Manufacturing construction involves designing and building facilities for manufacturing products such as automobiles, electronics, and consumer products. It requires specialized equipment, infrastructure, and careful planning to ensure that facilities meet specifications, comply with regulations and safety standards, and operate efficiently. The construction of these facilities requires specialized knowledge and equipment to ensure safe and efficient operations. GAO RFID Inc., one of the global top 10 RFID leaders, is based in New York and Toronto and has deployed many RFID, BLE, and IoT projects in the manufacturing construction industry.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for the Manufacturing Construction
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for all kinds of industries, including the manufacturing construction industry:
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including the manufacturing construction industry:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including the manufacturing construction industry:
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including the manufacturing construction industry:
- High Frequency 13.56 MHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 134 kHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 125 kHz Passive RFID Readers
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including the manufacturing construction industry:
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
Digital I/O adapters:
and relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
- UHF 860 – 960 MHz RFID Modules
- 13.56 MHz High Frequency RFID Modules
- 125 kHz Low Frequency RFID Modules
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in the manufacturing construction industry:
People or workers tracking system:
- GAO RFID Construction Site People Tracking
- GAO RFID People Tracking System for Manufacturing Facilities
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
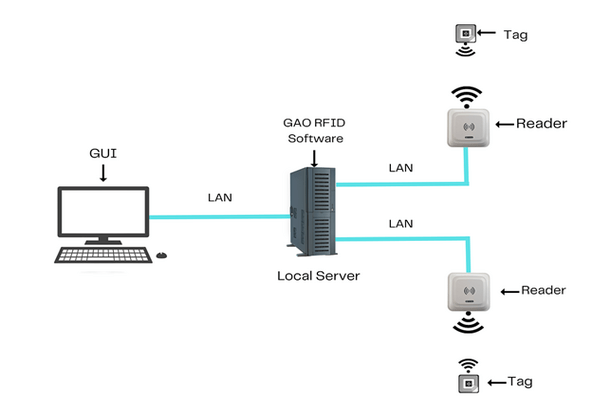
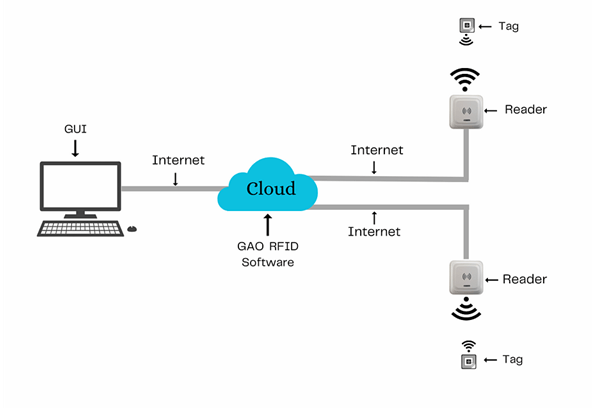
There are two versions of GAO’s software, one is running on a local server, and another running in the cloud.
GAO offers free samples of its RFID tags, labels, badges, and wristbands
GAO offers a free trial for all of its software available.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Manufacturing Construction
The manufacturing construction industry can significantly benefit from the integration of BLE, drones with RFID, and IoT with RFID technologies. These technologies can enhance the monitoring, tracking, and safety of workers and equipment, increase productivity, and reduce costs.
BLE technology can also be highly beneficial in manufacturing construction, which involves the construction of facilities for producing goods such as automobiles, electronics, and other products. With its long range of up to 300 meters, BLE can effectively track workers like welders, electricians and mechanics and equipment like SMT and AOI machines within the large manufacturing sites using beacons. BLE can also be used for access control, allowing authorized personnel like project managers to access specific zones while preventing unauthorized workers from entering therefore enhances security and safety in the manufacturing facility.
Drones with RFID readers can provide a portable and flexible solution for tracking workers, welders, machinists, mechanics, electricians, engineers, project managers, safety officers, inspectors and foremen, tools like drills, grinders, and sanders, and equipment like gauges, calipers, and scanners in large manufacturing construction sites. These drones can be used to detect safety hazards and provide a comprehensive view of the job site enabling safety management, automating time stamping and reducing the need for human intervention. The drones can also be employed for cost-effective asset tracking and people tracking throughout the manufacturing construction site, providing insights to project managers and site supervisors.
IoT sensors such as humidity, temperature, and vibration sensors can also be utilized in manufacturing construction sites to monitor inventory levels in real time and ensure that necessary components are available when needed. This reduces manual processes and allows workers to focus on critical tasks. By automating data such as storage area, supply levels, and usage through the use of BLE, workers can track conveyors, robotics, welding guns, and electronic components, stored in various locations. Strategically placed gateways can ensure that theft and loss of equipment are prevented. Manufacturing engineers, project managers, estimators, inspectors, foremen, and other construction workers can also use BLE to track which tools have been precisely calibrated, maintained, and properly utilized thus ensuring proper resource utilization. This helps project managers and warehouse managers create a decentralized inventory management system.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of the Manufacturing Construction
- ISO 18000-7 – This standard specifies the requirements for active RFID systems that operate at 433 MHz and can be used for tracking vehicles and equipment in manufacturing environments.
- International Building Code (IBC) – This code provides minimum requirements for the design, construction, and maintenance of buildings, including manufacturing facilities.
- American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standards – These standards cover various aspects of mechanical engineering, including materials, design, and testing of equipment and components that may be used in manufacturing facilities.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) – This federal agency sets and enforces safety and health standards for workers in the United States manufacturing construction industry.
- National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) codes and standards – These are standards for fire protection and life safety systems that may be relevant to manufacturing facilities.
- Clean Air Act (CAA) & Clean Water Act (CWA) – These laws regulates the emission of air pollutants from industrial facilities and the discharge of pollutants into navigable waters of the United States to prevent water pollution involved in manufacturing.
- National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) – This law requires federal agencies to consider the environmental impacts of their actions and decisions, and to involve the public in the decision-making process for manufacturing facilities.
- Canadian Standards Association (CSA)– The CSA is a non-profit organization providing guidelines and standards related to the design and testing of equipment and components that may be used in manufacturing facilities.
- Canadian Nuclear Safety and Control Act – This law regulates the use of nuclear materials and facilities in Canada, including the construction of manufacturing facilities involved in the production of nuclear materials or products.
GAO’s Software Provides API
GAO’s popular RFID software such as work-in-progress personnel tracking, work-in-progress asset tracking, work-in-progress access control, and work-in-progress parking system control offers a free trial and offers an API to each of the common applications in the manufacturing construction industry:
Personnel Management
-
- Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) – HRIS is a software application used to automate human resources functions such as employee data management, payroll processing, leave tracking, and performance monitoring.
- Time and Attendance Systems – Time and attendance systems are utilized to monitor employee attendance and working hours.
- Safety Management Systems – Safety management systems ensures that employees follow safety procedures and use the correct personal protective equipment (PPE) while working.
Equipment Management
-
- Equipment Maintenance System – Equipment maintenance systems are used to manage and schedule maintenance activities for manufacturing construction equipment to optimize equipment performance and efficiency.
- Asset Management System – Asset management systems are used to track equipment location and status, manage maintenance schedules, and monitor equipment performance.
- Robotics and Automation Software – Robotics and Automation Software is utilized in managing and controlling automated manufacturing and construction equipment, programming and controlling robotic systems.
Supply Chain Management
-
- Procurement Management System – Procurement management system streamlines the purchasing process by tracking supplier performance and managing contracts
- Inventory Management System – Inventory management system is utilized to monitor and control the levels of raw materials, work-in-progress items, and finished products.
- Supply Chain Visibility Systems – Supply chain visibility systems are used to monitor and track activities throughout the supply chain, from procurement to delivery of finished goods.
Other Application Software
-
- Reverse Logistics Systems – Reverse logistics system is used to manage the return of defective or surplus products, dispose of hazardous materials, reduce waste, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) Systems – CAD/CAM system is used to design and develop new products, optimize production processes, and improve product quality, reduce lead times, increase manufacturing efficiency, and reduce costs.
- Contract Management System – Contract management system is used to manage procurement contracts, construction contracts, and other agreements.
Case Studies Of RFID Applications
Here is a case study of RFID tracking for manufacturing equipment and inventory management. Xilinx, Inc. was facing challenges with keeping track of their expensive manufacturing equipment and inventory resulting in delays, increased costs, and decreased productivity. To address this problem, they implemented an RFID system where RFID tags were attached to each piece of equipment and inventory, which contained information such as the type of equipment, its location in the manufacturing facility, and its current status. RFID readers were installed at various checkpoints throughout the facility. Whenever a piece of equipment or inventory passed through a checkpoint, the RFID tag was read, and the equipment’s location was updated in the system. The company was able to track the location of their equipment and inventory in real-time and monitor their usage patterns. This allowed the company to optimize their equipment and inventory usage and reduce waste, resulting in significant cost savings.
Here is another case study of RFID tracking for construction equipment and worker safety. General Motors was looking for a way to improve safety and efficiency on their construction sites. They turned to RFID technology to track their construction equipment and workers in real-time. RFID tags were attached to each piece of equipment and to the safety vests worn by workers. The RFID readers were installed at various checkpoints throughout the construction site. Whenever a piece of equipment or worker passed through a checkpoint, the RFID tag was read, and the location of the equipment or worker was updated in the system. The manufacturing company was able to monitor the location of their equipment and workers in real-time, which helped to ensure their safety and improve efficiency. If a worker was missing or a piece of equipment was out of place, they could quickly locate them, resulting in a significant reduction in the time and cost associated with searching for missing equipment or workers. The RFID system also helped to improve safety by alerting the company if a worker or equipment entered a restricted area.
GAO Has Served the Manufacturing Construction Extensively
GAO RFID Inc., one of the global top 10 RFID leaders, is based in the cities of New York and Toronto and it has deployed RFID, BLE and IoT projects for many leading companies in the manufacturing construction industry including its various divisions such as:
- Civil and Structural Engineering: This involves the design and construction of the foundations, structures, and supporting systems of manufacturing facilities.
- Mechanical and Electrical Engineering: This involves the design and installation of mechanical and electrical systems used in manufacturing facilities, such as HVAC systems, electrical distribution systems, and process piping systems.
- Industrial Process Engineering: This involves the design and optimization of the production processes and equipment used in manufacturing facilities, including assembly lines, robotics, and other automated systems.
- Project Management and Construction: This involves the planning, scheduling, and management of the construction process, as well as the installation of equipment and machinery, testing, and commissioning of the facility.
- Environmental and Safety Compliance: This involves ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and safety standards during the construction and operation of manufacturing facilities
Some of the leading companies in the manufacturing construction industry in the US:
Some of the leading companies in the manufacturing construction industry in the Canada: