Index
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Space Research and Technology Industry
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
Case Studies of RFID Applications
GAO Makes Efforts to Satisfy Customers
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Space Research and Technology Industry
GAO Has Served Space Research and Technology Industry Extensively
Overview
The Space Research and Technology Industry encompasses a wide range of activities related to the exploration, study, and utilization of outer space. It involves the development of technologies, tools, and methods to understand and interact with the space environment, as well as to create applications and innovations that benefit humanity both on Earth and beyond. This industry includes government space agencies, private companies, research institutions, and international collaborations, all working together to advance our knowledge of space and develop technologies for space exploration, satellite communication, Earth observation, scientific research, and more. Key areas within the industry include spacecraft design and manufacturing, rocket propulsion systems, satellite technology, space science research, space tourism, and the development of sustainable and reusable space transportation systems. The Space Research and Technology Industry plays a crucial role in expanding our understanding of the universe, driving technological innovation, and opening new possibilities for scientific discovery and economic growth.
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in Space Research and Technology Industry to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials, and operational equipment such as Launch Vehicles, Spacecraft, Spacecraft Components, Ground Control Infrastructure, Laboratory Equipment, Telescopes, and Observatories, Scientific Instruments, Communication Infrastructure, Space Suits, and EMUs, Robotics and Rovers, Testing Equipment, Propulsion Technologies, Navigation and Positioning Systems, Materials and Coatings, Life Support Systems, Space Debris Monitoring Equipment, Space Tourism Infrastructure, Reusable Rocket Technology.
Ranked as one of the top 10 global RFID suppliers, GAO RFID Inc. is based in New York City, U.S. and Toronto, Canada. GAO offers a comprehensive selection of UHF, HF (including NFC) and LF RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags, BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. RFID and BLE products and systems, as well as its IoT and drone technologies, have been successfully deployed for the Space Research and Technology Industry. Its sister company, GAO Tek Inc. Gao Tek , is a leading supplier of industrial or commercial testers and analyzers, drones, and network products.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Space Research and Technology Industry
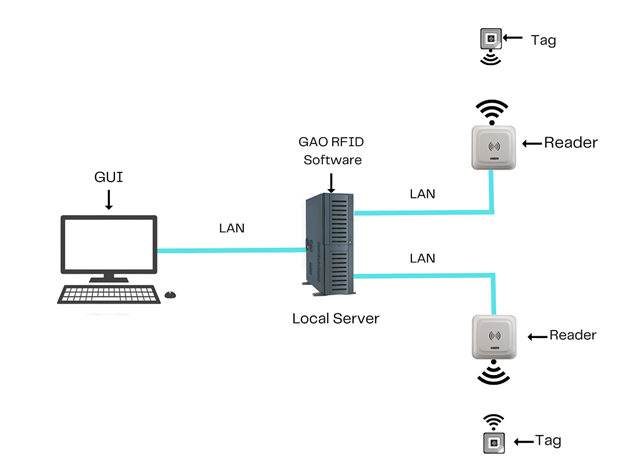
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for Space Research and Technology Industry are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server that normally is on our client’s premises, and another version runs in the cloud. The cloud server could be GAO’s cloud server, client’s own cloud server or a cloud server from one of the leading cloud server providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud (formerly SoftLayer), Oracle Cloud, RedHat, Heroku, Digital Ocean, Cloudflare, Linode and Rackspace. The above illustrates GAO system for Space Research and Technology Industry with its software running on a local server.
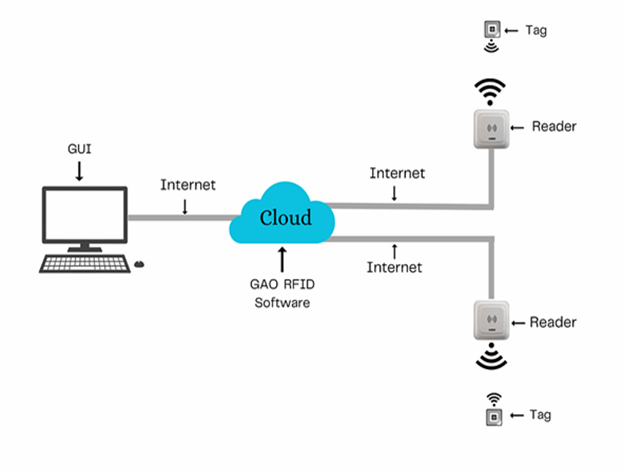
The above illustrates GAO system for Space Research and Technology Industry with its software running in cloud.
GAO’s RFID and BLE technologies, consisting of RFID readers, RFID tags, BLE gateways, BLE beacons, software, cloud services and their systems, have the following applications in Space Research and Technology Industry:
- Inventory Management: RFID tags can be attached to equipment, tools, and supplies, enabling efficient tracking and management of inventory in space stations, spacecraft, and ground facilities.
- Asset Tracking: RFID can help monitor the location and status of critical assets, such as scientific instruments, components, and tools, ensuring they are readily accessible and accounted for during missions.
- Security and Access Control: RFID-based access control systems can restrict unauthorized access to sensitive areas in space facilities, ensuring the security of valuable equipment and information.
- Maintenance and Repair: RFID tags can store maintenance history and repair information for equipment and components, aiding in predictive maintenance and streamlining repair processes.
- Sample Tracking: In scientific missions involving sample collection (e.g., from other planets or moons), RFID can track and identify the origin and characteristics of collected samples.
- Supply Chain Management: RFID can be used to trace the movement of materials, components, and equipment throughout the supply chain, ensuring timely and accurate delivery for space missions.Satellite Identification: RFID tags on satellites can assist in identifying and verifying satellite identities during deployment and operational phases.
- Payload Management: RFID technology can help manage payloads on rockets and spacecraft, ensuring correct handling, positioning, and deployment.
- Equipment Configuration: RFID tags can store configuration information for equipment and instruments, ensuring they are correctly set up for specific experiments and tasks.
- Real-time Monitoring: RFID sensors can be integrated into equipment to provide real-time monitoring of environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, pressure) during space missions.
- Emergency Response: RFID can aid in locating crew members, equipment, and emergency supplies in case of an emergency or unexpected situation.
- Logistical Efficiency: RFID streamlines logistics operations by automating tracking, reducing manual data entry, and minimizing errors in space operations.
- Asset Lifecycle Management: RFID assists in tracking the entire lifecycle of assets, from procurement to retirement, helping organizations make informed decisions about equipment retirement or replacement.
- Spacewalk Safety: RFID-equipped spacesuits and tools can enhance safety during spacewalks by providing information about the status and location of astronauts and equipment.
- Laboratory Research: RFID tags can help identify and track lab samples and experimental setups, improving the accuracy of results in microgravity research.
- Payload Integration: RFID can aid in the integration of multiple payloads within a single launch, ensuring proper positioning and sequencing of experiments.
- Space Tourism: RFID can be used for identification, access control, and tracking of tourists and their belongings during space tourism activities.
GAO’s drone technologies find the following applications in the space research and technology industry:
- Planetary Exploration: Drones can be used for aerial exploration of planets, moons, and other celestial bodies, capturing high-resolution images and collecting data from previously inaccessible areas.
- Satellite Deployment and Maintenance: Drones can assist in deploying and maintaining satellites in orbit, reducing the need for costly and complex human interventions.
- Spacecraft Testing: Drones can simulate spacecraft entry, descent, and landing conditions on Earth, helping validate and refine landing technologies.
- Spaceport Operations: Drones can monitor launch and landing operations at spaceports, enhancing safety and providing real-time data for decision-making.
- Environmental Monitoring: Drones equipped with sensors can monitor environmental changes on Earth, helping scientists understand climate patterns, natural disasters, and more.
- Space Debris Cleanup: Drones could potentially be used to capture and remove space debris, reducing the risk of collisions with operational satellites.
- Astronomical Observations: Drones equipped with telescopes or cameras can provide new perspectives for astronomical observations, especially in hard-to-reach or hazardous areas.
- Sample Collection: Drones can collect samples from hard-to-reach or dangerous areas on Earth, aiding in studies that simulate space conditions.
- Remote Sensing: Drones can carry remote sensing instruments to study Earth’s surface, atmosphere, and oceans, providing valuable data for research and environmental monitoring.
- Communication Infrastructure: Drones can act as relay stations for communication between ground stations and spacecraft in deep space, improving data transmission.
- Aerial Surveys: Drones can conduct surveys of potential landing sites, assess terrain conditions, and identify hazards for future planetary missions.
- Geological Studies: Drones can help study geology, geomorphology, and mineralogy of remote and challenging terrains, aiding in planetary science.
- Technology Testing: Drones can serve as testbeds for new technologies that could be used in space, allowing researchers to evaluate their performance in a controlled environment.
- Space Tourism: Drones could play a role in space tourism by providing guided aerial tours of spaceports, launch facilities, and other relevant locations.
- Search and Rescue: Drones can aid in locating and rescuing astronauts during emergencies, especially during planetary exploration missions.
- Educational Outreach: Drones can be used as educational tools to engage the public and students in space science and technology, providing visual and interactive experiences.
- Remote Exploration: Drones can explore remote areas on Earth, such as extreme environments, analog sites, or locations relevant to astrobiology studies.
- Infrastructure Inspection: Drones can inspect and monitor space infrastructure, such as launch pads and antenna arrays, for maintenance and safety purposes.
GAO’s IoT technologies, consisting of IoT sensors, sensors networks and systems, find the following applications in the space research and technology industry:
- Satellite Monitoring and Control: IoT sensors can monitor the health and performance of satellites in real time, facilitating remote troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Payload Monitoring: IoT devices can monitor the status and conditions of scientific payloads on spacecraft, providing researchers with valuable data.
- Spacecraft Health Monitoring: IoT-enabled sensors can monitor various parameters of spacecraft systems, helping ensure their proper functioning during missions.
- Remote Sensing and Data Collection: IoT sensors on satellites and space probes can collect and transmit environmental and atmospheric data from space.
- Orbital Debris Tracking: IoT-based tracking devices can help monitor and manage orbital debris, providing data for collision avoidance strategies.
- Space Weather Monitoring: IoT networks can gather data about space weather conditions, helping predict and mitigate potential impacts on satellites and infrastructure.
- Communication and Navigation: IoT technologies can enhance communication and navigation systems for spacecraft and ground stations.
- Environmental Monitoring: IoT devices can be used to study the space environment, such as radiation levels and microgravity conditions, for scientific research.
- Launch Vehicle Health Monitoring: IoT sensors can monitor the status of launch vehicles, ensuring their readiness and safety before lift-off.
- Spaceport Operations: IoT can streamline spaceport operations by monitoring fuel levels, equipment status, and weather conditions, aiding launch decisions.
- Astrophysics and Astronomy: IoT sensors on telescopes and observatories can collect data about celestial objects and phenomena, contributing to research.
- Planetary Exploration: IoT devices can provide real-time data from planetary rovers and landers, enabling scientists to study distant worlds remotely.
- Microgravity Research: IoT-enabled experiments can study how materials and biological systems behave in microgravity environments.
- Extravehicular Activities (EVA): IoT sensors can enhance spacesuit design and monitor astronaut health during spacewalks.
- Remote Control of Robots: IoT technologies can remotely control and operate robots on distant planets or moons for exploration and analysis.
- Education and Outreach: IoT can engage the public and students in space science by allowing remote access to space-related experiments and data.
- Satellite Fleet Management: IoT can optimize satellite fleet operations, including coordination, data sharing, and collision avoidance.
- Astronaut Health Monitoring: IoT devices can monitor astronauts’ health, collecting vital signs and other health-related data during missions.
- Resource Management: IoT can assist in managing resources on space stations, optimizing energy consumption, water usage, and waste disposal.
- Automated Systems: IoT can automate routine tasks on spacecraft and space stations, reducing the need for direct human intervention.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Space Research and Technology Industry
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in Space Research and Technology Industry to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates, and government regulations:
RFID, BLE, IoT, & Drone Standards & Mandates
- ISO 18000 Series
- ISO 17386
- NASA-STD-6002
- ECSS-E-ST-10-04C
- ASTM F2970
- Bluetooth SIG Specifications
- IEEE 802.15.4
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol)
- OMA LWM2M (Open Mobile Alliance Lightweight M2M)
- OneM2M
- ISO/IEC 30141
- ASTM F38 Committee
- ISO 21384 Series
- RTCA DO-362 / EUROCAE ED-251
- NASA NPR 8715.5
- ANSI/UL 3030
- Regulatory Compliance
- Data Privacy Regulations
- Security Standards
- Wireless Spectrum Regulations
- Data Privacy Regulations
- Security Requirements
- Spectrum Regulations and Allocation
- Data Security and Privacy Requirements
- Interoperability Standards and Guidelines
- Remote Device Management Protocols
- Environmental and Safety Regulations for IoT Devices
- Ethical Considerations in IoT Data Collection and Usage
- Unmanned Aircraft Regulations
- Safety and Airworthiness Standards
- Data Privacy and Security
- Remote Pilot Certification
- Airspace Integration Guidelines
- Payload and Equipment Certification
US. Government Regulations
- National Aeronautics and Space Act of 1958
- Commercial Space Launch Act
- International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR)
- Export Administration Regulations (EAR)
- Commercial Remote Sensing Regulatory Affairs
- Federal Acquisition Regulations (FAR)
- Federal Aviation Regulations (FAR Part 400)
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Regulations
- National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA)
- Outer Space Treaty
- Space Launch Liability Indemnification
Canadian Government Regulations
- Canadian Space Agency Act
- Remote Sensing Space Systems Act
- Export Control List (ECL)
- Canadian Aviation Regulations (CARs)
- Radiocommunication Act
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations (TDGR)
- National Security Space Policy
- Nuclear Safety and Control Act
- Environmental Impact Assessment Regulations
- Space Debris Mitigation Guidelines
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in Space Research and Technology Industry such as:
Personnel Management:
- Astronaut Selection and Training
- Mission Crew Scheduling
- Health Monitoring for Astronauts
- Human Resources for Research Staff
Equipment Management:
- Satellite Component Tracking
- Spacecraft Maintenance Scheduling
- Instruments Calibration and Tracking
- Rocket Propulsion System Management
Access Control:
- Secure Facility Access for Personnel
- Controlled Access to Sensitive Data
- Access to Launch Pads and Ground Stations
Warehouse Management:
- Storage of Spacecraft Components
- Management of Payloads and Instruments
- Inventory Tracking for Equipment
Supply Chain Management:
- Procurement of Spacecraft Materials
- Tracking Supplier Deliveries
- Managing Spare Parts Inventory
Other Applications:
- Space Debris Monitoring and Mitigation
- Earth Observation and Remote Sensing
- Space Weather Forecasting
- Satellite Communication and Navigation
- Scientific Data Collection and Analysis
- Space Tourism Operations
- Space Exploration and Planetary Research
GAO has enabled its customers to make use of some of the leading software and cloud services in the Space Research and Technology Industry. Below are some of the popular software and cloud services in Space Research and Technology Industry.
Personnel Management: SAP SuccessFactors, Workday Human Capital Management, Oracle HCM Cloud, BambooHR, ADP Workforce Now. Equipment Management: IBM Maximo, Infor EAM, Fiix, Asset Panda, UpKeep. Access Control: Honeywell Pro-Watch, Lenel OnGuard, Genetec Security Center, Brivo Access Control, S2 Security NetBox. Warehouse Management: SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM), Manhattan Associates Warehouse Management, Oracle Warehouse Management Cloud, Blue Yonder (formerly JDA Warehouse Management), HighJump Warehouse Edge. Supply Chain Management: SAP Integrated Business Planning (IBP), Oracle Supply Chain Management Cloud, Blue Yonder (formerly JDA Supply Chain), Kinaxis RapidResponse, Logility Supply Chain Management. MATLAB, LabVIEW, STK (Systems Tool Kit), SolidWorks, CATIA, ANSYS, Zemax, LabChart, Orbitron, CST Studio Suite, Celestia, Agisoft, Metashape.
GAO has worked with some of the leading technology companies in Space Research and Technology Industry to provide integrated RFID, BLE, IoT and drone solutions to customers. Here are some of the technology leaders in Space Research and Technology Industry:
IBM, Microsoft Amazon Web Services (AWS), Oracle, Siemens, SpaceX, Lockheed, Martin, Northrop, Grumman, Honeywell, Thales Group, Raytheon Technologies, Intel Corporation, Qualcomm, Texas Instruments, Maxwell Technologies (acquired by Tesla), Xilinx Microchip Technology, NVIDIA, Honeywell Aerospace, Teledyne Technologies, Analog Devices L3Harris Technologies, Cobham, Lockheed, Martin Northrop Grumman, Airbus Defence and Space Thales, Alenia Space Raytheon Technologies, SpaceX, Blue Origin, Rocket Lab, Arianespace, Virgin Galactic, and Sierra Nevada Corporation.
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Below are some RFID application cases in Space Research and Technology Industry.
RFID tags could be used to track and manage the maintenance schedules of equipment, tools, and components used in space missions, ensuring timely inspections and replacements.
RFID technology could help manage inventory and track the movement of critical components used in building and launching spacecraft, reducing errors and ensuring accurate parts availability.
RFID-enabled space suits and equipment could monitor parameters like oxygen levels and temperature during spacewalks, enhancing astronaut safety.
RFID tags attached to space debris could aid in tracking and monitoring their trajectories, helping to predict potential collisions and their impact on operational satellites.
RFID tags could be utilized for secure access control to restricted areas of space research facilities, ensuring only authorized personnel enter sensitive locations.
RFID tags could be employed to track and monitor the status of payloads on satellites, providing real-time data on their condition and performance.
RFID sensors could be used to collect environmental and atmospheric data during satellite missions, helping researchers analyze various parameters.
RFID tags could be used to track and monitor the status of payloads on Canadian satellites, providing valuable data on their performance and condition.
RFID-enabled equipment and supplies could be used to manage and track astronaut gear during training and space missions, ensuring accurate inventory and reducing errors.
RFID technology could aid in tracking and scheduling maintenance tasks for spacecraft components and systems, enhancing operational efficiency.
RFID tags could be employed for secure access control to Canadian ground stations, ensuring that only authorized personnel are allowed entry.
RFID tags could be used to track space debris and monitor their trajectories, contributing to the understanding and management of potential collisions.
RFID-enabled tracking systems could manage and locate laboratory equipment and instruments used in Canadian space research facilities.
Many applications of RFID by GAO can be found here.
Case Studies of IoT Applications
Below are some IoT application cases in Space Research and Technology Industry.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is using IoT to monitor the health of its satellites. JPL has deployed a network of IoT sensors on its satellites to collect data on temperature, vibration, and other factors that could impact the satellites’ performance. This data is used to identify potential problems early on, so that they can be addressed before they cause a mission failure.
The US Air Force is using IoT to track its aircraft. The Air Force has deployed a network of IoT sensors on its aircraft to collect data on location, speed, and other flight parameters. This data is used to track the aircraft’s movements and to identify potential problems, such as fuel leaks or engine malfunctions.
he National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) is using IoT to monitor weather conditions. NOAA has deployed a network of IoT sensors across the United States to collect data on temperature, humidity, wind speed, and other weather conditions. This data is used to create weather forecasts and to monitor extreme weather events.
The US Department of Defense is using IoT to develop autonomous spacecraft. The DoD is funding research into the development of autonomous spacecraft that can operate without human intervention. IoT sensors will be used to collect data on the spacecraft’s environment and to make decisions about its course of action.
The commercial space industry is using IoT to develop new space-based services. Companies like SpaceX and OneWeb are using IoT to develop new space-based services, such as satellite internet and global positioning systems. IoT sensors will be used to monitor the performance of these services and to ensure that they are reliable and secure.
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA) is using IoT to monitor the health of its satellites. The CSA has deployed a network of IoT sensors on its satellites to collect data on temperature, vibration, and other factors that could impact the satellites’ performance. This data is used to identify potential problems early on, so that they can be addressed before they cause a mission failure.
The University of Toronto is using IoT to develop a lunar rover. The University of Toronto is developing a lunar rover that will be equipped with IoT sensors to collect data on the lunar surface. This data will be used to map the lunar surface and to identify potential hazards for future astronauts.
The company UrtheCast is using IoT to monitor forests. UrtheCast is using a constellation of IoT satellites to monitor forests around the world. The satellites collect data on forest cover, tree density, and other factors that can be used to track deforestation and forest degradation.
The company Kepler Communications is using IoT to provide connectivity to remote areas. Kepler Communications is developing a constellation of IoT satellites that will provide connectivity to remote areas of the world. This connectivity can be used to support a variety of applications, such as environmental monitoring, disaster relief, and education.
The company ThinSat is developing a small satellite that can be used to deploy IoT sensors. ThinSat is developing a small satellite that can be used to deploy IoT sensors in remote locations. The sensors can be used to collect data on a variety of environmental factors, such as air quality, water quality, and soil moisture.
Case Studies of Drone Applications
Below are some drone application cases in Space Research and Technology Industry.
NASA is using drones to inspect launch pads and other infrastructure at Kennedy Space Center. Drones can fly in difficult-to-reach areas and can be equipped with sensors to detect damage or corrosion. This allows NASA to inspect its infrastructure more frequently and to identify potential problems before they cause a major disruption.
The US Air Force is using drones to train pilots for space missions. Drones can be used to simulate the conditions of space flight, such as weightlessness and microgravity. This allows pilots to train for space missions without having to travel to a spaceport.
The company Planet Labs is using drones to map the Earth from space. Planet Labs’ drones can fly at high altitudes and can collect images of the Earth’s surface. This data is used to create high-resolution maps of the Earth, which can be used for a variety of applications, such as environmental monitoring and disaster response.
The company Skydio is developing drones that can be used to inspect satellites. Skydio’s drones are equipped with obstacle avoidance sensors and can fly autonomously. This makes them ideal for inspecting satellites in space, where there is no human pilot to intervene if something goes wrong.
The company Matternet is developing drones that can deliver medical supplies to remote areas. Matternet’s drones can fly long distances and can carry a payload of up to 10 pounds. This makes them ideal for delivering medical supplies to remote areas, where it is difficult or impossible to reach by road.
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA) is using drones to inspect its infrastructure. The CSA is using drones to inspect its launch pads, ground stations, and other infrastructure. Drones can fly in difficult-to-reach areas and can be equipped with sensors to detect damage or corrosion. This allows the CSA to inspect its infrastructure more frequently and to identify potential problems before they cause a major disruption.
The University of Toronto is using drones to study the aurora borealis. The University of Toronto is using drones to study the aurora borealis, or northern lights. Drones can fly high altitudes and can collect images of the aurora borealis in detail. This data is used to study the aurora borealis and to better understand how it works.
The company Draganfly is developing drones that can be used to inspect pipelines. Draganfly’s drones are equipped with thermal imaging cameras and can fly autonomously. This makes them ideal for inspecting pipelines in remote areas, where it is difficult or dangerous for humans to access.
The company Aerobotics is developing drones that can be used to map forests. Aerobotics’ drones are equipped with high-resolution cameras and can fly autonomously. This makes them ideal for mapping forests, which can be difficult or time-consuming to map using traditional methods.
The company Drone Delivery Canada is developing drones that can deliver medical supplies to remote communities. Drone Delivery Canada’s drones can fly long distances and can carry a payload of up to 10 pounds. This makes them ideal for delivering medical supplies to remote communities, where it is difficult or impossible to reach by road.
GAO Makes Efforts to Satisfy Customers
Large Choice of Products
In order to satisfy the diversified needs of their corporate customers, GAO RFID Inc. and its sister company GAO Tek Inc. together offer a wide choice of RFID, BLE, IoT, drones, testing and measurement devices, and network products.
Overnight Delivery
In order to shorten the delivery to our customers, GAO has maintained a large stock of its products and is able to ship overnight within continental U.S. and Canada, and fast delivery to anywhere in Mexico and Europe from the nearest warehouse.
Local to Our Customers
We are located in both the U.S. and Canada. We travel to customers’ premises if necessary. Hence, we provide a very strong local support to our customers in North America, particularly the U.S., Canada and Mexico, and Europe. Furthermore, we have built partnerships with some integrators, consulting firms and other service providers in different cities to further strengthen our services. Here are some of the service providers in Sub-Industry we have worked with to serve our joint customers:
- Deloitte
- Accenture
- IBM Global Business Services
- Leidos
- Booz Allen Hamilton
- Northrop Grumman
- Lockheed Martin
- Raytheon Technologies
- BAE Systems
- Honeywell Aerospace
- L3Harris Technologies
- Aerojet Rocketdyne
- Jacobs Engineering Group
- SAIC (Science Applications International Corporation)
- General Dynamics Information Technology
- MDA (MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates)
- Magellan Aerospace
- Neptec Design Group
- COM DEV International (Honeywell Aerospace)
- OSI Maritime Systems
- Canadensys Aerospace Corporation
- GHGSat
- ABB Canada
- C-CORE
- Kepler Communications
- Geocentrix Technologies
- Canadian Space Services
- NGC Aerospace
- Space Strategies Consulting
- Astroinformatics Canada
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Space Research and Technology Industry
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including Space Research and Technology Industry.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including Space Research and Technology Industry.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including Space Research and Technology Industry:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including Space Research and Technology Industry:
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including Space Research and Technology Industry:
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including Space Research and Technology Industry:
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
Digital I/O adapters:
and relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
- Find Your 860-960 MHz RFID Module
- Find Your 13.56 MHz High Frequency RFID Module
- Find Your 125 kHz RFID Reader Modules
In collaboration with its sister company GAO Tek Inc, a wide selection of high-quality drones are offered:
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in Space Research and Technology Industry:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include
Telescopes, Satellites, Rovers and Landers, Space Probes, Spacecraft, Space Suits, Thrusters and Propulsion Systems, Scientific Instruments, Space Telemetry and Communication Systems, Landing and Recovery Systems, Space Habitats and Modules, Solar Panels and Power Systems, Ion and Electric Propulsion, Space Manipulators and Robotic Arms, Space Radiation Shields, Cryogenic Systems, Space Environmental Testing Chambers, Microgravity Research Facilities, Ground-based Tracking and Control Systems, Lunar and Planetary Sample Return Equipment.
People or workers tracking system:
- PERSONNEL TRACKING SOFTWARE
- Personnel or people access control system:
- ACCESS CONTROL SOFTWARE
Parking or vehicle control system:
Furthermore, GAO provides the customization of RFID tags, RFID readers, BLE beacons and BLE gateways, IoT, drones, and systems and consulting services for Space Research and Technology Industry and for various industries in all metropolitans in the U.S. and Canada: Services
GAO Has Served Space Research and Technology Industry Extensively
GAO RFID Inc. and its sister company GAO Tek Inc. together offer a wide choice of RFID, BLE, IoT, drone, testing and measurement devices, and network products.
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in Space Research and Technology Industry to achieve success in Commercial Space Exploration, Small Satellites, Reusable Rockets, Space Tourism, Lunar Exploration, Satellite Constellations, International Collaboration, Space Debris Mitigation, Interplanetary Travel, Astrophysics, Exoplanets, Quantum Communication, In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU), Cislunar, Space Mining, Autonomous Spacecraft, Habitability, Space Weather, Orbital Dynamics, and Heliophysics.
GAO RFID Inc. has deployed RFID, BLE and IoT projects for many companies in Space Research and Technology Industry, including many in its various divisions such as
- Satellite Technology: This includes the design, manufacturing, and operation of satellites for communication, Earth observation, navigation, scientific research, and more.
- Spacecraft Manufacturing: Focuses on building spacecraft for various missions, such as scientific exploration, communication, and remote sensing.
- Launch Services: Involves developing launch vehicles to carry payloads such as satellites, scientific instruments, and crewed missions into space.
- Astronomy and Astrophysics: The study of celestial objects, cosmic phenomena, and the nature of the universe.
- Planetary Science: Concentrates on the study of planets, moons, asteroids, and comets to understand their formation and evolution.
- Human Spaceflight: Focuses on sending astronauts into space for research, exploration, and potential colonization efforts.
- Space Exploration: Involves robotic and crewed missions to explore other planets, moons, asteroids, and beyond.
- Space Research and Experimentation: Includes scientific experiments conducted in microgravity environments and space stations to study various phenomena.
- Space Communications and Navigation: Involves developing technologies for communication with spacecraft and providing global navigation services.
- Space Technology Development: Encompasses the creation of advanced technologies, materials, and instruments for space missions.
- Space Weather and Environment: Focuses on understanding the impact of solar activity on Earth and space-based technologies.
- Space Debris Mitigation: Addresses the challenges of managing and preventing space debris to ensure sustainable use of orbits.
- Space Tourism and Commercialization: Emerging sub-industry focused on offering space travel experiences for civilians and commercializing space-related activities.
- Space Policy and Regulations: Involves creating and enforcing regulations, treaties, and policies governing space activities on an international level.
- Satellite Services: Encompasses services provided by satellites, such as communication, remote sensing, weather forecasting, and navigation.
- Space Industry Infrastructure: Includes ground control centers, launch facilities, testing laboratories, and research institutions supporting space missions.
GAO’s technologies enable its customers in “Space Research and Technology Industry” to effectively track their workforces such as Aerospace Engineer, Astrophysicist, Mission Specialist, Satellite Technician, Spacecraft Designer, Flight Controller, Planetary Scientist, Navigation Specialist, Astronaut/Cosmonaut/Taikonaut, Mission Planner, Data Analyst, Payload Engineer, Space Weather Forecaster, Ground Control Operator, Systems Engineer, Research Scientist, Spacecraft Mechanic, Materials Scientist, Propulsion Engineer, Space Policy Analyst effectively track operational assets such as Telemetry System, Command and Data Handling System, Navigation and Tracking Systems, Payload Instruments, Satellite Antennas, Ground Control Station, Satellite Communication Systems, Solar Panels, Reaction Control System, Spacecraft Propulsion System, Radiation Shields, Life Support Systems, Satellite Imaging Systems, Thermal Control Systems, Launch Vehicles, Satellite Ground Stations, Remote Sensing Instruments, Scientific Payloads, Propellant Tanks, Solar Arrays, Orbital Maneuvering Systems, Telescopes and Observatories, Rovers and Landers, Laboratory Modules, Space Suits.
Here are some of the leading companies in Space Research and Technology Industry:
Lockheed Martin Space Systems
- Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems
- Raytheon Technologies
- MIT Lincoln Laboratory
- Draper
- Harris Corporation
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
- Ball Aerospace
- NASA’s Glenn Research Center
- United Launch Alliance (ULA)
- Blue Canyon Technologies
- Astro Aerospace
- NanoRacks
- SpaceX
- Blue Origin
- Aerojet Rocketdyne
- Virgin Galactic
- Rocket Lab
- Maxar Technologies
- Moon Express
- NASA
- Jacobs
- JPL (Jet Propulsion Laboratory)
- Aerojet Rocketdyne
- Made In Space
- Astrobotic
- KinetX Aerospace
- Relativity Space
- Collins Aerospace
- Airbus Defence
You Are Invited to Contact Us!
If you interested in our products, services or partnering with us, please feel
free to contact us by filling out this form:
or email us at sales@gaorfid.com