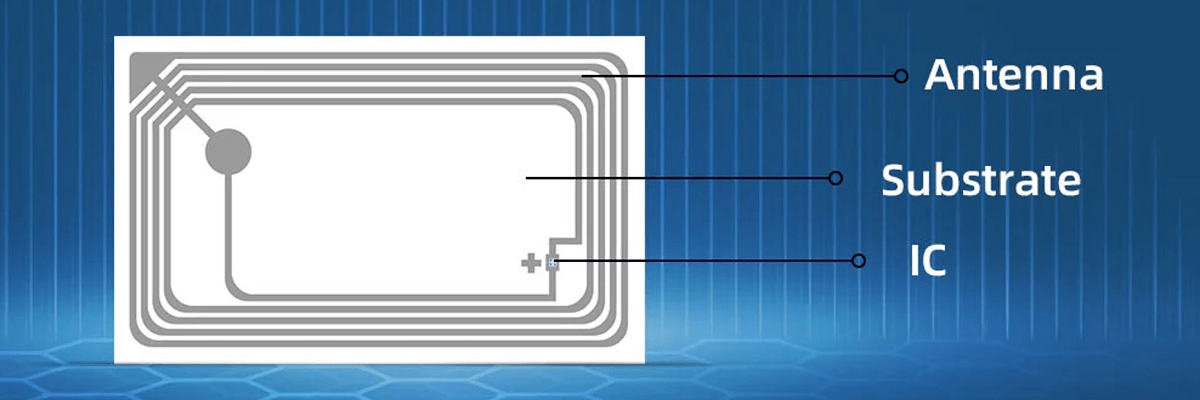
A UHF RFID tag, also known as an ultra-high frequency RFID transponder, is a compact electronic device that enables wireless data transmission to an RFID reader. These tags typically contain several key components: an integrated circuit (IC), an antenna, and a substrate or encapsulation that holds the circuitry together. The integrated circuit stores data and manages the communication between the RFID reader and the tag. The antenna, which is either printed, etched, or wound, captures and transmits radio frequency signals to the reader, enabling the tag to communicate over distances ranging from a few centimeters to several meters.
An example of a vital internal component includes the IC’s memory block, which holds unique identification data or other encoded information. Another example is the rectifier circuit, which converts the reader’s RF signal into usable power to operate the tag in passive RFID systems. These elements are crucial for enabling the non-battery-powered, long-range operation that UHF RFID tags are known for, making them ideal for inventory tracking, logistics, and supply chain management.
Mechanically, UHF RFID tags are designed to be durable and versatile. Depending on their intended application, these tags are made from a variety of materials, such as plastic, paper, or ceramic, and may be enclosed in ruggedized housings for use in harsh environments like construction sites or outdoor warehouses. The tags can also be embedded in or affixed to various surfaces like metal, glass, or plastic, with specific designs to ensure signal integrity and reliable communication in challenging conditions.
In terms of software, UHF RFID tags are encoded with standardized data structures, such as those defined by the EPC Gen2 standard (ISO/IEC 18000-6C). This ensures compatibility with UHF RFID readers across various industries and locations. Software platforms or middleware often manage large-scale deployments, providing functionalities like tag identification, data logging, and asset tracking integration.
GAO RFID Inc. ensures that its UHF RFID tags comply with regulatory requirements, including FCC Part 15 in the United States and ISED regulations in Canada. Compliance with these standards ensures that the tags operate without interference and meet legal frequency and power requirements. In addition, GAO RFID tags undergo comprehensive quality assurance testing, including performance testing for read range, durability tests for environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity), and compliance verification with ISO and EPC standards.
The quality assurance process at GAO RFID is rigorous, involving multiple stages of testing to ensure optimal performance under real-world conditions. Tags are subjected to environmental testing, electromagnetic interference (EMI) tests, and durability checks, including wear and tear simulations for long-term reliability. Furthermore, we focus on ensuring the highest levels of accuracy and durability, making these tags ideal for demanding applications in logistics, healthcare, and industrial automation.
UHF RFID tags can interface with external systems through various methods, typically via RFID readers. These readers, which may have serial ports, USB, or Ethernet connections, transfer the tag data into software systems for processing. The data can be integrated with enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms, asset tracking systems, or cloud-based databases, streamlining business operations.
Our products are in stock and can be shipped overnight to Continental U.S. and Canada from one of our local warehouses. If you have any questions, our technical experts can help you. Please fill out this form or email us.