RFID and the Supply Chain Industry
The Supply Chain & Logistics industries consist of sectors such as rail, vessel, and pipeline transport, freight trucking, warehousing and storage, and even couriers and postal services.
Moving goods from location to location depends on effective inventory management, efficient maintenance of vehicles and overall security. GAO RFID’s solutions provide technology that enable the accurate and effective management of supply chain & logistics to ensure business success.
SPECIFIC RFID SOLUTIONS
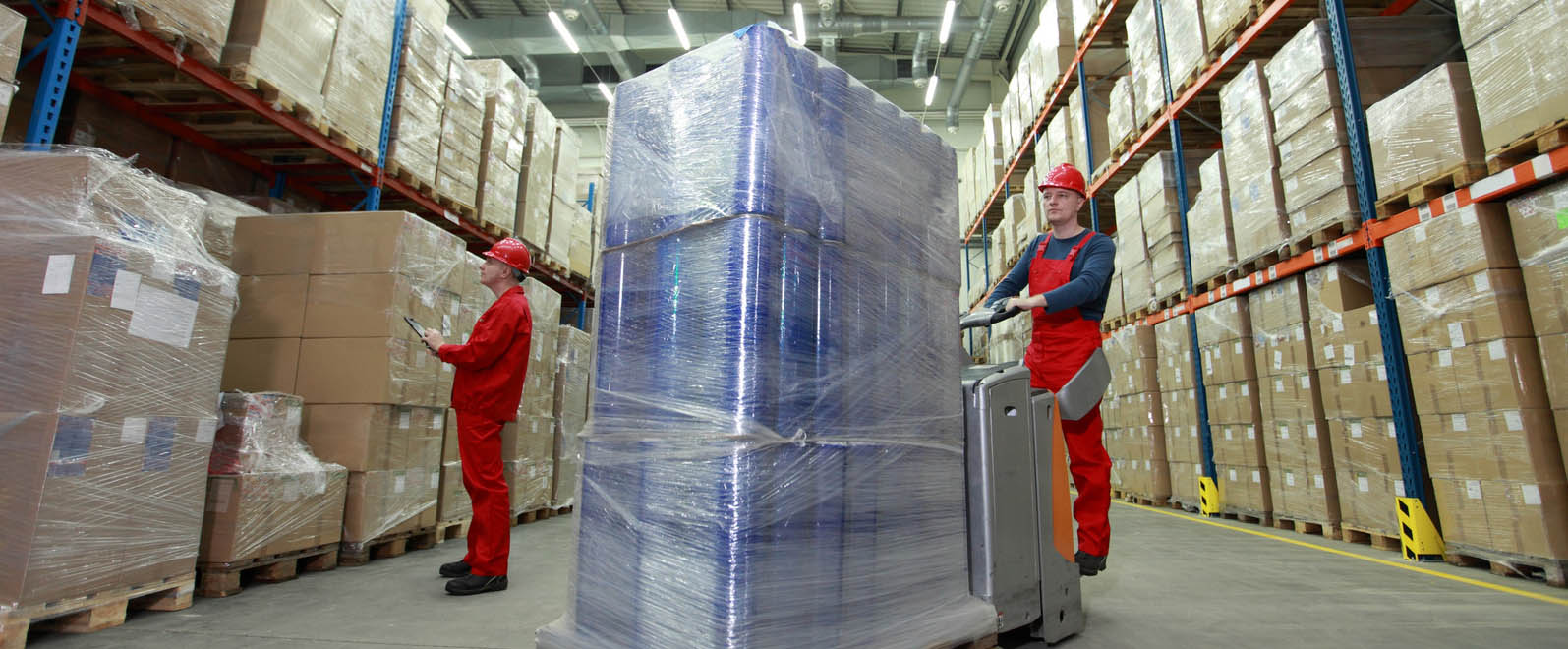
Warehouse & Storage
Warehouse and Storage Industry Solutions
Postal Industry
Postal & Courier Solutions
MORE SUPPLY CHAIN TOPICS
Employee Management – One of the greatest difficulties truck drivers face has to do with time management. By law, truck drivers are required to follow the 14-hour rule, which dictates that shifts can last 14 hours. However, drivers cannot drive without stopping for 11 hours straight and must take a minimum half hour break after driving straight for 8. Both companies and drivers can be held liable if this rule is not followed. With the help of RFID, employees can log in and out for driving duty and breaks, with the added safety regulation of being able to confirm a truck is in fact at a standstill. These RFID systems can be incorporated into the cabins of trucks matched with driver badges. RFID can also help with payroll by confirming when an employee clocks in or out, thereby creating a more efficient system.
Inventory and Maintenance – Multiple shipments come in and out of freight transportation facilities, all made the more complicated by the abundance of trucks, on-the-road issues, traffic, cargo weight, and refrigeration systems. RFID tags can follow different packages, boxes, and cargo to collect data on location, speed, and safety. RFID technology can also track the movement of trucks within a facility or on the road to deliveries, all of which are essential to freight trucking efficiency and safety. In addition, RFID technology provides data on equipment maintenance by informing personnel where trucks are due for mechanical checks.
Facility Safety – RFID technology does more than protect high value items transported via trucks. It can prevent intrusion from falsely marked vehicles into facilities by tagging the freight trucks that have the given authority. Security measures can also be taken to ensure that dispatched drivers are properly identified via RFID tagged badges. This also means that certain employees will have badges allowing them limited access, while others will have wider duties at higher levels. Each badge is uniquely matched to its employee, thereby creating a safe system where the protection of high value items is maintained. Information regarding the movement of both items and employees can then be stored in real time and prove delivery accuracy.
Oil and Gas Operations – The oil and gas industries heavily rely on pipeline transportation to support their operations. From facility to delivery of the completed product, RFID can then also support this process. Pipes are tagged for the purpose identifying which has been used for each process and when it has been used. This is important in determining its age, length, history, and therefore preventing the usage of an unhealthy pipe for drilling, all over creating increased safety in operations. Finally, the transportation of these pipes to and from these sites, during exploration and production, is essential to the success of the Oil and Gas operations, all which is benefitted by using RFID tags to maintain localization of pipes being transported.
Construction and Maintenance of Oil and Gas Pipeline Facilities – Harsh temperatures and strenuous conditions age and deteriorate the health of pipes at facilities in which they are put to work. Pipeline joints, as well as their assembly, obviously need to be under immense scrutiny. RFID therefore helps provide information regarding factors such as oil leakage from pipes, joint pressure of pipes, correct assembling of pipes prior to exploration. One of the most important tasks that RFID helps workers with is tracing any factors that might be detrimental to sea life and marine environments. By also tracing vehicles in which employees might be reaching remote areas, RFID helps protect the facilities and industries of oil and gas pipelines from which they will be transported to or from facilities.
Pipeline Transportation Security and Safety – RFID protects workers and employees working in gas and oil industries and facilities. RFID tagged badges are given to trace employees traveling to far off site destinations or divers in the exploration process at remote sites. RFID will then also provide data to make sure head count numbers are the same during drills. RFID ensures the safety of workers transporting pipes and therefore keeps the transportation system efficient and healthy.
Package Monitoring – Automation of package monitoring is one of the most cost-effective benefits of RFID technology. Monitoring delivery, safety, and speed at which a package is being delivered is made efficient through the use of RFID tagging and through the data collection that tagging can provide. Estimates on journey times depending on which direction a package is going can also be more accurate after analyzing data trends. Route safety can be closely followed through tags in order to maintain the supply flow. Delays or traffic issues can also be monitored through RFID packages and can provide awaiting customers with warning and explanation.
Facility Inventory of Packages – Knowing where a package is at all times is necessary to the success of couriers and messengers. RFID technology prevents any human-made mistakes by correctly storing packages and confirming location, safety, and preservation in case a package requires special conditions such as refrigeration. Tracking the movement of a package outside a facility is important but internal facility tracking maintains a quick turnaround, as well as safety from misplacement. RFID can also provide the maintenance of equipment needed to properly count and manage incoming and outgoing packages.
Facility Safety and Package Security – Access to certain levels in a facility for couriers and messengers can be better limited to authorized personnel through the use of RFID technology. Employee badges that are uniquely linked to their owners, allow the tracking of moments within a facility. Employee badges also limit the access some employees have to other levels. This acts as an extra layer of safety for high value packages and prevents their misplacement. Movement can be tracked through doorway scanners and readers to ensure that only employees with certain badges are permitted access.
Maritime Container-tracking – In vessel transportation, maritime container-tracking is one of the most important and relevant factors benefitted by RFID. Vessel transportation is often used for heavyweight products or large quantities of cargo, and vessels are not the only part of the supply chain that needs to be tracked. Cargo and container tracking is key to the success of vessel transportation and efficiency, thereby creating a safe environment for production chain flow. RFID tags can be placed on both vessels and containers. This ensures the tracking and locating of a container journey. It also protects both companies and transport operations by creating a more transparent flow.
Port and Harbor Operations – In order to efficiently run and maintain port and harbor operations, RFID provides efficient tracking for itinerary and location. Transparent identification of time and journey of certain vessels, containers, or products themselves ensure the efficiency of a port or harbor in what can usually be a very chaotic business. RFID tags allow for identifying the port of last shipment to ensure the safe handling and protection of products, as well. This allows for transparency and easy management of any possible lost revenue as it prevents it from occurring. RFID can also ensure the protection of harbors through the use of personnel badges, which prevents intruders from having access to handling operations.
Tracking Mail – One of the most important benefits of RFID technology in postal services is the decrease in information costs, by producing large quantities of data without the labor cost of needing to read bar codes through a scan. RFID tags can, for instance, provide information on the journey of a package, of delays, of fees and taxes it might accrue at borders, of weight and category. RFID is essential to the effective delivery of mail not just for clients but for post offices themselves. Having access to this data, then allows them to inform clients or provide clients with explanations for unforeseen situations. It also ensures that information is accurate as data can be sent in real time.
Managing lost packages scenarios – Unforeseen situations can cause any client distress and mistrust in postal services, but with the implementation of RFID, a lot of these situations can be either fully prevented or easily resolved. RFID tags allow the management of misplaced packages and therefore giving postal services an opportunity to provide real time explanations and information regarding the location of that package. If a package is identified as misplaced before a client complaint, the mistake can be easily corrected, and further delay can then be prevented. Information regarding the package’s journey can then also be relayed to awaiting customers.
Monitoring time sensitive efficiency – RFID helps postal services by gathering data about package delivery speed. Tagging certain packages through random “seeding” can then provide data on more than location and speed. It can further benefit postal services by providing enough information that data analysis will be able to provide journey speed trends. For instance, packages might be delayed more at certain cities, and postal services can then provide clients and customers with better estimates on when their packages will arrive. It can also provide information on fee estimates, misplacement rates, and location tracking.
Tracking and Shipping – General Warehousing and Storage facilities often deal with receiving or sending packages back and forth to customers. One of their largest tasks is confirming recipience of packages and being capable of tracking incoming packages. RFID can assure packages are safely delivered or received through tagging and allowing customers to be kept up to date on the journey of their packages. Time logs and inventory checks are necessary to keep up to date on when clients move items out of or into storage facilities; this system can be fully automated via RFID whilst ensuring efficient and timely movements.
Storage facility maintenance – Storage facility maintenance is one of the most important factors in which RFID benefits users. Without proper maintenance, the unique needs of different clients cannot be held up. Some warehouse or storage facilities will indeed require unique equipment to properly store certain goods (for instance, refrigeration, temperature stabilization, etc.). This means equipment needs to be regularly checked and updated. An automated RFID system can maintain facilities by sending information about when quality checks are up to standards, where the equipment is, or when maintenance is due.
Inventory – Keeping an up to date inventory of goods and products located in warehouses and facilities is essential to maintaining storage companies. RFID can protect the flow of supply and demand by offering a way to track the amount of materials available and uploading it to internal networks in charge of inventory. Asset Tracking Systems are the best way to keep inventory data up to date, follow any changes, and restock when products are running low. It also helps provide a history of business trends and growths do to access to supply and demand, which in turn protects company interests and investment needs.
Rolling Stock Freight Wagons – Rolling stock freight wagons provide a fertile field for RFID products. Information on rolling stock at all times is essential to safe processing, transport, and delivery. RFID products increase and develop efficiency in rolling stock freight wagons through the scanning of rail wagons, engines, wheels, doors, coaches, or axles. Constant monitoring and maintenance are also helped by the existence of RFID technology. Rail RFID readers release data and information right from the tracks at a train station. RFID also simplifies the process of transporting goods at border crossing stations and generally improves operational efficiency in rail transportation and management.
Railway Revenue Growth – The first signs of RFID technology began with bar code scanning, which was inefficient due to environmental disruption. Throughout the years and specifically beginning in 1990, however, RFID technology has greatly improved railways’ supply chain with major global impacts. For instance, railway systems in China rely heavily on RFID technology to maintain reliability and performance for locomotives in both cargo and passenger based rail cars. According to the National University Rail Center, the global smart railways market can have an increase of up to 200% due to RFID technology.
Equipment Inventory and Management – Warehousing and Storage already benefit from RFID technology significantly but Refrigerated Warehousing and Storage deal with the added constraint of possible expiration for some products if refrigeration maintenance cannot be controlled. For equipment and inventory, this means that maintenance is absolutely essential, along with quality checks, greater space for high density equipment and weight, and temperature control. RFID technology allows for data storage and analysis in order to best estimate when maintenance should be due, to stay up to date on equipment efficiency on a daily basis, to check for temperature management, and to test different variables within equipment.
Temperature Control – Without temperature control, refrigerated warehousing and storage would imminently fail as their premise is maintaining the cooling and protection of the products in their care. RFID technology creates a more efficient process of maintenance and checks by allowing these to be done remotely. Temperature sensors are attached to cooling equipment and are built to function at extremes in order to best collect data and inform personnel if any changes occur. It also prevents loss of revenue by collecting information on quality and endurance of equipment for future needs.