Overview
The Electrical Equipment, Appliance, and Component Manufacturing industry encompasses a wide range of businesses involved in the design, production, and distribution of various electrical equipment, appliances, and components. This diverse sector includes companies that manufacture products such as electric motors, lighting fixtures, wiring devices, batteries, transformers, circuit boards, and household appliances like refrigerators, ovens, and washing machines.
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing industry to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials and operational equipment such as CNC Machines, Injection Molding Machines, Die-Casting Machines, Laser Cutting and Engraving Machines, Welding Machines, Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Manufacturing Equipment, Electroplating Equipment, Testing and Quality Control Equipment, Assembly Line Equipment, Environmental Testing Chambers, Soldering Stations, Electrical Discharge Machines (EDM), Wire Drawing Machines, Ultrasonic Welding Machines, Power Presses, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Machines, Transformer Winding Machines, Testing Fixtures and Jigs, Material Handling Equipment, Packaging Machinery, Safety Equipment, CAD/CAM Software, Maintenance Tools, Environmental Monitoring Equipment, Energy Efficiency Testing Equipment, Quality Assurance and Inspection Systems, Spectrum Analyzers, Materials Testing Equipment, Electrical Safety Testing Equipment, and Drying and Curing Ovens.
Ranked as one of the top 10 global RFID suppliers, GAO RFID Inc. is based in New York City, U.S. and Toronto, Canada. GAO offers a comprehensive selection of UHF, HF (including NFC) and LF RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags, BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. Such RFID and BLE products and systems, as well as its IoT and drone technologies, have been successfully deployed for electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing. Its sister company, GAO Tek Inc. https://gaotek.com, is a leading supplier of industrial or commercial testers and analyzers, drones, and network products.
The targeted markets of both GAO RFID Inc. and GAO Tek Inc. are North America, particularly the U.S., Canada, Mexico, and Europe. As a result, this website gaorfid.com is offered in English and other major languages of North America and Europe such as Spanish, French, German, Italian, Polish, Ukrainian, Romanian, Russian, Dutch, Turkish, Greek, Hungarian, Swedish, Czech, Portuguese, Serbian, Bulgarian, Croatian, Danish, Finnish, Norwegian, Slovak, Catalan, Lithuanian, Bosnian, Galician, Slovene, Latvian, Estonian, Welsh, Icelandic, and Irish.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Electrical Equipment, Appliance, and Component Manufacturing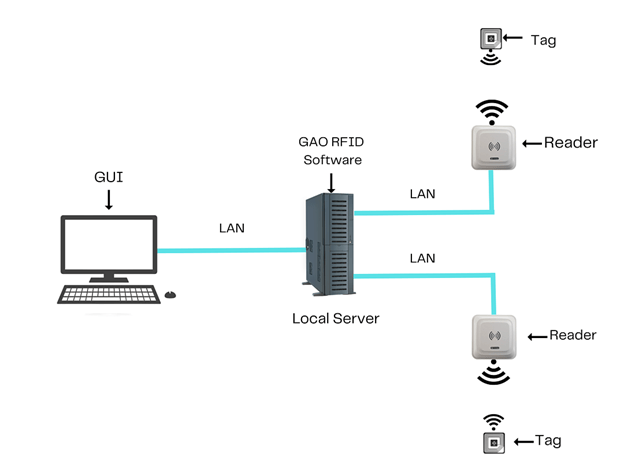
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server that normally is on our client’s premise, and another version runs in the cloud. The cloud server could be GAO’s cloud server, client’s own cloud server or a cloud server from one of the leading cloud server providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud (formerly SoftLayer), Oracle Cloud, RedHat, Heroku, Digital Ocean, CloudFlare, Linode and Rackspace. The above illustrates GAO system for electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing with its software running on a local server.
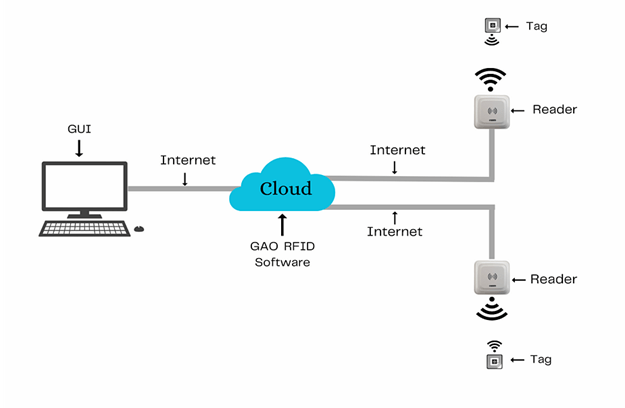 The above illustrates GAO system for electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing with its software running in cloud.
The above illustrates GAO system for electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing with its software running in cloud.
GAO’s RFID and BLE technologies, consisting of RFID readers, RFID tags, BLE gateways, BLE beacons, software, cloud services and their systems, have the following applications in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing industry:
- Inventory Management: GAO RFID tags can be attached to raw materials, components, and finished products, enabling real-time tracking of inventory levels. This helps reduce stockouts, overstock situations, and improves supply chain management.
- Asset Tracking: GAO’s Manufacturers use RFID to monitor the location and status of equipment, tools, and machinery, reducing loss and optimizing asset utilization.
- Work-in-Progress (WIP) Tracking: GAO RFID technology helps track the progress of products through the manufacturing process, ensuring that each step is completed correctly and efficiently.
- Quality Control: GAO RFID can be used to associate quality control data with specific components or products, making it easier to identify and address defects in the manufacturing process.
- Tool and Equipment Management: GAO RFID tags on tools and equipment help ensure they are in the right place when needed, reducing downtime and improving worker efficiency.
- Production Line Optimization: GAO RFID-enabled sensors and tags can monitor the performance of machinery and production lines, facilitating predictive maintenance and minimizing production disruptions.
- Workforce Management: GAO RFID badges or cards can be used for access control and time tracking, ensuring that only authorized personnel access critical areas.
- Product Authentication: GAO’s Manufacturers can use RFID tags to verify the authenticity of components and products, reducing the risk of counterfeiting.
- Traceability and Recall Management: GAO’s RFID enables rapid identification and recall of products in case of safety or quality issues, enhancing consumer safety.
- Energy Management: GAO RFID sensors can monitor energy usage in manufacturing facilities, helping identify opportunities for energy savings.
- Supply Chain Visibility: GAO RFID provides end-to-end visibility into the supply chain, allowing manufacturers to track the movement of materials and products from suppliers to end-users.
- Maintenance and Repairs: GAO RFID tags can store maintenance histories and repair records for equipment, making it easier to schedule and track maintenance activities.
- Shipping and Receiving: GAO RFID simplifies shipping and receiving processes by automating data capture, reducing errors, and expediting shipments.
- Customization and Configuration: GAO RFID can be used to configure and customize products based on specific customer requirements, improving flexibility in manufacturing.
- Anti-Theft and Security: GAO RFID-based security systems can protect valuable equipment and products from theft or unauthorized access.
- Compliance and Reporting: GAO RFID data can be used to ensure compliance with industry regulations and reporting requirements.
- Just-in-Time Manufacturing: GAO RFID enables accurate tracking of components and materials, facilitating just-in-time manufacturing practices.
- Product Serialization: GAO RFID tags can be used for unique product serialization, aiding in product recalls and warranty management.
- Environmental Monitoring: GAO RFID sensors can monitor environmental conditions in manufacturing facilities, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
- Workplace Safety: GAO RFID can be integrated into safety protocols to track the location and movement of workers in hazardous areas, enhancing safety measures.
GAO’s drone technologies find the following applications in the electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing:
- Facility Inspection: GAO Drones equipped with cameras and sensors can perform visual inspections of manufacturing facilities, identifying maintenance needs, safety hazards, and equipment issues.
- Inventory Management: GAO Drones with RFID and barcode scanning capabilities can help automate inventory counts and track the movement of materials and components within the manufacturing facility.
- Equipment Maintenance: GAO Drones can access hard-to-reach areas and perform predictive maintenance by inspecting machinery, identifying wear and tear, and detecting potential faults before they cause downtime.
- Environmental Monitoring: GAO Drones can monitor environmental conditions within manufacturing facilities, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards related to air quality, temperature, and emissions.
- Security and Surveillance: GAO Drones equipped with surveillance cameras enhance security by monitoring and patrolling manufacturing sites, helping prevent unauthorized access and theft.
- Site Surveying and Mapping: GAO Drones can create accurate 3D maps and models of manufacturing facilities, aiding in facility planning, expansion, and layout optimization.
- Emergency Response: In case of emergencies, drones can be deployed to assess the situation quickly, identify safety risks, and provide real-time data to responders.
- Quality Control: GAO Drones with high-resolution cameras and sensors can capture detailed images and data for quality control inspections of electrical components and appliances.
- Supply Chain Tracking: GAO Drones can monitor the movement of raw materials, components, and finished products within the supply chain, ensuring efficient logistics.
- Energy Efficiency Audits: GAO Drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras can conduct energy audits to identify sources of energy loss and areas for improvement in manufacturing processes.
GAO’s IoT technologies, consisting of IoT sensors, sensors networks and systems, find the following applications in the electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing industry:
- Predictive Maintenance: GAO IoT sensors on machinery and equipment collect data on performance and wear. Predictive analytics use this data to schedule maintenance proactively, reducing downtime and extending equipment life.
- Asset Tracking: GAO IoT tags and sensors track the location and status of tools, equipment, and components in real-time, preventing loss and optimizing asset utilization.
- Energy Management: GAO IoT devices monitor energy consumption in manufacturing facilities. This data helps identify energy-saving opportunities and reduce operational costs.
- Quality Control: GAO IoT sensors monitor production processes, ensuring product quality and consistency. Deviations from set standards trigger alerts for immediate corrective action.
- Supply Chain Visibility: GAO IoT provides end-to-end visibility into the supply chain, from component suppliers to distribution centers. Manufacturers can track materials and products in real-time, improving logistics and reducing lead times.
- Remote Equipment Monitoring: GAO IoT enables remote monitoring of equipment performance and conditions. Manufacturers can access real-time data and perform diagnostics without being physically present.
- Environmental Monitoring: GAO IoT sensors monitor environmental conditions within manufacturing facilities, including temperature, humidity, and air quality, ensuring compliance with safety and regulatory standards.
- Inventory Management: GAO IoT tags and sensors automate inventory tracking, reducing manual errors, and ensuring accurate stock levels.
- Production Line Optimization: GAO IoT sensors on production lines collect data on equipment performance and production rates. This information is used to optimize production processes for efficiency and quality.
- Worker Safety: GAO IoT wearables and sensors enhance worker safety by monitoring conditions such as temperature, noise levels, and hazardous gas concentrations. Alerts are generated in case of safety risks.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates and government regulations:
RFID, BLE, IoT, & Drone Standards & Mandates
- ISO 18000
- ISO 14443
- ISO 15693
- ISO 18092 (NFC – Near Field Communication)
- EPC Global
- ISO 17363
- GS1
- IEC 62675
- IEC 62225
- ASTM EPC/RFID
- NEMA Standards
- Bluetooth 4.0
- Bluetooth 4.1
- Bluetooth 4.2
- Bluetooth 5
- Bluetooth 5.1
- Bluetooth 5.2
- GATT (Generic Attribute Profile)
- ATT (Attribute Protocol)
- SIG (Bluetooth Special Interest Group) Profiles
- IEEE 802.15.1
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol)
- HTTP/HTTPS
- OPC UA (Unified Architecture)
- DDS (Data Distribution Service)
- Zigbee
- LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network)
- Thread
- Modbus
- BACnet (Building Automation and Control Networks)
- AllJoyn (now part of Project CHIP – Connected Home over IP)
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
- Thread Group Standards
- Industrial IoT (IIoT) Standards
- IoT Security Standards
- ISO 27001
- ISO 21384 (Part 1-3)
- ASTM F3322
- ANSI/UL 3030
- ISO 19684 (Part 1-4)
- AS/NZS 4815
- ANSI/ASSP A10.9
- JARUS (Joint Authorities for Rulemaking on Unmanned Systems)
- FAA (Federal Aviation Administration) Regulations
- EASA (European Union Aviation Safety Agency) Regulations
- Transport Canada Regulations
- CASA (Civil Aviation Safety Authority) Regulations
- DGCA (Directorate General of Civil Aviation) Regulations
US Government Regulations
- CFR Title 21 Part 1040 (Performance Standards for Light-Emitting Products)
- CFR Title 29 Part 1910 (Occupational Safety and Health Standards)
- CFR Title 40 Part 82 (Protection of Stratospheric Ozone)
- CFR Title 47 Part 15 (Radio Frequency Devices)
- CFR Title 49 Part 171 (General Information, Regulations, and Definitions)
- CFR Title 49 Part 178 (Specifications for Packaging)
- CFR Title 50 Part 18 (Electronic Code of Federal Regulations)
Canadian Government Regulations
- General Requirements -CSA C22.2 No. 1 Motors and Generators
- CSA C22.2 No. 14 Industrial Control Equipment
- CSA C22.2 No. 24.1 Flameproof Enclosures for Electrical Equipment for Use in Hazardous Locations
- CSA C22.2 No. 30 Enclosures for Electrical Equipment
- CSA C22.2 No. 100-04 Motors and Generators
- CSA C22.2 No. 105 Electric Storage-Tank Water Heaters
- CSA C22.2 No. 144 Portable Electric Tools
- CSA C22.2 No. 191 Panelboards and Enclosed Panelboards
- CSA C22.2 No. 204 Fuses and Fuse Accessories
- CSA C22.2 No. 223 Industrial Control Equipment
- CSA C22.2 No. 229 Solid-State Controls for Appliances
- CSA C22.2 No. 286 Molded-Case Circuit Breakers, Molded-Case Switches, and Circuit-Breaker Enclosures
- CSA C22.2 No. 291 Panelboards
- CSA C22.2 No. 314 Electric Industrial Cable Tray Systems
- CSA C22.2 No. 317 Terminal Blocks
- CSA C22.2 No. 60947-4-1 Low-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear – Part 4-1: Contactors and Motor Starters
GAO’s Software Provides API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing such as:
Personnel Management:
- Employee Attendance Tracking
- Workforce Scheduling and Shift Management
- Performance Management
- Training and Certification Tracking
- Health and Safety Compliance Monitoring
- Employee Skill and Certification Database
Equipment Management:
- Asset Tracking and Inventory Management
- Predictive Maintenance
- Equipment Calibration Management
- Energy Management and Monitoring
- Quality Control and Testing Equipment Management
Access Control:
- Data Center Access and Security
- Secure Remote Access for Maintenance
- Visitor Management Systems
- Identity Verification and Authentication
Warehouse Management:
- Material Handling and Storage Optimization
- Order Fulfillment and Pick-and-Pack
- RFID-Based Inventory Management
- Demand Forecasting and Planning
- Supplier Collaboration and Vendor Management
Supply Chain Management:
- Procurement and Purchase Order Management
- Demand and Supply Planning
- Logistics and Transportation Management
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory Management
- Supply Chain Visibility and Analytics
Other Applications:
- Compliance and Regulatory Reporting
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Tracking
- Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
- Document Management and Digital Records
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- E-commerce and Online Sales Platforms
- Warranty Management and After-Sales Service
GAO has enabled its customers to make use of some of the leading software and cloud services in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing industry. Below are some of popular software and cloud services in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing industry SAP successFactors, Oracle Human Capital Management (HCM), Workday Human Capital Management, ADP Workforce Now, and Kronos Workforce Central. These solutions offer a wide range of human capital management tools, covering workforce planning, payroll, and talent development. IBM Maximo, Infor EAM, Oracle Maintenance Cloud, Dude Solutions, and eMaint CMMS. Oracle Cloud HCM, SAP SuccessFactors, Workday, ADP Workforce Now, and Kronos Workforce Dimensions lead the way. These cloud-based solutions deliver a comprehensive suite of HR and talent management tools, ensuring flexibility and scalability in workforce management. Honeywell Access Control, LenelS2, Genetec Security Center, Brivo, and Avigilon Access Control Manager (ACM). These solutions provide advanced access control features like card readers, biometric access, visitor management, and security monitoring for secure facility access.
GAO has worked with some of the leading technology companies in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing to provide integrated RFID, BLE, IoT and drone solutions to customers. Here are some of the technology leaders in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing industry such as IBM, Siemens, Schneider Electric, Honeywell, ABB, Emerson Electric, Rockwell Automation, Microsoft, Oracle, and Cisco. Intel Corporation, Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics, NXP Semiconductors, Analog Devices, Inc., Cypress Semiconductor, Maxim Integrated, Microchip Technology, ON Semiconductor, and Infineon Technologies. Siemens, Rockwell Automation, ABB, Emerson Electric, Schneider Electric, Honeywell, General Electric (GE), Mitsubishi Electric, Yokogawa Electric, and FANUC.
Case Studies of RFID, IoT & Drone Applications
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Below are some RFID application cases in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing industry.
Inventory Management: A major appliance manufacturer in the USA adopts RFID technology to track the movement of components and finished products within their manufacturing facility. By implementing RFID tags on components and appliances, they streamline inventory management, reduce manual errors, and improve supply chain visibility.
Quality Control: An electrical equipment manufacturer utilizes RFID tags with embedded sensors to monitor the quality and condition of critical components during the manufacturing process. RFID sensors provide real-time data on temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors, ensuring that products meet stringent quality standards.
Work-in-Progress Tracking: A component manufacturer deploys RFID systems to track the progress of work-in-progress (WIP) items on the factory floor. RFID readers at various production stations collect data on the status of each component, allowing for real-time monitoring and efficient production planning.
Maintenance and Servicing: An appliance service provider in the USA integrates RFID technology into its maintenance operations. RFID tags on appliances store maintenance history and service schedules, allowing technicians to access relevant information quickly and provide more efficient and accurate service.
Supply Chain Optimization: A Canadian electrical equipment manufacturer adopts RFID technology to optimize its supply chain. RFID tags are attached to components and products, allowing the company to monitor inventory levels, track shipments in real-time, and enhance demand forecasting. This results in reduced lead times and improved overall supply chain efficiency.
Quality Assurance: A Canadian appliance manufacturer implements RFID-based quality assurance processes. RFID tags with embedded sensors are used to monitor temperature and humidity conditions during the manufacturing and transportation of appliances. This real-time data ensures that products meet quality standards upon delivery to consumers.
Asset Management: A component manufacturing company in Canada deploys RFID for asset management. RFID tags are affixed to manufacturing equipment and tools, enabling real-time tracking of their usage and maintenance schedules. This ensures that equipment is properly maintained, reducing downtime and improving productivity.
Production Efficiency: An electrical component manufacturer in Canada uses RFID to enhance production efficiency. RFID-enabled workstations and tools allow for accurate tracking of work-in-progress (WIP) components, reducing errors and bottlenecks in the production process.
Warranty Tracking: A Canadian appliance manufacturer utilizes RFID technology to track warranty information. RFID tags on appliances store warranty details, making it easier for customers to access warranty information and for the manufacturer to process warranty claims efficiently.
Energy Management: A Canadian company specializing in electrical equipment integrates RFID into its energy management systems. RFID sensors monitor energy usage in real-time, helping the company identify opportunities for energy savings and sustainability improvements.
Supply Chain Visibility: A multinational electrical equipment manufacturer implements RFID across its supply chain to enhance visibility. RFID tags on shipments and components enable real-time tracking, reducing transit times, minimizing loss, and ensuring on-time deliveries to customers.
Inventory Management: A large appliance manufacturer in the USA implements UHF RFID for inventory management. RFID tags are attached to components and appliances at various stages of production. This enables real-time tracking of inventory levels, reduces manual counting errors, and streamlines the restocking process.
Work-in-Progress Tracking: A component manufacturing facility in the USA adopts UHF RFID for tracking work-in-progress (WIP) items on the factory floor. RFID readers installed at key production points automatically record data on the status and location of components, improving production visibility and scheduling.
Asset Tracking: An electrical equipment manufacturer in the USA uses UHF RFID to track and manage its valuable manufacturing equipment. RFID tags are affixed to machinery, tools, and other assets, allowing for real-time monitoring of asset location and maintenance schedules, reducing downtime.
Quality Control: A manufacturer of electrical components integrates UHF RFID tags with sensors to monitor the environmental conditions of components during production and transportation. This data helps ensure that products meet quality standards upon delivery to customers.
Supply Chain Visibility: A multinational component supplier in the USA employs UHF RFID for supply chain optimization. RFID tags on shipments and products provide real-time tracking data, improving supply chain visibility, reducing transit times, and minimizing inventory carrying costs.
Maintenance and Servicing: An appliance service provider in the USA uses UHF RFID to streamline maintenance operations. RFID tags on appliances store maintenance history and service schedules, enabling technicians to access relevant information quickly and provide more efficient service.
Inventory Optimization: A Canadian appliance manufacturer adopts UHF RFID technology to optimize inventory management. RFID tags are applied to components and appliances, enabling real-time tracking of stock levels. This data helps reduce overstocking, minimize out-of-stock situations, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Production Efficiency: A component manufacturer in Canada integrates UHF RFID for improved production efficiency. RFID tags on work-in-progress (WIP) items and production equipment provide real-time data on production progress. This enhances visibility into manufacturing processes, reduces bottlenecks, and improves production planning.
Asset Tracking: A Canadian electrical equipment manufacturer utilizes UHF RFID for asset tracking and management. RFID tags are attached to valuable manufacturing equipment and tools. This ensures efficient tracking of asset location, maintenance schedules, and reduces equipment downtime.
Quality Assurance: An appliance manufacturer in Canada implements UHF RFID tags with embedded sensors to monitor the quality of appliances during production and transportation. The real-time data on environmental conditions helps ensure product quality upon delivery to customers.
Supply Chain Visibility: A Canadian component supplier deploys UHF RFID for enhanced supply chain visibility. RFID tags on shipments and products provide real-time tracking information, reducing transit times, improving demand forecasting, and minimizing carrying costs.
Maintenance and Service Records: An appliance service provider in Canada integrates UHF RFID technology for managing appliance maintenance and service records. RFID tags on appliances store detailed service histories, making it easier for technicians to access relevant information and provide efficient service.
Inventory Management: A major appliance manufacturer in Mexico adopts UHF RFID technology for inventory management. RFID tags are attached to components and appliances, enabling real-time tracking of stock levels. This data helps reduce excess inventory, minimize stockouts, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Production Process Optimization: A component manufacturing facility in Mexico integrates UHF RFID for optimizing the production process. RFID tags on work-in-progress (WIP) items and machinery provide real-time data on production progress. This enhances visibility into manufacturing processes, reduces production bottlenecks, and improves production scheduling.
Asset Tracking: A Mexican electrical equipment manufacturer utilizes UHF RFID for asset tracking and management. RFID tags are affixed to valuable manufacturing equipment and tools, allowing for efficient tracking of asset location, maintenance schedules, and reducing equipment downtime.
Quality Control: An appliance manufacturer in Mexico implements UHF RFID tags with embedded sensors to monitor the quality of appliances throughout production and transportation. The real-time data on environmental conditions ensures that products meet quality standards upon delivery to customers.
Supply Chain Visibility: A component supplier in Mexico deploys UHF RFID for improved supply chain visibility. RFID tags on shipments and products provide real-time tracking information, reducing transit times, enhancing demand forecasting, and minimizing inventory carrying costs.
Maintenance and Service Records: An appliance service provider in Mexico integrates UHF RFID technology for managing maintenance and service records. RFID tags on appliances store detailed service histories, enabling technicians to access relevant information quickly and provide efficient service.
Supply Chain Optimization: A European electrical equipment manufacturer implements UHF RFID for supply chain optimization. RFID tags are attached to components and products, allowing real-time tracking of inventory levels. This results in reduced lead times, lower inventory carrying costs, and improved demand forecasting.
Production Process Efficiency: A component manufacturer in Europe integrates UHF RFID technology to enhance production process efficiency. RFID tags on work-in-progress (WIP) items and machinery provide real-time data on production progress. This improves visibility into manufacturing processes, reduces production bottlenecks, and enhances production scheduling.
Asset Tracking: A European appliance manufacturer utilizes UHF RFID for asset tracking and management. RFID tags are affixed to valuable manufacturing equipment and tools, enabling efficient tracking of asset location and maintenance schedules. This helps minimize equipment downtime.
Quality Assurance: An appliance manufacturer in Europe adopts UHF RFID tags with embedded sensors to monitor the environmental conditions of appliances during production and transportation. Real-time data on temperature and humidity ensures that products meet quality standards upon delivery to customers.
Supply Chain Visibility: A European component supplier deploys UHF RFID for enhanced supply chain visibility. RFID tags on shipments and products provide real-time tracking data, improving supply chain transparency, reducing transit times, and optimizing inventory management.
Maintenance and Service Records: An appliance service provider in Europe integrates UHF RFID technology for managing appliance maintenance and service records. RFID tags on appliances store detailed service histories, making it easier for technicians to access relevant information and provide efficient service.
Many applications of RFID by GAO can be found here https://gaorfid.com/rfid-systems-by-industry/
Case Studies of IoT Applications
Below are some IoT application cases in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing industry.
Predictive Maintenance: A U.S.-based electrical equipment manufacturer implements IoT sensors in its production equipment and appliances. These sensors collect real-time data on machine performance and component wear. Using predictive analytics, the company can identify potential maintenance issues before they cause breakdowns, reducing downtime and saving on repair costs.
Smart Appliances: An appliance manufacturer in the USA develops a line of IoT-enabled smart appliances. These appliances are equipped with sensors and Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing users to control them remotely through a mobile app. Users can adjust settings, receive notifications about maintenance needs, and monitor energy consumption, enhancing convenience and energy efficiency.
Energy Monitoring: A component manufacturer in the USA deploys IoT sensors throughout its manufacturing facilities to monitor energy consumption. The data collected helps identify energy-saving opportunities and optimize production processes to reduce overall energy costs and environmental impact.
Quality Control: A U.S. appliance manufacturer utilizes IoT sensors to monitor the quality of products in real-time during the manufacturing process. Sensors collect data on temperature, humidity, and other critical variables. If any deviations from quality standards are detected, the system automatically initiates corrective actions, ensuring consistent product quality.
Inventory Management: An electrical component supplier in the USA implements IoT-based inventory management. Sensors placed in storage areas and on products provide real-time data on inventory levels and location. This system improves inventory accuracy, reduces stockouts, and enhances order fulfillment efficiency.
Smart Factory: An electrical equipment manufacturer in the USA transforms its production facility into a smart factory using IoT technologies. Sensors and connected devices are integrated into every aspect of the manufacturing process, from raw material monitoring to finished product quality control. This results in increased production efficiency, reduced waste, and improved overall operations.
Predictive Maintenance: A Canadian electrical equipment manufacturer integrates IoT sensors into its machinery and components. These sensors continuously collect data on equipment performance and wear. Through predictive analytics, the company can forecast maintenance needs, reduce downtime, and lower maintenance costs.
Smart Appliances: A Canadian appliance manufacturer develops a range of IoT-enabled smart appliances. These appliances feature sensors and Wi-Fi connectivity, enabling users to control them remotely via a mobile app. Users can adjust settings, receive maintenance alerts, and monitor energy usage, enhancing convenience and energy efficiency.
Energy Management: A component manufacturer in Canada employs IoT sensors across its manufacturing facilities to monitor energy consumption. The data helps identify energy-saving opportunities and optimize production processes to reduce energy expenses and environmental impact.
Quality Assurance: A Canadian appliance manufacturer deploys IoT sensors to monitor product quality in real-time during the manufacturing process. Sensors capture data on variables like temperature, humidity, and performance. If any deviations from quality standards occur, the system triggers corrective actions to maintain consistent product quality.
Inventory Optimization: A Canadian electrical component supplier implements IoT-based inventory management. Sensors placed in storage areas and on products provide live inventory data, including levels and locations. This system improves inventory accuracy, minimizes stockouts, and streamlines order fulfillment.
Smart Factory: A Canadian electrical equipment manufacturer transforms its production facility into a smart factory using IoT technologies. Sensors and connected devices are integrated into every stage of the manufacturing process, from raw material monitoring to final product quality control. This results in heightened production efficiency, reduced waste, and enhanced overall operations.
Predictive Maintenance: A Mexican electrical equipment manufacturer integrates IoT sensors into its production machinery and components. These sensors continuously gather data on equipment performance and wear. By applying predictive analytics, the company can forecast maintenance needs, reduce downtime, and minimize maintenance costs.
Smart Appliances: A Mexican appliance manufacturer develops a line of IoT-enabled smart appliances. These appliances incorporate sensors and Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing users to control them remotely through a mobile app. Users can adjust settings, receive maintenance alerts, and monitor energy consumption, enhancing convenience and energy efficiency.
Energy Management: A component manufacturer in Mexico deploys IoT sensors across its manufacturing facilities to monitor energy consumption. The collected data aids in identifying opportunities for energy conservation and optimizing production processes to reduce energy expenses and environmental impact.
Quality Control: A Mexican appliance manufacturer utilizes IoT sensors to monitor product quality in real-time during the manufacturing process. Sensors capture data on variables like temperature, humidity, and performance. If any deviations from quality standards occur, the system triggers corrective actions to ensure consistent product quality.
Inventory Optimization: A Mexican electrical component supplier implements IoT-based inventory management. Sensors placed in storage areas and on products provide real-time inventory data, including levels and locations. This system enhances inventory accuracy, reduces stockouts, and streamlines order fulfillment.
Smart Factory: A Mexican electrical equipment manufacturer transforms its production facility into a smart factory using IoT technologies. Sensors and connected devices are integrated into every phase of the manufacturing process, from monitoring raw materials to conducting final product quality control. This results in improved production efficiency, reduced waste, and enhanced overall operations.
Predictive Maintenance: A European electrical equipment manufacturer integrates IoT sensors into its machinery and components. These sensors continuously collect data on equipment performance and wear. Through predictive analytics, the company can forecast maintenance needs, reduce downtime, and lower maintenance costs.
Smart Appliances: A European appliance manufacturer develops a range of IoT-enabled smart appliances. These appliances feature sensors and Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing users to control them remotely via a mobile app. Users can adjust settings, receive maintenance alerts, and monitor energy usage, enhancing convenience and energy efficiency.
Energy Management: A component manufacturer in Europe employs IoT sensors across its manufacturing facilities to monitor energy consumption. The data helps identify energy-saving opportunities and optimize production processes to reduce energy expenses and environmental impact.Quality Assurance: A European appliance manufacturer deploys IoT sensors to monitor product quality in real-time during the manufacturing process. Sensors capture data on variables like temperature, humidity, and performance. If any deviations from quality standards occur, the system triggers corrective actions to maintain consistent product quality.
Inventory Optimization: A European electrical component supplier implements IoT-based inventory management. Sensors placed in storage areas and on products provide live inventory data, including levels and locations. This system improves inventory accuracy, minimizes stockouts, and streamlines order fulfillment.
Smart Factory: A European electrical equipment manufacturer transforms its production facility into a smart factory using IoT technologies. Sensors and connected devices are integrated into every stage of the manufacturing process, from raw material monitoring to final product quality control. This results in heightened production efficiency, reduced waste, and enhanced overall operations.
Case Studies of Drone Applications
Below are some drone application cases in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing industry
Inventory Management: A U.S. electrical equipment manufacturer uses drones to conduct regular inventory checks in its large warehouses. Drones equipped with RFID scanners and cameras fly through the storage areas, quickly and accurately scanning barcodes and RFID tags on products and components. This streamlines inventory management, reduces manual labor, and minimizes errors.
Facility Inspections: An appliance manufacturing plant in the USA employs drones for routine facility inspections. Drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras and high-resolution cameras are used to inspect machinery, electrical systems, and the overall condition of the manufacturing facility. This allows for early detection of potential issues and preventive maintenance.
Supply Chain Monitoring: A component manufacturer uses drones to monitor the movement of raw materials and finished products within its supply chain. Drones equipped with GPS and RFID technology track shipments, ensuring that components arrive on time and are stored properly. This enhances supply chain visibility and reduces the risk of delays.
Quality Control: In a USA-based appliance manufacturing facility, drones with high-resolution cameras are deployed to inspect finished products on the assembly line. The drones capture detailed images of appliances, allowing for real-time quality control checks. Any defects or imperfections are flagged, ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
Environmental Compliance: An electrical component manufacturer in the USA employs drones to monitor emissions and environmental compliance at its manufacturing facilities. Drones equipped with gas sensors and cameras survey the premises to ensure compliance with environmental regulations. This helps the company maintain a positive environmental record.
Security and Surveillance: Drones are used for security and surveillance purposes in manufacturing facilities, particularly during non-operational hours. They patrol the premises, providing live video feeds to security personnel. In the event of any unauthorized access or suspicious activity, the drones can alert security and record footage for investigation.
Inventory Management: A Canadian electrical equipment manufacturer utilizes drones for efficient inventory management. Drones equipped with RFID scanners and cameras are employed to conduct regular inventory checks in large warehouses. They swiftly scan barcodes and RFID tags on products and components, streamlining inventory control and minimizing errors.
Facility Inspections: An appliance manufacturing plant in Canada employs drones for routine facility inspections. Equipped with thermal imaging cameras and high-resolution cameras, the drones inspect machinery, electrical systems, and the overall condition of the manufacturing facility. This enables early detection of potential issues and facilitates preventive maintenance.
Supply Chain Monitoring: A Canadian component manufacturer deploys drones to monitor the movement of raw materials and finished products within its supply chain. Drones equipped with GPS and RFID technology track shipments, ensuring that components arrive on schedule and are stored appropriately. This enhances supply chain visibility and minimizes the risk of delays.
Quality Control: In a Canadian appliance manufacturing facility, drones with high-resolution cameras are used to inspect finished products on the assembly line. These drones capture detailed images of appliances, enabling real-time quality control checks. Any defects or imperfections are promptly identified, ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
Environmental Compliance: A Canadian electrical component manufacturer uses drones to monitor emissions and environmental compliance at its manufacturing sites. Drones equipped with gas sensors and cameras survey the premises to ensure adherence to environmental regulations. This assists the company in maintaining a positive environmental record.
Security and Surveillance: Drones are deployed for security and surveillance purposes in manufacturing facilities in Canada, particularly during non-operational hours. They conduct patrols, providing live video feeds to security personnel. In the event of unauthorized access or suspicious activity, the drones can alert security and record footage for investigation.
Inventory Management: A Mexican electrical equipment manufacturer utilizes drones for efficient inventory management. Drones equipped with RFID scanners and cameras conduct regular inventory checks in large warehouses. They quickly scan barcodes and RFID tags on products and components, streamlining inventory control and minimizing errors.
Facility Inspections: An appliance manufacturing plant in Mexico employs drones for routine facility inspections. Equipped with thermal imaging cameras and high-resolution cameras, the drones inspect machinery, electrical systems, and the overall condition of the manufacturing facility. This enables early detection of potential issues and facilitates preventive maintenance.
Supply Chain Monitoring: A Mexican component manufacturer deploys drones to monitor the movement of raw materials and finished products within its supply chain. Drones equipped with GPS and RFID technology track shipments, ensuring that components arrive on schedule and are stored appropriately. This enhances supply chain visibility and minimizes the risk of delays.
Quality Control: In a Mexican appliance manufacturing facility, drones with high-resolution cameras are used to inspect finished products on the assembly line. These drones capture detailed images of appliances, enabling real-time quality control checks. Any defects or imperfections are promptly identified, ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
Environmental Compliance: A Mexican electrical component manufacturer uses drones to monitor emissions and environmental compliance at its manufacturing sites. Drones equipped with gas sensors and cameras survey the premises to ensure adherence to environmental regulations. This assists the company in maintaining a positive environmental record.
Security and Surveillance: Drones are deployed for security and surveillance purposes in manufacturing facilities in Mexico, particularly during non-operational hours. They conduct patrols, providing live video feeds to security personnel. In the event of unauthorized access or suspicious activity, the drones can alert security and record footage for investigation.
Inventory Management: A European electrical equipment manufacturer employs drones for efficient inventory management. Drones equipped with RFID scanners and cameras conduct regular inventory checks in large warehouses. They quickly scan barcodes and RFID tags on products and components, streamlining inventory control and minimizing errors.
Facility Inspections: An appliance manufacturing plant in Europe utilizes drones for routine facility inspections. Equipped with thermal imaging cameras and high-resolution cameras, the drones inspect machinery, electrical systems, and the overall condition of the manufacturing facility. This enables early detection of potential issues and facilitates preventive maintenance.
Supply Chain Monitoring: A European component manufacturer deploys drones to monitor the movement of raw materials and finished products within its supply chain. Drones equipped with GPS and RFID technology track shipments, ensuring that components arrive on schedule and are stored appropriately. This enhances supply chain visibility and minimizes the risk of delays.
Quality Control: In a European appliance manufacturing facility, drones with high-resolution cameras are used to inspect finished products on the assembly line. These drones capture detailed images of appliances, enabling real-time quality control checks. Any defects or imperfections are promptly identified, ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
Environmental Compliance: A European electrical component manufacturer uses drones to monitor emissions and environmental compliance at its manufacturing sites. Drones equipped with gas sensors and cameras survey the premises to ensure adherence to environmental regulations. This assists the company in maintaining a positive environmental record.
Security and Surveillance: Drones are deployed for security and surveillance purposes in manufacturing facilities in Europe, particularly during non-operational hours. They conduct patrols, providing live video feeds to security personnel. In the event of unauthorized access or suspicious activity, the drones can alert security and record footage for investigation.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Electrical Equipment, Appliance, and Component Manufacturing
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including electrical equipment, appliances, and component manufacturing.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including electrical equipment, appliances, and component manufacturing.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including electrical equipment, appliances, and component manufacturing:
Gen 2 UHF 902-928 MHz RFID Readers
Find Your UHF 865-868 MHz RFID Readers
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including electrical equipment, appliances, and component manufacturing:
Gen 2 UHF 902-928 MHz RFID Tags
Gen 2 UHF 865-868 MHz RFID Tags
Semi Passive UHF Gen2 RFID Tags
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
UHF 860 – 960 MHz RFID Antennas
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including electrical equipment, appliances, and component manufacturing:
HF 13.56 MHz Passive RFID Readers
LF 134 kHz Passive RFID Readers
LF 125 kHz Passive RFID Readers
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including electrical equipment, appliances, and component manufacturing:
High Frequency 13.56 MHz RFID Tags
Low Frequency 134 kHz RFID Tags
Low Frequency 125 kHz RFID Tags
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
Digital I/O adapters:
and relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
Find Your 860-960 MHz RFID Module
Find Your 13.56 MHz High Frequency RFID Module
Find Your 125 kHz RFID Reader Modules
In collaboration with its sister company GAO Tek Inc, a wide selectioon of high quality drones are offered:
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in electrical equipment, appliances, and component manufacturing:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include circuit board manufacturing equipment, such as pick and place machines, reflow ovens, and solder paste printers. Transformer winding machines, encompassing coil winding machines, core cutting machines, and insulation tape machines, are crucial. Injection molding and die-casting machines are employed for producing plastic and metal components and housings, respectively. Quality control and testing equipment, such as electrical testing machines, multimeters, and oscilloscopes, along with environmental test chambers and X-ray inspection machines.
People or workers tracking system:
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
Furthermore, GAO provides the customization of RFID tags, RFID readers, BLE beacons and BLE gateways, IoT, drones, and systems and consulting services for electrical equipment, appliances, and component manufacturing and for various industries in all metropolitans in North America, particularly the U.S., Canada and Mexico, and Europe: GAO Services
GAO Makes Efforts to Satisfy Customers
Large Choice of Products
To satisfy the diversified needs of their corporate customers, GAO RFID Inc. and its sister company GAO Tek Inc. together offer a wide choice of RFID, BLE, IoT, drones, testing and measurement devices, and network products.
Overnight Delivery
To shorten the delivery to our customers, GAO has maintained a large stock of its products and is able to ship overnight within continental U.S. and Canada, and fast delivery to anywhere in Mexico and Europe from the nearest warehouse.
Local to Our Customers
We are in both the U.S. and Canada. We travel to customers’ premises if necessary. Hence, we provide a very strong local support to our customers in North America, particularly the U.S., Canada and Mexico, and Europe. Furthermore, we have built partnerships with some integrators, consulting firms and other service providers in different cities to further strengthen our services. Here are some of the service providers in electrical equipment, appliances, and component manufacturing we have worked with to serve our joint customers:
- IBM Global Services
- Deloitte
- Accenture
- Capgemini
- Cognizant
- Wipro
- Infosys
- DXC Technology
- CGI
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)
- Tech Mahindra
- HCL Technologies
- PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) Advisory Services
- KPMG Advisory
- Ernst & Young (EY) Advisory Services
- BCG (Boston Consulting Group)
- McKinsey & Company
- Booz Allen Hamilton
- Atos Consulting
- NTT Data Consulting
- IBM Canada
- Deloitte Canada
- Accenture Canada
- Capgemini Canada
- Cognizant Canada
- Wipro Canada
- Infosys Canada
- CGI Canada
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) Canada
- Tech Mahindra Canada
- HCL Technologies Canada
- IBM Mexico
- Deloitte Mexico
- Accenture Mexico
- Capgemini Mexico
- Cognizant Mexico
- WEG Mexico
- Toshiba Mexico
- SolarEdge Mexico
- Schlumberger Mexico
- IBM Europe
- Deloitte Europe
- Accenture Europe
- Capgemini Europe
- Cognizant Europe
- Wipro Europe
- Infosys Europe
- CGI Europe
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) Europe
- Tech Mahindra Europe
- HCL Technologies Europe
GAO Has Served Electrical Equipment, Appliance, and Component Manufacturing Extensively
GAO RFID Inc. and its sister company GAO Tek Inc. together offer a wide choice of RFID, BLE, IoT, drone, testing and measurement devices, and network products.
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing Industry to achieve success in Industry 4.0, IoT (Internet of Things), Smart Manufacturing, Digital Twins, AI (Artificial Intelligence), Predictive Maintenance, Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing), Energy Efficiency, Supply Chain Visibility, Sustainability, Cybersecurity, Robotics, Big Data Analytics, Renewable Energy Integration, Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR), 5G Connectivity, Blockchain, Circular Economy, Human-Machine Collaboration, and Edge Computing. These trends and buzzwords represent the industry’s ongoing transformation through technology adoption, data-driven decision-making, sustainability efforts, and increased connectivity.
GAO RFID Inc. has deployed RFID, BLE and IoT projects for many companies in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing Industry, including many in its various divisions such as:
- Electrical Equipment Manufacturing: This division involves the production of a wide range of electrical equipment, such as transformers, generators, circuit breakers, and switchgear.
- Appliance Manufacturing: Companies in this sub-industry manufacture household and commercial appliances, including refrigerators, washing machines, ovens, and HVAC systems.
- Electronic Component Manufacturing: This sector focuses on producing electronic components like semiconductors, capacitors, resistors, and printed circuit boards (PCBs).
- Battery and Energy Storage Manufacturing: Companies in this division manufacture batteries, energy storage systems, and related components used in various applications, including renewable energy and electric vehicles.
- Lighting Equipment Manufacturing: This sub-industry includes the production of lighting fixtures, bulbs, LEDs, and other lighting products.
- Wiring Device Manufacturing: This division involves the manufacturing of wiring devices, outlets, plugs, switches, and related electrical components.
- Industrial Control and Automation Equipment Manufacturing: Companies in this category produce control systems, automation equipment, and instrumentation used in industrial processes and manufacturing facilities.
- Power Distribution and Control Manufacturing: This sub-industry focuses on products like electrical panels, switches, and power distribution equipment used in electrical systems.
- Electrical Connector and Cable Manufacturing: Manufacturers in this division produce electrical connectors, cables, and wiring harnesses used in various industries.
- Electronic Equipment Repair and Maintenance: This segment involves the repair and maintenance of electrical and electronic equipment, including appliances and industrial machinery.
- Renewable Energy Equipment Manufacturing: Companies within this sub-industry manufacture equipment and components for renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines, solar panels, and energy storage solutions.
GAO’s technologies enable its customers in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing to effectively track their workforces such as workers in the electrical equipment, appliance, and component, technicians operators managing machinery, maintenance personnel, electricians handling wiring and installation, supervisors managing production, r&d specialists working on innovation, logistics and supply chain personnel managing materials, safety and compliance officers and effectively track operational assets such as machinery Production lines, Robotics, Presses Testing and inspection, Material handling equipment, Ovens and Wiring and cable.
Here are some of the leading companies in electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing industry GAO has served:
- General Electric (GE)
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Whirlpool Corporation
- Eaton Corporation
- Cooper Industries
- Schneider Electric Canada Inc.
- Siemens Canada Limited
- ABB Canada
- General Electric (GE) Canada
- Honeywell Canada
- Rockwell Automation Canada
- Schneider Electric Mexico
- Siemens Mexico
- ABB Mexico
- General Electric (GE) Mexico
- Honeywell Mexico
- Emerson Electric Mexico
- Siemens AG (Germany)
- Schneider Electric SE (France)
- ABB Ltd (Switzerland)Philips (Netherlands)
- Legrand S.A. (France)
- Alstom (France)
- Electrolux AB (Sweden)
























You Are Invited to Contact Us!
If you are interested in our products, services or partnering with us, please feel free to contact us by filling out this form:
or email us at sales@gaorfid.com

