
Related Products & Systems on Other Pages on This Website
People Tracking System for Manufacturing Facilities
GAO RFID Dry Pasta Manufacturing Asset Management System
GAO RFID Snack Food Manufacturing Asset Management System
GAO RFID Coffee and Tea Manufacturing Asset Management System
Employee & Attendance Access Control System
Work In Process WIP Asset Tracking System
BLE | Bluetooth Low Energy | BLE Gateways & Beacons – GAO RFID
RFID Readers | Buy RFID Readers | RFID Reader Writers – GAO RFID
RFID Tags | Buy RFID Tags – GAO RFID
Overview
Food manufacturing industry is a sector involved in the production, processing, and packaging of food products for consumption. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including sourcing raw materials, transforming them into finished products, and distributing them to retailers, wholesalers, or directly to consumers. Food manufacturing companies utilize various techniques and technologies to preserve and enhance the quality, taste, and safety of food.
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in food manufacturing industry to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials and operational equipment such as mixers, cutting and slicing machines, ovens and cookers, packaging machines, food processors, extruders, cooling and refrigeration equipment, conveyors, filling and bottling machines, cleaning and sanitation equipment, quality control and testing equipment, and storage and handling equipment.
Ranked as a top 10 global RFID supplier and based in New York City and Toronto, GAO RFID Inc offers a wide choice of RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags at ultra-high frequency (UHF), high frequency (HF, including NFC) and low frequency (LF), BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. Such RFID and BLE products and systems, together with its IoT and drone technologies, have been widely used in food manufacturing industry.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Food Manufacturing
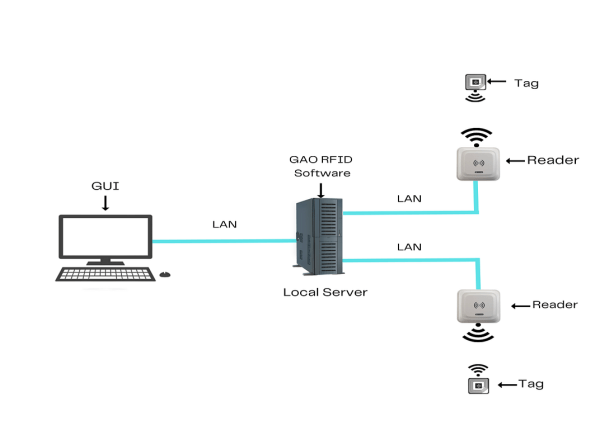
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for food manufacturing industry are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server, and another version is that its software runs in the cloud. The above illustrates GAO system for food manufacturing industry with its software running on a local server.
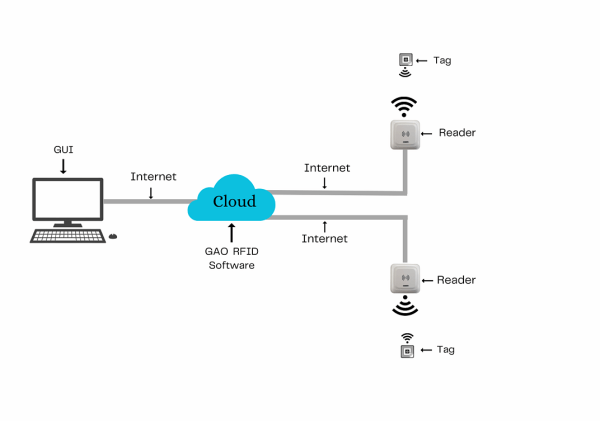
Above illustrates GAO system for food manufacturing industry with its software running in cloud.
GAO’s RFID technologies bring the many benefits to food manufacturing industry:
- Enhanced product authentication and anti-counterfeiting: GAO’s RFID tags with unique identifiers can be applied to products such as nutritional supplements, ingredients and additives allowing manufacturers and consumers to verify their authenticity.
- Improved food safety and quality control: GAO’s RFID solutions can monitor critical parameters such as temperature, humidity, and storage conditions.
- Efficient supply chain management: GAO’s RFID solutions improve supply chain efficiency by providing real-time data on product movement, location, and status.
GAO’s BLE technologies offer longer reading range and particularly attractive for applications with larger work spaces within food manufacturing industry:
- Improved workflow efficiency: GAO’s BLE devices can enable seamless communication and data exchange between different processes and equipment such as conveyers, slicers and cutters within food manufacturing facility.
- Energy efficiency: Food manufacturing industry with GAO’s BLE devices can reduce energy consumption and contribute to sustainability efforts.
- Worker safety and productivity: By equipping workers such as production control line workers, supervisors with GAO’s BLE devices, their movements can be tracked, ensuring compliance with safety protocols, and enabling quick response in case of emergencies.
GAO’s RFID and drone technologies are often combined and such solutions offer the following benefits to food manufacturing industry:
- Process optimization: The combination of GAO’s RFID and drones allows for data-driven process optimization in food manufacturing industry. Drones can collect data from GAO’s RFID tags and sensors throughout the production line, providing insights into bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and potential areas for improvement.
- Pest control and monitoring: Drones equipped with GAO’s RFID readers can aid in pest control and monitoring efforts. By scanning GAO’s RFID tags placed on pest control devices or traps, such as electronic monitoring devices, pheromone dispensers.
- Rapid response and emergency management: Drones equipped with GAO’s RFID readers can quickly locate and assess the status of tagged items and assets such as storage containers, pallets.
Here are benefits of GAO’s IoT technologies to food manufacturing industry:
- Enhanced quality control and predictive maintenance: GAO’s IoT sensors can continuously collect data on various factors, including product quality and equipment performance.
- Remote monitoring and predictive analytics: GAO’s IoT solutions enable remote monitoring of production lines, storage areas, and equipment such as packaging machines, conveyer systems.
- Improved traceability and transparency: GAO’s IoT devices provide comprehensive traceability and transparency, reducing foodborne illnesses and supporting regulatory compliance.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Food Manufacturing
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in food manufacturing industry to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates and government regulations.
RFID, BLE, IoT, & Drone Standards & Mandates
- EPCglobal Gen2: EPCglobal Gen2 is a globally recognized standard for UHF RFID systems. It defines the air interface protocol for RFID tags and readers, facilitating interoperability and data exchange among different stakeholders in food manufacturing industry.
- OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture): OPC UA is a widely adopted industrial communication standard for interoperability between devices and systems in various industries, including food manufacturing.
- International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Standards: ICAO standards is essential for safe and lawful drone operations in any industry.
- GS1 Standards: GS1 provides guidelines and best practices for RFID implementation in various industries, including food manufacturing. These standards help improve traceability, inventory management, and visibility within the supply chain.
- Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA): The FSMA emphasizes preventive measures to ensure food safety. It encourages the use of technology and data to implement effective hazard analysis and risk-based preventive controls in food manufacturing process.
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): GMP regulations with IoT solutions can help in monitoring and controlling critical parameters such as temperature, humidity, and hygiene, supporting compliance with GMP standards.
- Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) Regulations: These regulations typically cover aspects such as registration, pilot certification, flight restrictions, and safety requirements. Compliance with the CAA regulations in your country is crucial for legal drone operations in food manufacturing industry.
US. Government Regulations
- Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA): The FSMA aims to prevent foodborne illnesses by shifting the focus from responding to contamination incidents to preventing them
- Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs): The FDA enforces cGMP regulations that establish guidelines for food processing, manufacturing, packing, and holding operations.
- Food Labeling Regulations: The FDA mandates specific labeling requirements for food products, including nutrition facts, allergen declarations, ingredient statements, and health claims.
- Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) Regulations: The FSIS oversees the safety and labeling of meat, poultry, and processed egg products.
- Organic Certification: The USDA’s National Organic Program (NOP) establishes standards for organic agricultural products, including processed foods.
- Pesticide Regulations: The EPA regulates the use of pesticides in food manufacturing industry, ensuring that pesticide residues in food products remain within safe limits.
- Truth-in-Advertising Regulations: The FTC enforces regulations related to advertising and marketing practices, including those for food products.
- Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) Regulations: TTB regulations govern the manufacturing, labeling, and distribution of alcoholic beverages, including beer, wine, and spirits.
Canadian Government Regulations
- Safe Food for Canadians Regulations (SFCR): The SFCR consolidates several food-related regulations and sets out requirements for food businesses.
- Food Safety Enhancement Program (FSEP): FSEP is a CFIA program that establishes food safety requirements and guidelines for food manufacturers.
- Food and Drug Regulations: Health Canada’s regulations cover a wide range of aspects related to food, including standards for food additives, maximum residue limits for pesticides, nutritional labeling, and health claims.
- Natural Health Products Regulations: Health Canada regulates natural health products, including certain food-like products, to ensure their safety and efficacy.
- Canadian Agricultural Products Act (CAPA): CAPA regulates agricultural products, including processed foods, to ensure their quality and grade standards.
- Consumer Packaging and Labeling Act (CPLA): CPLA establishes requirements for the labeling and packaging of consumer products, including food products.
Competition Bureau Regulations
The Competition Bureau enforces regulations related to false or misleading advertising and deceptive marketing practices.

Bluetooth 5

OPC UA

GS 1

ICIAO

CAA

EPCglobal Gen2

NPS

USDA

NIH

CFIA

CIHR

EPA
GAO’s Software Provides API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in food manufacturing industry such as
Personnel Management
- Employee scheduling and shift management software.
- Human resources management system (HRMS) for managing employee records, performance, and benefits.
- Training and development software for employee onboarding and skill enhancement.
- Time and attendance tracking systems for managing employee working hours.
- Performance management software to track and evaluate employee performance.
Equipment Management
- Asset management software to track and maintain equipment inventory.
- Preventive maintenance software to schedule and manage equipment maintenance.
- Equipment tracking systems using RFID or barcode technology.
- Calibration management software to ensure equipment accuracy and compliance.
- Energy management systems to optimize equipment energy consumption.
Access Control
- Visitor management systems to control access to manufacturing facilities.
- Biometric systems (such as fingerprint or facial recognition) for employee access.
- Access card or key fob systems for restricted areas within the facility.
- CCTV surveillance systems to monitor access points and deter unauthorized entry.
- Gate control systems for vehicle access management.
Warehouse Management
- Inventory management software to track and manage raw materials, ingredients, and finished goods.
- Warehouse layout and optimization tools for efficient storage and retrieval.
- Pick and pack management systems to streamline order fulfillment processes.
- Barcode or RFID systems for real-time inventory tracking.
- Warehouse automation solutions like robotic systems for material handling.
Supply Chain Management
- Demand forecasting software to predict product demand and plan production.
- Supplier relationship management (SRM) systems for vendor selection and management.
- Transportation management systems (TMS) to optimize shipping and logistics.
- Quality management systems to ensure compliance and track product quality.
- Collaboration platforms for sharing information with suppliers, distributors, and retailers.
Other Applications
- Food safety management systems to ensure compliance with food regulations.
- Quality control and inspection software for monitoring product quality.
- Recipe management systems for managing product formulations and variations.
- Traceability and recall management systems for tracking products throughout the supply chain.
- Data analytics and business intelligence tools for analyzing operational and financial data.
GAO has enabled its customers to make use of some of leading software and cloud services in food manufacturing industry. Below are some of popular software and cloud services in food manufacturing industry
- Maintenance Connection: While not specific to personnel management, Maintenance Connection is a widely used computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) that can be applied to equipment management in food manufacturing industry. It helps track and manage maintenance activities, preventive maintenance scheduling, work orders, and equipment performance.
- ADP Workforce Now: ADP Workforce Now is a scalable, cloud-based human capital management platform designed for medium to large-sized businesses. It offers features such as HR management, payroll, benefits administration, time and attendance tracking, talent management, and analytics.
- Microsoft 365 (formerly Office 365): Microsoft 365 offers a range of cloud-based productivity tools, including Microsoft Teams for communication and collaboration, SharePoint for document management, and Power Platform for building custom applications. These tools can be utilized for personnel management, such as employee communications, document sharing, and workflow automation.
- Google Workspace (formerly G Suite): Google Workspace provides cloud-based productivity and collaboration tools, including Gmail, Google Drive, Google Docs, and Google Sheets. These tools can be utilized for personnel management tasks like employee communication, document sharing, and collaborative project management.
- Oracle NetSuite: Oracle NetSuite offers a comprehensive cloud-based solution that integrates warehouse management, supply chain management, and enterprise resource planning (ERP). It provides features such as inventory management, order fulfillment, demand planning, and supply chain visibility.
- SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM): SAP EWM is a robust warehouse management system that provides end-to-end visibility and control over warehouse operations. It offers features like inventory management, order processing, labor management, and integration with transportation and supply chain systems
- Microsoft Azure: Microsoft Azure is a comprehensive cloud computing platform that offers a range of services suitable for access control, warehouse management, and supply chain management. It provides services like Azure Active Directory for access control, Azure IoT Hub for device connectivity and data collection, and Azure Logic Apps for workflow automation.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS is a widely used cloud computing platform that provides various services for access control, warehouse management, and supply chain management. AWS offers services such as AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for access control, AWS IoT Core for device connectivity, and AWS Step Functions for workflow automation.
- Infor Food & Beverage: Infor Food & Beverage is a comprehensive software suite designed specifically for food and beverage industry. It covers various aspects such as recipe management, product lifecycle management, supply chain management, quality control, and compliance.
- JustFoodERP: JustFoodERP is an industry-specific ERP software designed for food manufacturers and distributors. It covers various modules such as recipe management, inventory control, production planning, quality control, lot traceability, and compliance with food safety regulations.
- Salesforce Platform: Salesforce Platform is a cloud-based platform that offers a suite of services for food manufacturing industry. It provides tools for customer relationship management (CRM), sales automation, marketing automation, and data analytics, helping food manufacturers enhance customer engagement and streamline business processes.
- Plex Manufacturing Cloud: Plex Manufacturing Cloud is a cloud-based platform specifically designed for manufacturing industries, including food manufacturing. It offers modules for production management, inventory control, quality management, compliance, and analytics, providing a comprehensive solution for food manufacturers.

Maintenance Connection

ADP Workforce Now

Microsoft 365

Google Workspace

Oracle NetSuite

SAP EWM

Microsoft Azure

Amazon Web Services

Infor Food & Beverage

JustFoodERP

Salesforce Platform

Plex Manufacturing Cloud
GAO has worked with some of the leading technology companies in food manufacturing industry in to provide integrated its RFID, BLE, IoT and drone solutions to customers. Here are some of the technology leaders in food manufacturing industry:
- Siemens AG: Siemens offers industrial automation and digitalization solutions for food manufacturing industry, including manufacturing execution systems (MES) and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems.
- Schneider Electric: Schneider Electric provides solutions for energy management, industrial automation, and sustainability in food manufacturing sector, helping companies optimize their operations and reduce energy consumption.
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.: Rockwell Automation specializes in industrial automation and offers solutions for food industry, including process control systems, manufacturing execution systems, and plant-wide optimization.
- Honeywell International, Inc.: Honeywell offers a range of technologies for food industry, including process automation, control systems, and software solutions for safety, productivity, and sustainability.
- TOMRA Systems ASA: TOMRA develops sensor-based sorting and grading solutions for food industry. Their technologies enable the sorting and removal of defects, foreign materials, and substandard produce in various food processing applications.
- Ishida Corporation.: Ishida offers a wide range of weighing, packaging, and inspection solutions for food manufacturing sector. Their equipment includes multihead weighers, checkweighers, X-ray inspection systems, and seal testers.
- JBT Corporation: JBT provides food processing and preservation solutions, including high-pressure processing (HPP) systems, fruit and vegetable processing equipment, and industrial freezers.
- Heat and Control, Inc.: Heat and Control specializes in food processing and packaging equipment. Their offerings include fryers, ovens, coating systems, and seasoning equipment for snack food production.
- GE Digital: GE Digital provides industrial software solutions, including manufacturing operations management (MOM) systems, data analytics platforms, and asset performance management (APM) solutions for food manufacturing sector.
- Aspen Technology, Inc.: AspenTech offers software solutions for process optimization and simulation in food manufacturing industry. Their technologies enable companies to improve production efficiency, reduce waste, and optimize quality.
- ABB Ltd.: ABB provides automation and control systems for food industry, including process control systems, robotics, and industrial IoT (Internet of Things) solutions.
- OSIsoft, LLC: OSIsoft specializes in data management and analytics software for food manufacturing industry. Their PI System collects and analyzes real-time operational data, enabling companies to optimize their processes and improve efficiency.

Siemens AG Company

Schneider Electric Company

Rockwell Automation Company

Honeywell International, Incorporation

TOMRA Systems ASA

Ishida Corporation

JBT Corporation

Heat and Control, Incorporation

GE Digital

Aspen Technology, Incorporation

ABB Limited

OSIsoft, Limited Liability Limited
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Below are some case studies of RFID and UHF RFID applications in food manufacturing industry:
- Walmart: Walmart, a leading retail corporation, initiated a pilot program to implement RFID technology in their food supply chain. The program aimed to improve inventory management, reduce waste, and enhance product freshness. By using RFID tags on individual food items, Walmart achieved better visibility into their inventory, resulting in reduced out-of-stock situations and improved product rotation.
- Nestlé USA: Nestlé USA, a multinational food and beverage company, utilized RFID technology to enhance their distribution operations. They deployed RFID tags on shipping containers and pallets to enable real-time tracking and monitoring of products throughout the supply chain. This resulted in improved shipment accuracy, reduced delivery errors, and enhanced efficiency in their distribution centers.
- Maple Leaf Foods: Maple Leaf Foods, a leading Canadian food processing company, implemented RFID technology to enhance food safety and traceability. They utilized RFID tags to track individual products, enabling real-time monitoring of temperature conditions and ensuring proper handling throughout the supply chain. This helped Maple Leaf Foods to improve product quality and reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses.
- Loblaw Companies Limited: Loblaw, one of Canada’s largest grocery retailers, implemented RFID technology to improve inventory management and reduce out-of-stock situations. They utilized RFID tags on individual products to enhance visibility and accuracy in their supply chain operations. By leveraging RFID data, Loblaw achieved better inventory accuracy, optimized replenishment processes, and provided customers with improved product availability.
- Dole Fresh Vegetables: Dole Fresh Vegetables, a major producer and distributor of fresh produce, implemented UHF RFID technology to improve inventory management and traceability. They utilized UHF RFID tags on shipping containers and pallets to track and monitor the movement of products throughout their supply chain. This enabled real-time visibility, reduced manual labor, and enhanced inventory accuracy.
- Cargill: Cargill, a multinational food corporation, integrated UHF RFID technology into their meat processing and supply chain operations. They used UHF RFID tags on meat products to enhance traceability, quality control, and inventory management. This enabled Cargill to improve product tracking, reduce waste, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Dairy Farmers of Canada: The Dairy Farmers of Canada implemented UHF RFID technology to improve traceability and quality control in the dairy industry. They utilized UHF RFID tags on milk containers and pallets to track and monitor the movement of products from farm to processing facilities. This enhanced traceability allowed for improved product recall management and ensured the freshness and safety of dairy products.
- Loblaw Companies Limited: Loblaw, one of the largest grocery retailers in Canada, implemented UHF RFID technology to optimize inventory management and enhance supply chain efficiency. They utilized UHF RFID tags on individual products and cases to automate inventory tracking and improve accuracy. This resulted in reduced out-of-stock situations, improved product availability, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Many applications of RFID by GAO can be found here.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Food Manufacturing
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including food manufacturing industry.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including the Sub-Industry.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including food manufacturing industry
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, includin food manufacturing industry
and an array of antennas to address different applications
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including food manufacturing industry
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including food manufacturing industry
and antennas
GAO also offers RFID printers
Digital I/O adapters
and relay controllers
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in food manufacturing industry
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include
- Mixing and Blending Equipment: These machines are used to mix and blend ingredients to create uniform and consistent food products. Examples include mixers, blenders, and homogenizers.
- Cutting and Slicing Equipment: This equipment is used to cut and slice ingredients or finished food products. It includes machines like vegetable cutters, dicers, slicers, and portioning machines.
- Cooking and Baking Equipment: These machines are used for cooking, baking, and heating food products. Examples include ovens, grills, fryers, steamers, and microwave ovens.
- Food Processing Machinery: This category includes a wide range of equipment used for various food processing activities such as grinding, milling, extruding, and forming. Examples include grinders, mills, extruders, and forming machines.
- Packaging Machinery: These machines are used to package food products into containers, bags, or other packaging materials. They include equipment like fillers, sealers, cappers, labeling machines, and shrink-wrapping machines.
- Canning and Bottling Equipment: This equipment is specifically designed for canning and bottling food products. It includes machines like canning lines, can seamers, bottle fillers, and cappers.
- Refrigeration and Cooling Systems: These systems are used to store and preserve perishable food products at low temperatures. Examples include walk-in refrigerators, freezers, blast chillers, and cold storage rooms.
- Conveying and Material Handling Equipment: These machines are used to transport raw materials, ingredients, and finished products within the production facility. They include conveyors, elevators, loaders, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
- Food Safety and Quality Control Equipment: This equipment is used to ensure food safety and quality throughout the production process. Examples include metal detectors, X-ray machines, checkweighers, and quality control testing instruments.
- Cleaning and Sanitation Equipment: These machines are essential for maintaining hygiene and cleanliness in food manufacturing facilities. They include industrial washers, steam cleaners, sanitizing equipment, and air purification systems.
People or workers tracking system
Personnel or people access control system
Parking or vehicle control system
GAO Has Served Food Manufacturing Extensively
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in food manufacturing industry to achieve success in plant-based, clean label, sustainability, transparency, functional foods, free-from, locally sourced, smart manufacturing, personalization, food safety, circular economy, novel ingredients, convenience and on-the-go, farm-to-table, traceability.
GAO RFID Inc. has served many customers in food manufacturing industry, including its various divisions such as:
- Baked goods and snacks: This division includes the production of bread, pastries, cakes, cookies, crackers, and snack foods like chips, pretzels, and popcorn.
- Dairy products: This division focuses on the manufacturing of milk, cheese, butter, yogurt, ice cream, and other dairy-based products.
- Meat and poultry: This division involves the processing and manufacturing of meat and poultry products, including fresh and processed meats, sausages, bacon, ham, and deli meats.
- Beverages: This division encompasses the production of various beverages, such as soft drinks, juices, bottled water, coffee, tea, energy drinks, and alcoholic beverages.
- Canned and preserved foods: This division involves the manufacturing of canned fruits, vegetables, soups, sauces, jams, pickles, and other preserved food products.
- Frozen foods: This division focuses on the production of frozen food products, including frozen fruits and vegetables, frozen meals, pizzas, desserts, and ice cream.
- Confectionery: This division specializes in the manufacturing of confectionery items, such as chocolates, candies, gums, mints, and other sweet treats.
- Sauces, dressings, and condiments: This division involves the production of various sauces, dressings, condiments, and seasonings, including ketchup, mayonnaise, salad dressings, marinades, and spices.
- Grain and cereal products: This division focuses on the manufacturing of grain-based products, including cereals, pasta, rice, flour, and bakery mixes.
- Specialty and health foods: This division includes the production of specialty and health-oriented food products, such as organic foods, gluten-free products, functional foods, and dietary supplements.
- Pet food: This division involves the manufacturing of food products specifically formulated for pets, including dry and wet pet food, treats, and pet supplements.
- Ingredients and additives: This division focuses on the production of food ingredients and additives, such as flavorings, food colorings, sweeteners, emulsifiers, preservatives, and nutritional supplements.
Here are some of the leading companies in food manufacturing industry:

Nestlé USA

Tyson Foods, Incorporation

Kraft Heinz Company

The Coca-Cola Company

PepsiCo Incorporation

Mondelēz International, Incorporation

Cargill Incorporation

Danone North America

Unilever United States

MARS, Incorporation

General Mills, Incorporation

Kellogg Company

The Hershey Company

Conagra Brands Incorporation

The J.M. Smucker Company

Campbell Soup Company

Dean Foods
Company

Hormel Foods Corporation

Saputo Incorporation

McCain Foods Limited

Agropur Cooperative
Company

George Weston Limited

Maple Leaf Foods Incorporation

Lassonde Industries Incorporation
