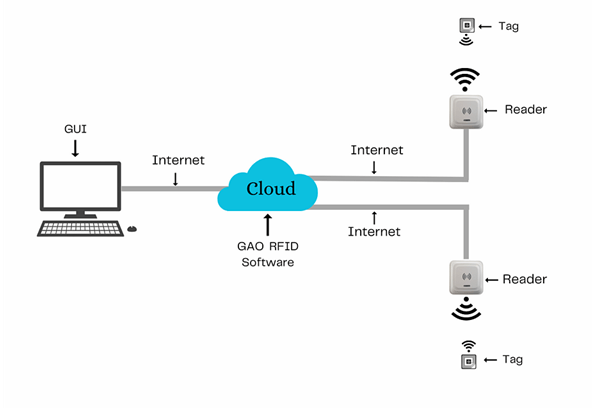
There are two versions of GAO’s software, one is running on a local server, and another running in the cloud.
Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for the Electrical Construction
RFID, BLE, IoT and drone technologies from GAO RFID Inc. offer many benefits for the electrical construction industry. These technologies can enhance the monitoring, tracking, and safety of workers and equipment, increase productivity, and reduce costs.
BLE technology is particularly useful on construction sites as it has a long range of up to 300 meters, which is more than the normal RFID range. This makes it an excellent choice for tracking workers and equipment at large construction sites. BLE can be used for access control, where authorized personnel can access specific zones while unauthorized individuals are restricted. By adding beacons to equipment such as power tools, test equipment, transformers, switchgear, panels, trucks, cranes, excavators, hard hats, gloves, safety glasses, harnesses, wires, cables, conduits, and pipes, workers can easily track them within the construction site. This reduces the need for manual processes and ensures that the necessary equipment is available when needed.
Drones equipped with RFID readers offer a portable and flexible option for tracking workers, tools, and equipment at large construction sites. They can detect safety hazards and provide a bird’s-eye view of the job site, allowing for better planning and monitoring of the construction process. Safety officers can use drones with RFID readers for safety management, eliminating the need for human intervention and automating time stamping. Drones flying around the site can be used to do cost-effective asset tracking and people tracking all over the active electrical construction site.
IoT sensors, such as humidity, temperature, and vibration sensors, can monitor inventory levels in real-time, ensuring that necessary components are available when needed. This reduces manual processes and allows workers to focus on critical tasks. By automating data such as storage area, supply levels, and usage, which can be achieved with BLE, workers can track wires, cables, conduits, and pipes that are often stored in various locations. Strategically placed gateways can ensure that theft and loss of equipment are prevented. Electricians, electrical engineers, project managers, estimators, inspectors, foremen, and other construction workers can also use BLE to track which tools have been tested and which ones have not, depending on the requirements of the work at an active electrical construction site. The system can also be customized to track the utilization of each supplied part, ensuring proper resource utilization. This helps project managers and warehouse managers create a decentralized inventory management system.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in electrical construction companies to deploy RFID systems and to ensure such deployments comply with the applicable industry standards, mandates and government regulations:
- National Electrical Code (NEC): The NEC, developed by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and adopted in the United States, sets the minimum safety standards for electrical systems in buildings.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations: OSHA is a federal agency that sets and enforces safety and health regulations in the workplace, including regulations covering various aspects of electrical safety such as electrical wiring, grounding, and the use of electrical equipment.
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations: Electrical construction companies must comply with EPA regulations related to hazardous waste, air quality, and water quality, as the agency is responsible for enforcing such regulations and ensuring proper disposal of hazardous waste or emissions from equipment used in their operations.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) regulations: NIOSH is a federal agency that conducts research and provides guidance on occupational safety and health issues, including electrical safety in the workplace through the development of guidelines and recommendations.
- Department of Energy (DOE) regulations: The DOE is responsible for regulating energy efficiency standards for electrical equipment and appliances, as well as promoting the use of renewable energy sources and electrical construction companies must comply with DOE regulations.
- Canadian Electrical Code (CEC): It covers all aspects of electrical installations, including wiring, grounding, protection, and more.
- Occupational Health and Safety Regulations: They cover issues such as training, protective equipment, and hazard identification and control.
- Environmental Protection Regulations: These regulations cover issues such as waste disposal, emissions, and more.
- Canadian Standards Association (CSA) Standards: Some of the key CSA standards for this industry include those related to electrical equipment, wiring, and more.
- Building Codes: These codes often include requirements for electrical installations, and they are enforced by municipal and provincial governments.
- Trade Regulations: These regulations ensure that workers have the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their jobs safely and effectively.
- ISO 18000-6C: This is a UHF Gen2 RFID standard that is commonly used in construction and industrial applications to track assets and manage inventory.
- ANSI C136.41: This is a standard for RFID-enabled street lighting control systems, which are commonly used in smart city applications.
- IEEE 802.11: This is a standard for Wi-Fi networks, which can be used in conjunction with RFID systems to provide wireless connectivity and location tracking.
- ZigBee: This is a standard for low-power wireless networks that are commonly used in building automation and smart home applications.
These standards, mandates and government regulations are important for ensuring interoperability between different RFID systems and ensuring that they meet the specific needs of the electrical construction industry.
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Here’s a brief case study of an RFID application in the electrical construction industry:
RFID implementation in the electrical construction industry is at the construction site of a large office building in a major city. Power tools, test equipment, transformers, switchgear, panels, trucks, cranes, excavators, hard hats, gloves, safety glasses, harnesses, wires, cables, conduits, and pipes were tagged with RFID tags, which included information such as the type of material, its location on the site, and its current status (e.g., in transit, in storage, in use). The RFID tags were read using handheld RFID scanners, and the data was uploaded to a central database in real time. This allowed the construction company to track the movement of materials and prevent theft or loss of materials, as any unauthorized movement of tagged items would be immediately detected.
Here is another case study of RFID application in the electrical construction industry:
A large electrical contractor was experiencing difficulties with tracking power tools, test equipment, transformers, switchgear, panels, trucks, cranes, excavators, hard hats, gloves, safety glasses, harnesses, wires, cables, conduits, and pipes at job sites. They were constantly losing expensive equipment, which resulted in delays, increased costs, and decreased productivity. In order to solve this problem, they turned to RFID technology. The contractor implemented an RFID system that tracked the location of each piece of equipment in real time by attaching RFID tags to them and installing RFID readers at the entrance and exit of job sites. Whenever a piece of equipment entered or exited a job site, the RFID tag was read, and the equipment’s location was updated in the system.
By implementing an RFID system, the contractor could monitor equipment location in real-time, reducing search time and costs for lost equipment, and deterring theft by alerting unauthorized equipment movement.
GAO Has Served the Electrical Construction Extensively
GAO RFID Inc., a global top 10 leader in RFID, has served many leading companies in the electrical construction industry, including its various divisions such as:
- Residential electrical work – This includes the installation and maintenance of electrical systems in single-family homes, multi-family housing units, and other residential buildings.
- Commercial electrical work – This involves the installation and maintenance of electrical systems in commercial buildings such as offices, retail stores, and other commercial facilities.
- Industrial electrical work – This includes the installation and maintenance of electrical systems in industrial facilities such as factories, power plants, and other heavy industrial settings.
- Power and energy systems – This involves the installation and maintenance of electrical systems related to power generation, transmission, and distribution.
- Telecommunications and data systems – This includes the installation and maintenance of electrical systems related to telecommunications and data networking, including cabling, fiber optics, and other advanced technologies.
List of the Leading Companies in the electrical construction industry in the U.S.:
List of the Leading Companies in the electrical construction industry in the Canada: