
Index
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for the Motion Picture and Sound Recording
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
Case Studies of RFID Applications
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for the Motion Picture and Sound Recording
GAO Has Served the Motion Picture and Sound Recording Extensively
Overview
The motion picture and sound recording industry is responsible for the development and production of movies, television shows, and music albums. It involves activities such as scriptwriting, casting, filming, editing, sound design, special effects, and post-production. The industry also involves marketing, promotion, and distribution of the final products to reach audiences through theaters, television networks, online streaming platforms, and physical media. The industry has undergone significant changes due to technological advances and changes in consumer behavior. The rise of digital streaming and distribution services has transformed the way movies and music are consumed, creating new business models and challenges for traditional distribution channels.
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in the motion picture and sound recording industries to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials and operational equipment such as camera accessories (filters, matte boxes, follow focus systems), tripods and camera supports, lenses, digital cinema cameras, studio lights, reflectors and diffusion materials, gels and color correction filters, sound recording equipment, microphones, audio recorders, microphone stands and more.
Ranked as one of the top 10 global RFID suppliers, GAO RFID Inc. is based in New York City, U.S. and Toronto, Canada. GAO offers a comprehensive selection of UHF, HF (including NFC) and LF RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags, BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. Such RFID and BLE products and systems, as well as its IoT and drone technologies, have been successfully deployed for the motion picture and sound recording industries.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for the Motion Picture and Sound Recording
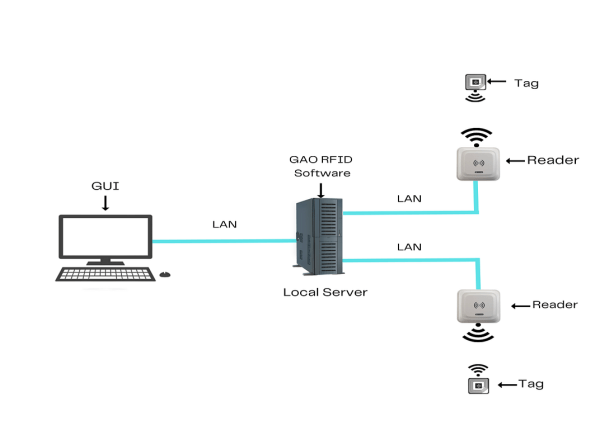
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for the motion picture and sound recording industries are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server, and another version is that its software runs in the cloud. The above illustrates GAO system for the motion picture and sound recording industries with its software running on a local server.
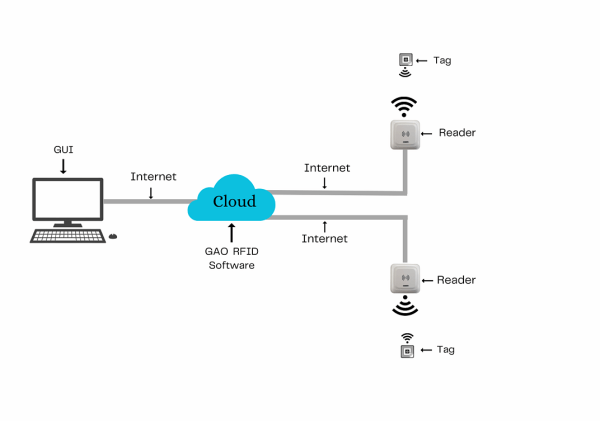
The above illustrates GAO system for the motion picture and sound recording industries with its software running in cloud.
GAO’s RFID technologies bring the many benefits to the motion picture and sound recording industries:
- Asset Tracking and Management: Ours RFID tags can be attached to equipment, props, costumes, and other assets, allowing for accurate and real-time tracking. This helps in inventory management, reducing the chances of loss, theft, or misplacement. It enables efficient asset allocation, streamlines logistics, and improves overall production workflows.
- Enhanced Security: GAO’s RFID tags can provide an additional layer of security by monitoring the movement of valuable assets. They can trigger alerts or alarms if unauthorized movement is detected, helping prevent theft or unauthorized access to sensitive equipment or footage.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: GAO’s RFID technology can automate various manual processes, such as checking equipment in and out, recording inventory, and managing paperwork. This saves time and reduces human error, leading to increased productivity and smoother production workflows.
- Inventory Management: Ours RFID tags can facilitate quick and accurate inventory checks, eliminating the need for manual counting and reducing labor costs. Production companies can easily track the availability and location of equipment, costumes, and other resources, enabling better planning and utilization.
GAO’s BLE technologies offer longer reading range and particularly attractive for applications with larger work spaces within the motion picture and sound recording industries:
- Wireless Connectivity: GAO’s BLE enables wireless connectivity between devices, allowing for seamless communication and data transfer. This can simplify the setup and integration of various equipment and devices used in production, such as cameras, microphones, and monitoring systems.
- Remote Control and Monitoring: GAO’s BLE can be used to remotely control and monitor equipment and devices. For example, filmmakers can adjust camera settings, start/stop recording, or change audio settings using a smartphone or tablet with BLE capabilities. This enhances convenience, flexibility, and precision during production.
- Real-time Data Transfer: GAO’s BLE facilitates fast and reliable data transfer between devices. It enables the real-time streaming of audio and video feeds, which can be beneficial for monitoring and reviewing shots during filming. It also allows for instant access to recorded media files, reducing post-production delays.
- Location-based Services: GAO’s BLE can provide location-based services within production facilities or on-set. For instance, it can help track the movement of crew members, equipment, or props, ensuring that everyone and everything is in the right place at the right time. This improves coordination, efficiency, and overall production quality.
GAO’s RFID and drone technologies are often combined and such solutions offer the following benefits to the motion picture and sound recording industries:
- Streamlined Set Design and Planning: Our RFID technology can be utilized during set design and planning stages. RFID tags can be attached to set pieces, props, and furniture, providing information about their dimensions, placement, and specific requirements. Drones equipped with RFID readers can help visualize and simulate set designs, allowing filmmakers and production designers to make adjustments or test different layouts before physical construction begins.
- Faster Inventory Audits: GAO’s RFID technology integrated with drones can speed up inventory audits on large film sets or storage facilities. Drones equipped with RFID readers can autonomously scan and identify tagged items, reducing the time and effort required for manual inventory checks. This enables efficient asset management, accurate stock counts, and streamlined logistics.
- Efficient Crowd Control: In scenarios where filming involves large crowds or public spaces, drones with ours RFID technology can assist in crowd control and safety management. By detecting RFID tags embedded in access passes or identification cards, drones can help monitor crowd movement, identify potential bottlenecks or safety hazards, and provide real-time data to production crews for effective crowd management.
- Enhanced Data Collection and Analytics: Combining GAO’s RFID technology with drones enables the collection of comprehensive data sets for analysis. RFID tags can be used to gather information about asset usage, movement patterns, and filming locations. Drones can gather aerial data and visuals, providing a holistic view of production activities. This data can be analyzed to gain insights into operational efficiency, resource allocation, and decision-making during the production process.
Here are benefits of GAO’s IoT technologies to the motion picture and sound recording industries:
- Seamless Workflow Integration: GAO’s IoT devices can integrate various components of the production workflow, from pre-production to post-production. Connected devices, software, and platforms can streamline the exchange of information, automate tasks, and ensure smooth transitions between different stages of production.
- Personalized User Experiences: GAO’s IoT technology can enable personalized user experiences for both filmmakers and audiences. For filmmakers, IoT devices can provide customized interfaces, preferences, and settings based on individual roles and requirements. For audiences, IoT-enabled platforms can deliver personalized content recommendations, interactive features, and immersive experiences.
- Data-driven Decision Making: GAO’s IoT-generated data can provide valuable insights for decision-making in the motion picture and sound recording industries. By analyzing data collected from IoT devices, production companies can gain a deeper understanding of audience preferences, content performance, and market trends. This data-driven approach helps optimize creative choices, marketing strategies, and investment decisions.
- Remote Collaboration: GAO’s IoT technology facilitates remote collaboration among geographically dispersed teams. Filmmakers, producers, editors, and other stakeholders can connect and collaborate in real time, regardless of their physical locations. This enables efficient communication, reduces travel costs, and promotes collaboration between talent from different parts of the world.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of the Motion Picture and Sound Recording
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in the motion picture and sound recording industries to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates and government regulations:
RFID, BLE, IoT, & Drone Standards & Mandates
- SMPTE Timecode: Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) Timecode is a standard that provides a standardized method of identifying specific frames, hours, minutes, seconds, and frames within a recording.
- Bluetooth Core Specification: It defines the protocols, procedures, and features necessary for Bluetooth devices to communicate with each other.
- Generic Attribute Profile (GATT): It enables devices to exchange information such as device characteristics, sensor data, and control commands.
- Color Bars: SMPTE Color Bars are a set of standardized color bars used to calibrate and test video monitors and broadcast equipment.
- OMF (Open Media Framework): OMF is an open standard for exchanging and managing digital media files and metadata in the production and post-production workflows.
- SMPTE ST 2071 (Media Device Control): SMPTE ST 2071 is a standard that defines a control protocol for managing and controlling media devices, such as cameras, audio recorders, and other equipment, over IP networks.
- National Association of Broadcasters (NAB) Drone Standards: NAB has published guidelines for the safe and effective use of drones in broadcast and cinematography applications. These guidelines provide recommendations on drone operations, crew qualifications, safety protocols, and privacy considerations.
- AES67 (Audio over IP interoperability): It enables interoperability between different audio devices, allowing for seamless integration of audio sources, mixers, and processors in a networked environment.
- Broadcast Wave Format (BWF): Broadcast Wave Format is an audio file format widely used in broadcast and professional audio applications. BWF is commonly used for audio recording and post-production in the film and sound recording industries.
- Digital Cinema Package (DCP): DCP ensures compatibility and consistency among digital cinema projection systems, enabling the distribution and playback of high-quality digital movies in theaters.
U.S. Government Regulations
- Copyright Law (Title 17): The U.S. Copyright Law provides protection for original works of authorship, including motion pictures and sound recordings.
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Regulations: Regulates broadcasting, wireless communication, and telecommunications in the United States. Their regulations cover areas such as radio and television broadcasting, spectrum allocation, signal interference, licensing, and more.
- Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA): Issues permits that ensure compliance with safety and security regulations, environmental considerations, and other requirements associated with filming in specific locations.
- Cable Television Regulations: Regulates cable TV providers, including licensing, franchise agreements, channel carriage requirements, and consumer protection.
- Department of Labor (DOL): The DOL sets regulations related to minimum wage, overtime pay, and child labor in the United States. These regulations apply to employees within the motion picture and sound recording industries, ensuring fair and lawful employment practices.
- Wireless Microphones and Broadcast Auxiliary Services (BAS) Regulations: Addresses spectrum allocation, licensing, and operating rules for wireless microphones and BAS equipment used in production.
Canadian Government Regulations
- Canadian Radio Television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) Regulations: Covers licensing, Canadian content requirements, ownership restrictions, advertising limits, and accessibility requirements for radio and television broadcasters.
- Copyright Act: Provides protection for original works of authorship, including motion pictures and sound recordings. It governs rights, licensing, registration, and infringement claims.
- National Film Board Act: Governs the operations and mandate of the National Film Board of Canada, a government film agency that supports the production and distribution of Canadian films and documentaries.
- Labor Standards and Health and Safety Regulations: Each province in Canada has its own labor standards and health and safety regulations that apply to the motion picture and sound recording industries. These regulations cover areas such as workplace safety, employment standards, and workers’ compensation.
- Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA): Regulates the collection, use, and disclosure of personal information by private sector organizations, including production companies, post-production facilities, and distributors.
- Employment Standards Regulations: Regulates employment conditions for workers in the motion picture and sound recording industries, including provisions related to minimum wage, working hours, overtime, and vacation pay.

Department of Labour(DOL)
Federal Communications Commission
Federal Emergency Management Agency(FEMA)
Canadian Radio Television and Telecommunication Commission

National Film Board(NFB)

Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA)
National Institute of Standards and Technology
Approved American National Standards
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in the motion picture and sound recording industries such as:
Personnel Management:
- Crew and Talent Management: Managing the hiring, scheduling, and coordination of crew members, actors, and other personnel involved in productions.
- Casting and Audition Management: Facilitating the casting process, scheduling auditions, and managing talent databases.
- Payroll and Contract Management: Handling payroll, contracts, and compliance with labor regulations for cast and crew members.
Equipment Management:
- Equipment Inventory and Tracking: Tracking and managing the inventory of cameras, lighting equipment, sound equipment, props, and other production-related assets.
- Maintenance and Repair Management: Scheduling and tracking equipment maintenance, repairs, and servicing to ensure optimal performance and minimize downtime.
- Equipment Rental Management: Facilitating the rental process, including availability, reservations, contracts, and returns of equipment from rental providers.
Access Control:
- Set Access and Security: Implementing access control measures to restrict entry to production sets and sensitive areas, ensuring only authorized personnel can access specific locations.
- Digital Asset Management (DAM) Access: Managing access and permissions for digital assets, such as film footage, audio recordings, and post-production files, to maintain confidentiality and prevent unauthorized use or distribution.
Warehouse Management:
- Prop and Set Piece Inventory: Tracking and managing the inventory of props, set pieces, costumes, and other materials used in productions.
- Asset Storage and Retrieval: Organizing and optimizing storage of equipment, props, and other production assets to facilitate efficient retrieval and usage.
- Material Replenishment: Monitoring stock levels of consumables, such as film stock, batteries, tapes, and ensuring timely replenishment to avoid production delays.
Supply Chain Management:
- Vendor Management: Managing relationships with suppliers, negotiating contracts, and ensuring timely delivery of goods and services required for production.
- Logistics and Transportation: Coordinating transportation logistics for equipment, props, and personnel to various filming locations.
- Procurement and Purchase Order Management: Streamlining the procurement process, including issuing purchase orders, tracking deliveries, and managing supplier invoices.
Other Applications:
- Script and Storyboard Management: Facilitating the creation, review, and revision processes for scripts, storyboards, and other creative assets.
- Production Scheduling and Budgeting: Creating and managing production schedules, allocating resources, and tracking expenses to ensure projects stay on track and within budget.
- Location Scouting and Management: Identifying, evaluating, and securing filming locations, obtaining permits, and managing logistics for on-location shoots.
GAO has enabled its customers to make use of some of leading software and cloud services in the motion picture and sound recording industries. Below are some of popular software and cloud services in the motion picture and sound recording industries:
- Entertainment Partners: Offers a range of software solutions for personnel management, including EP Global Vista for production management, scheduling, and crew management.
- Media Services Payroll: A complete payroll and production management software specializing in personnel management functions for crew onboarding, time card management, and labor compliance.
- SIMPLY: A cloud-based personnel management and payroll solution specifically tailored for the Canadian entertainment industry. It includes features for crew scheduling, timecard management, and payroll processing.
- CrewSense: A cloud-based personnel management platform that offers features for crew scheduling, availability tracking, communication, and automated call-outs.
- Manhattan Associates Warehouse Management System: Offers a robust warehouse management solution that streamlines operations, including receiving, inventory management, order fulfillment, and shipping.
- SAP Supply Chain Management (SCM): Offers a range of solutions for supply chain planning, demand management, procurement, and logistics.
- Brivo: Offers cloud-based access control and security management solutions that allow for centralized control and monitoring of access points.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Provides a wide range of cloud services, including IoT storage, analytics, and training, to support various aspects of the manufacturing process.
- Celtx: A pre-production software that allows for scriptwriting, storyboard creation, and scheduling. It offers collaboration features and is widely used in the film and television industry.
- Nuendo: A professional audio production software that offers advanced features for sound editing, mixing, and post-production. It is particularly popular in the film and TV industry.
- Sony Ci: A cloud-based media collaboration and management platform that enables secure sharing, reviewing, and distribution of media assets. It offers file transcoding, and project collaboration.
- Frame.io: A cloud-based platform designed for video collaboration and review. It allows for real-time feedback, version control, and seamless collaboration among team members

Entertainment Partners, Inc.

Media Services Payroll, Inc.

Cloud Payroll

CrewSense

Manhattan Associates

SAP SE

Brivo

Amazon Web Services

Celtx Inc.

Nuendo

Sony Ci

Frame.io
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Below are some RFID application cases in the motion picture and sound recording industries:
Skywalker Sound, a highly regarded company specializing in sound design and mixing, has successfully integrated RFID technology into their sound recording procedures. Through the implementation of RFID tags on their audio equipment and media assets, they have achieved a more efficient and streamlined approach to asset tracking and management. The utilization of an RFID system has provided them with the ability to monitor the location of their equipment in real-time, ensuring easy accessibility and significantly reducing the time spent searching for specific items. Moreover, the RFID tags have greatly facilitated inventory management, enabling accurate and precise asset counts while minimizing the risk of loss or misplacement. As a result of their RFID implementation, Skywalker Sound has witnessed notable enhancements in their operational efficiency, a reduction in equipment downtime, and overall improvements in their production workflows.
Another case study for RFID applications in the motion picture and sound recording industries:
Incorporating RFID technology into their film production and post-production workflows, Technicolor, a prominent worldwide provider of visual effects and post-production services, has significantly improved their asset tracking and supply chain visibility. This achievement was made possible by employing RFID tags on film reels and production assets. The implementation of the RFID system enabled Technicolor to monitor their film inventory in real-time, ensuring precise inventory counts and reducing instances of stockouts. Additionally, the RFID tags played a vital role in efficient equipment management by enabling swift identification and availability of production tools. As a result of their RFID implementation, Technicolor has experienced streamlined operations, a reduction in production delays, and an overall increase in customer satisfaction. This technology has undoubtedly proven to be instrumental in enhancing their film production and post-production processes.
A case study for UHF RFID applications in the motion picture and sound recording industries:
Sony Pictures Entertainment, a prominent film production and distribution company, has integrated UHF RFID technology into their film production workflows to enhance asset tracking and logistical efficiency. Through the use of RFID tags on film reels and production assets, they have achieved real-time visibility into the location and status of their film assets, resulting in streamlined production scheduling and reduced equipment search time. The implementation of RFID tags has also facilitated efficient inventory management, minimizing the risk of loss or misplacement. As a result, Sony Pictures Entertainment has witnessed notable improvements in operational productivity, cost reduction, and overall production quality. The incorporation of RFID technology has undoubtedly had a positive impact on their film production processes, allowing them to deliver high-quality content more efficiently.
Another case study for UHF RFID applications in the motion picture and sound recording industries:
Deluxe Entertainment, a renowned provider of post-production services, has integrated UHF RFID technology into their sound recording operations to enhance asset tracking and inventory management. Through the utilization of RFID tags on recording equipment and media assets, they have successfully achieved streamlined asset tracking and efficient inventory management. The RFID system has enabled precise identification and location tracking of sound recording devices, leading to optimized equipment utilization and reduced downtime. Moreover, the implementation of RFID tags has facilitated seamless management of media assets, guaranteeing quick and reliable access to recorded sound files. As a result of their RFID implementation, Deluxe Entertainment has experienced improved operational efficiency, minimized equipment loss, and heightened customer satisfaction. This integration of RFID technology has undoubtedly had a positive impact on their sound recording processes, enabling them to deliver exceptional post-production services.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for the Motion Picture and Sound Recording
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including the motion picture and sound recording industries.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including the motion picture and sound recording industries.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including the motion picture and sound recording industries:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including the motion picture and sound recording industries:
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including the motion picture and sound recording industries:
- High Frequency 13.56 MHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 134 kHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 125 kHz Passive RFID Readers
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including the motion picture and sound recording industries:
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
Digital I/O adapters:
and relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
- UHF 860 – 960 MHz RFID Modules
- 13.56 MHz High Frequency RFID Modules
- 125 kHz Low Frequency RFID Modules
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in the motion picture and sound recording industries:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include
- Camera Equipment: High-end digital cameras, film cameras, lenses, and camera support systems.
- Lighting Equipment: Professional lighting fixtures, control systems, and accessories for setting up the desired lighting conditions.
- Sound Recording Equipment: Microphones, mixers, recorders, and boom poles for capturing high-quality audio.
- Editing Software and Hardware: Advanced editing software, workstations, and peripherals for post-production editing and processing.
- Sound Mixing and Dubbing Equipment: Sound consoles, monitors, speakers, and software for mixing and dubbing soundtracks.
- Visual Effects (VFX) Equipment: High-performance computers, rendering servers, and specialized software for creating visual effects.
- Green Screens and Chroma Key Equipment: Backdrops and keying tools for compositing actors and objects into virtual or composited environments.
- Motion Capture Equipment: Optical or inertial systems for capturing the movements of actors or objects for animation purposes.
- Drone Cameras: Remote-controlled aerial cameras for capturing unique perspectives and aerial shots.
People or workers tracking system:
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
GAO Has Served the Motion Picture and Sound Recording Extensively
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in the motion picture and sound recording industries to achieve success in artificial intelligence, immersive audio, virtual production, augmented reality, streaming services, live streaming and virtual events, real-time visual effects, interactive and transmedia storytelling, remote recording and mixing, 360-degree video and virtual reality.
GAO RFID Inc. has served many customers in the motion picture and sound recording industries, including its various divisions such as
- Animation: This division focuses on the creation of animated films, TV shows, and commercials using various techniques such as traditional hand-drawn animation, computer-generated imagery (CGI), and stop-motion animation.
- Music Production: While not exclusive to the motion picture and sound recording industries, music production plays a significant role in providing original scores, soundtracks, and songs for films and sound recordings.
- Film Production: This division involves the creation and production of motion pictures, including feature films, documentaries, and short films. It includes activities such as scriptwriting, casting, production design, cinematography, and film editing.
- Talent Agencies: Talent agencies play a crucial role in representing and managing actors, directors, producers, composers, and other industry professionals. They help facilitate contracts, negotiate deals, and connect talent with various projects within the industry.
- Equipment and Technology: This division encompasses companies that specialize in manufacturing and providing equipment, software, and technologies used in the production, post-production, and distribution processes. This includes camera manufacturers, sound equipment providers, editing software developers, and technology service providers.
Here are some of the leading companies in the motion picture and sound recording industries:

Warner Bros. Entertainment Inc

The Walt Disney Studios

Universal City Studios LLC

Paramount Pictures Corp

Columbia Pictures Industries, Inc.

Twentieth Century Fox Film Corporation

Sony Pictures Entertainment, Inc

Lions Gate Entertainment Corporation

Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Studios, Inc.

DreamWorks Animation LLC

Netflix, Inc

Amazon Studios

CBC Television

Cineplex Inc.

Entertainment One Ltd.

Blue Ant Media Inc

Astral Media Inc.

Corus Entertainment Inc.






