
Overview
Web Search Portals, Libraries, Archives, and Other Information Services industry includes online platforms like Google and Bing that enable users to search for information on the web. It also encompasses libraries and archives that curate and preserve valuable resources. Other information services may offer specialized databases, research tools, or content aggregation services. Overall, the industry focuses on facilitating information discovery, access, and organization for users.
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials and operational equipment such as: servers, routers, switches, storage devices, data centers, indexing software, search algorithms, web crawlers, databases, content management systems, digitization equipment, scanners, archival storage systems, metadata management tools, document management systems, access control systems, authentication mechanisms, backup and recovery systems, data analytics tools, user interface design software, content delivery networks (CDNs), and high-speed internet connectivity.
Ranked as one of the top 10 global RFID suppliers, GAO RFID Inc. is based in New York City, U.S. and Toronto, Canada. GAO offers a comprehensive selection of UHF, HF (including NFC) and LF RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags, BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. Such RFID and BLE products and systems, as well as its IoT and drone technologies, have been successfully deployed for web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Web Search Portals, Libraries, Archives, and Other Information Services
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server, and another version is that its software runs in the cloud.
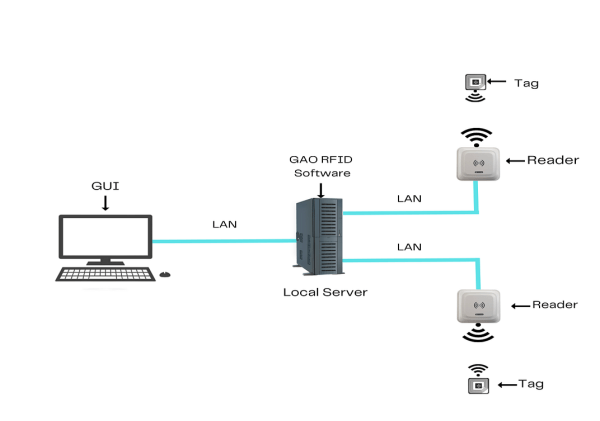
The above illustrates GAO system for web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry with its software running on a local server.
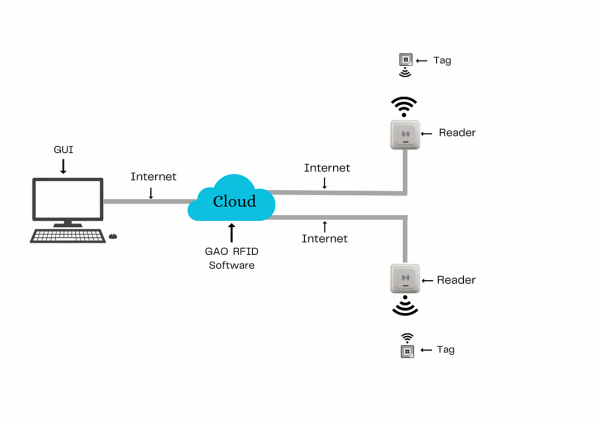
The above illustrates GAO system for web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry with its software running in cloud.
GAO’s RFID technologies bring the many benefits to web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry:
- Streamlined Check-in and Check-out Processes: GAO’s RFID technology can automate the check-in and check-out processes in libraries or information centers. For Example: By tagging items with our RFID tags, patrons can easily self-checkout books or other materials using RFID-enabled kiosks, reducing waiting times and enhancing operational efficiency.
- Efficient Asset Tracking: With RFID, Web Search Portals, Libraries, Archives, and Other Information Services can effectively track and locate valuable assets within their facilities. For Example: With our GAO’s RFID solutions can be utilized to monitor the movement of archival documents or rare manuscripts, ensuring their security and minimizing the risk of loss or misplacement.
- Improved Security and Anti-theft Measures: Implementing RFID technology can enhance security measures within information service organizations. For Example: By integrating our RFID tags into sensitive materials, GAO RFID can help prevent unauthorized removal or theft, triggering alarms if an item is taken out without proper authorization.
GAO’s BLE technologies offer longer reading range and particularly attractive for applications with larger work spaces within web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry:
- Enhanced Indoor Navigation: GAO BLE technology enables precise indoor positioning, allowing users to navigate through large libraries or information centers with ease. For Example: Our BLE beacons provide location-based information and interactive maps to help users find their desired resources efficiently.
- Personalized Content Delivery: With our BLE technology, Web Search Portals, Libraries, Archives, and Other Information Services can deliver personalized content to users based on their location within the facility. For Example: Our GAO BLE beacons can trigger relevant notifications or recommendations when a user approaches a specific section or exhibit.
- Interactive Exhibits and Tours: GAO BLE beacons can enhance the visitor experience by offering interactive exhibits and self-guided tours. For Example: By placing our beacons near exhibits, users can receive detailed information, multimedia content, or translations directly on their mobile devices, creating an engaging and educational experience.
GAO’s RFID and drone technologies are often combined and such solutions offer the following benefits to web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry:
- Remote Asset Tracking: By integrating our RFID technology with drones, Web Search Portals, Libraries, Archives, and Other Information Services can remotely track and locate assets within their facilities. For Example: Drones equipped with our RFID readers can quickly identify and locate specific items, even in hard-to-reach areas, improving asset management and retrieval processes.
- Enhanced Security and Monitoring: Deploying GAO RFID-enabled drones enhances security and monitoring capabilities in information service organizations. For Example: Drones equipped with our RFID readers can patrol and monitor restricted areas, ensuring that valuable resources are protected and detecting any unauthorized access or removal of items.
- Search and Rescue Operations: GAO RFID technology integrated with drones can be utilized in search and rescue operations. For Example: Drones equipped with our RFID readers can quickly locate and identify individuals or objects equipped with RFID tags, aiding in the search efforts and improving overall operational efficiency.
Here are benefits of GAO’s IoT technologies to the web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry:
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: By deploying GAO IoT sensors and smart devices, web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services can optimize energy consumption. For Example: Our IoT-enabled systems can automatically adjust lighting, heating, and cooling based on occupancy or environmental conditions, resulting in significant energy savings.
- Real-time Environmental Monitoring: GAO IoT sensors can provide real-time environmental monitoring in information service facilities. For Example: Our sensors can measure temperature, humidity, and air quality, ensuring optimal conditions for preserving delicate archival materials or protecting electronic resources.
- Personalized User Experience: With GAO IoT, information service providers can deliver personalized user experiences. For Example: Our IoT devices can gather user preferences and behavior data to tailor recommendations, search results, or content suggestions, enhancing user satisfaction and engagement.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Web Search Portals, Libraries, Archives, and Other Information Services
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates and government regulations:
RFID, BLE, IoT, & Drone Standards & Mandates
- FCC Regulations: The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the U.S. regulates the use of RFID, BLE, IoT, and drones to ensure compliance with radio frequency spectrum and interference guidelines.
- NIST Special Publication 800-53: The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the U.S. provides cybersecurity guidelines, including those related to IoT devices and systems used in information services, ensuring data protection and privacy.
- HIPAA: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S. imposes privacy and security requirements on healthcare-related information, including data collected through IoT devices and systems used in healthcare libraries or archives.
- UL 2900: Underwriters Laboratories (UL) 2900 is a cybersecurity standard that provides guidelines for assessing and certifying the security of IoT devices and systems used in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services.
- GDPR: The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union has implications for organizations operating in the U.S. and Canada, governing the protection and privacy of personal data collected through RFID, BLE, IoT, and drones.
- CPNI Guidelines: In the U.S., the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) provides guidelines to protect Customer Proprietary Network Information (CPNI) collected by telecommunication companies, which may be relevant in the context of IoT and networked systems.
- ADA Accessibility Guidelines: The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) provides guidelines for web accessibility, ensuring that web search portals and information services are accessible to individuals with disabilities.
- AODA: The Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act (AODA) in Ontario, Canada, establishes accessibility standards, including those related to web accessibility for individuals with disabilities.
- ANSI/NISO Standards: The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the National Information Standards Organization (NISO) develop standards for the interoperability, accessibility, and preservation of digital information resources used in web search portals, libraries, and archives.
- NARA Guidelines: The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) in the U.S. provides guidelines for the management, preservation, and access to federal records and archives, including considerations for digital resources and technologies.
US. Government Regulations
- FOIA: The FOIA allows the public to request access to federal agency records, ensuring transparency and accountability in the information services industry.
- CIPA: CIPA requires schools and libraries to implement internet filtering measures to protect minors from accessing inappropriate or harmful content.
- DMCA: The DMCA addresses copyright infringement online and provides guidelines for web search portals, libraries, and archives regarding the handling of copyrighted material.
Canadian Government Regulations
- Copyright Act: The Copyright Act of Canada governs the protection of intellectual property rights, including the reproduction and distribution of copyrighted works in the information services industry.
- PIPEDA: PIPEDA establishes rules for the collection, use, and disclosure of personal information by private sector organizations, including web search portals, libraries, and archives.
- CASL: CASL regulates the sending of commercial electronic messages, requiring consent and providing guidelines for electronic marketing practices in web search portals, libraries, and other information services.

Federal Communications Commission (FCC)

National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)

Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)

General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)

Freedom of Information Act (FOIA)

Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA)
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry such as:
Personnel Management:
- Staff scheduling and shift management: Efficiently manage and schedule staff members’ shifts and work hours.
- Employee performance tracking and evaluation: Monitor and assess employee performance to provide feedback and identify areas for improvement.
- Training and development programs for staff: Implement training initiatives to enhance employee skills and knowledge.
Equipment Management:
- Inventory tracking and management of books, documents, and media: Monitor and control the availability and location of physical resources.
- Maintenance and repair tracking of equipment and facilities: Maintain records and schedules for equipment maintenance and repair tasks.
- Equipment checkout and tracking system for patrons: Track the lending and return of equipment to ensure proper usage and accountability.
Access Control:
- Patron registration and management: Register and manage user accounts to grant access to services and resources.
- Access control systems for restricted areas or resources: Implement security measures to restrict access to sensitive areas or materials.
- User authentication and authorization for online services: Verify user identities and grant appropriate access privileges to online platforms.
Warehouse Management:
- Efficient storage and retrieval systems for physical resources: Optimize the organization and retrieval of physical resources such as books and documents.
- Automated sorting and shelving processes: Utilize automation to streamline the sorting and shelving of materials.
- Inventory optimization and demand forecasting: Optimize inventory levels and predict demand to ensure resource availability.
Supply Chain Management:
- Procurement and vendor management for acquiring resources: Manage the procurement process, including vendor selection and contract management.
- Supplier performance tracking and evaluation: Monitor and assess supplier performance to ensure quality and timely delivery.
- Supply chain visibility and tracking of orders and deliveries: Track the movement of resources from suppliers to end-users to enhance efficiency.
Other Applications:
- Digital asset management systems for organizing and accessing digital resources: Efficiently manage and provide access to digital content such as e-books, databases, and multimedia.
- Collection development and curation for libraries and archives: Strategically develop and curate collections to meet user needs and interests.
- Research and reference services for users: Offer assistance and guidance to users in their research and reference inquiries.
GAO has integrated its RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems with some of leading software and cloud services in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry. Below are some of popular software and cloud services in the web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry:
- SAP Success Factors: A comprehensive cloud-based human resource management system that offers modules for personnel management, performance tracking, and employee development.
- Oracle NetSuite: An integrated cloud-based ERP system that provides solutions for equipment management, inventory tracking, and warehouse management.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A suite of business applications that includes modules for supply chain management, warehouse management, and personnel management.
- IBM Maximo: A powerful asset management software that enables efficient equipment management, maintenance, and tracking for organizations in various industries.
- Infor CloudSuite WMS: A cloud-based warehouse management system that optimizes inventory control, order fulfillment, and labor management.
- Salesforce Commerce Cloud: A leading cloud-based platform that provides supply chain management solutions, including order management and fulfillment capabilities.
- Epicor ERP: An enterprise resource planning software that offers modules for supply chain management, warehouse management, and equipment tracking.
- JDA Warehouse Management: A comprehensive warehouse management system that optimizes operations, inventory control, and labor management for distribution centers.
- Manhattan Associates: A supply chain management software that offers solutions for warehouse management, inventory optimization, and order fulfillment.
- Blue yonder (formerly JDA Software): A leading provider of supply chain management solutions, including warehouse management and demand planning.
- Kronos Workforce Central: A workforce management solution that helps organizations manage employee schedules, time and attendance, and labor analytics.
- ADP Workforce Now: A cloud-based human capital management platform that provides personnel management, payroll, and time tracking functionalities

SAP SuccessFactors

Oracle NetSuite

Microsoft Dynamics 365

IBM Maximo

CloudSuite WMS – saleforce

Commerce Cloud

Manhattan Associates

Blue yonder (formerly JDA Software)

Kronos Workforce Central

ADP Workforce

JDA Warehouse Management

Epicor ERP
GAO has worked with some of the leading technology companies in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry in to provide integrated its RFID, BLE, IoT and drone solutions to customers. Here are some of the technology leaders in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry:
- Google: A leading information company and web search portal that provides search engine services and various online tools for information retrieval.
- Amazon: An electronic company and e-commerce giant that offers cloud services, digital content, and Kindle e-readers for accessing and managing information.
- Microsoft: A technology company that provides various software and cloud services, including Microsoft Office, Azure, and SharePoint, used in the information services industry.
- IBM: A prominent technology company offering solutions for data analytics, cognitive computing, and enterprise search to support information management in libraries and archives.
- ProQuest: An information company specializing in digital content and research solutions, offering access to academic journals, dissertations, and e-books for libraries and researchers.
- Elsevier: A leading information company in the scientific, technical, and medical fields, providing databases, journals, and research platforms for libraries and researchers.
- Apple: An electronic company known for its devices like iPhones, iPads, and Mac computers that are commonly used for accessing digital content and information services.
- Adobe Systems: A technology company offering software solutions like Adobe Acrobat and Creative Cloud for creating, managing, and accessing digital content in the information services industry.
- EBSCO Information Services: An information company providing research databases, e-books, and discovery tools for libraries, universities, and other information services.
- LexisNexis: A provider of legal and business information solutions, offering comprehensive databases and research tools for legal professionals and libraries.
- OCLC: A global library cooperative that provides technology services and research platforms like World Cat for library resource sharing and cataloging.
- Thomson Reuters: A leading information company offering research tools, news services, and legal solutions for professionals and libraries in various industries.
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Below are some RFID application cases in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry.
Case Study for RFID- applications in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services implemented in:
Library Thing, an online platform for cataloging personal book collections, implemented RFID technology to enhance its user experience. They leveraged programming libraries to enable users to easily tag their books with RFID tags. By scanning the RFID tags using RFID readers, users could quickly access book information, such as titles, authors, and summaries. This streamlined the process of cataloging and organizing personal libraries, saving users time and effort. The integration of RFID technology improved the accuracy of book identification and enhanced the overall usability of the platform, providing a seamless experience for book enthusiasts.
Another Case Study for RFID- applications in the web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services implemented in:
The University of Toronto Libraries incorporated RFID technology into their book circulation system to improve operational efficiency. By utilizing programming libraries, they seamlessly integrated RFID readers with their library management software. This integration enabled automated checkout and return processes, reducing the need for manual handling and expediting transactions. Students and faculty members could easily self-checkout and return books by scanning the RFID tags, enhancing the borrowing experience. The implementation of RFID technology significantly reduced wait times, minimized errors, and allowed library staff to focus on providing additional support and services to patrons.
Another Case Study for RFID- applications in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services implemented in:
McGill University Library implemented RFID technology to enhance the management of its archival collections. They employed programming libraries to integrate RFID readers with their archival database system, creating a comprehensive inventory management solution. The RFID tags attached to archival materials enabled efficient tracking and facilitated accurate item retrieval. Through the integration of RFID technology, the library improved accessibility to archival resources, ensuring researchers and scholars could easily locate and access specific items. The automation of inventory management enhanced the preservation efforts, safeguarding the valuable historical materials housed in the library’s archives.
Another Case Study for UHF RFID- applications in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services implemented in:
RFIDIOt is a Python library that enables developers to work with UHF RFID readers in web search portals, libraries, archives, and information services industry. With RFIDIOt, developers can create custom applications for reading and writing UHF RFID tags, allowing for efficient inventory management, tracking, and authentication of library materials. By leveraging the library’s capabilities, web search portals can incorporate UHF RFID technology to enhance search and retrieval processes, while libraries and archives can streamline operations, automate check-in/check-out processes, and improve item tracking accuracy. RFIDIOt’s flexible and robust features make it a valuable programming library for implementing UHF RFID solutions in the industry.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Web Search Portals, Libraries, Archives, and Other Information Services
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
As well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry:
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry:
- High Frequency 13.56 MHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 134 kHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 125 kHz Passive RFID Readers
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry:
And antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
Digital I/O adapters:
And relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
- UHF 860 – 960 MHz RFID Modules
- 13.56 MHz High Frequency RFID Modules
- 125 kHz Low Frequency RFID Modules
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include: Servers, Computers, Scanners, RFID Readers, Barcode Scanners, Digital Preservation Systems, and Content Management Systems.
People or workers tracking system:
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
GAO Has Served Web Search Portals, Libraries, Archives, and Other Information Services Extensively
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry to achieve success in Artificial intelligence (AI), Machine learning (ML), Big data, Digital transformation, User experience (UX), Metadata, Semantic search, Content curation, Data analytics, Cloud computing, Virtual reality (VR), Augmented reality (AR), Internet of Things (IoT), Digital preservation, Open access, Linked data, Personalization, Information retrieval, Natural language processing (NLP), and knowledge management.
GAO RFID Inc. has deployed RFID, BLE and IoT projects for many companies in the web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry, including many in its various divisions such as:
- Web Search Portals: Platforms that provide search functionality, aggregating and indexing information from various sources to deliver search results to users.
- Libraries: Institutions that collect, organize, and provide access to a wide range of resources, including books, periodicals, multimedia materials, and digital content.
- Archives: Organizations responsible for preserving and providing access to historical records, manuscripts, photographs, audiovisual materials, and other valuable documents.
- Information Services: Entities that offer specialized information resources, research assistance, reference services, and knowledge management solutions to support information retrieval and decision-making processes.
- Content Curation: The process of collecting, selecting, and organizing relevant and high-quality content from diverse sources to meet the specific needs and interests of users.
Here are some of the leading companies in web search portals, libraries, archives, and other information services industry:

Google LLC

Microsoft Corporation

Amazon.com, Inc.

Apple Inc.

Facebook Inc.

Alphabet

Netflix, Inc.

Twitter, Inc.

IBM

Yahoo Inc.

LinkedIn Cooperation

eBay Inc.

Reddit Inc.

Mozilla

Dropbox, Inc.

Adobe Inc.

Spotify Technology S.A.

Pinterest Inc

Shopify Inc.

Nuance Communications Canada Inc.

Tucows Inc.

Stingray Group Inc.

Yellow Pages Limited

OpenText
