Automation and control system manufacturing involve the creation of equipment and software that automate and control industrial processes. This includes designing, manufacturing, and installing systems such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), sensors, and actuators. These systems help increase efficiency, productivity, and safety in various industries, such as manufacturing, energy, and transportation. Additionally, they enable remote monitoring and control of processes, improving operational flexibility and reducing downtime. GAO RFID Inc., a global top 10 RFID leader based in the cities of New York and Toronto, has served many companies in automation and control system manufacturing.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Automation and Control System Manufacturing
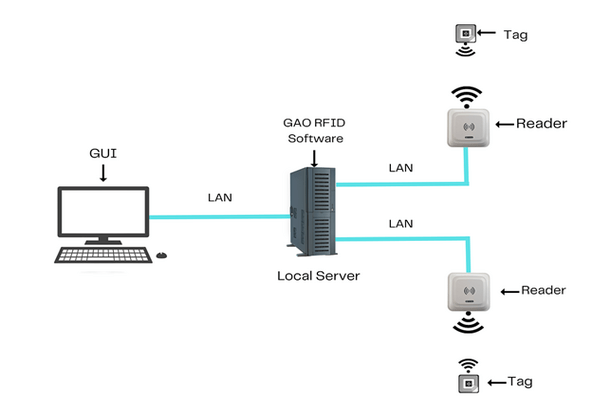
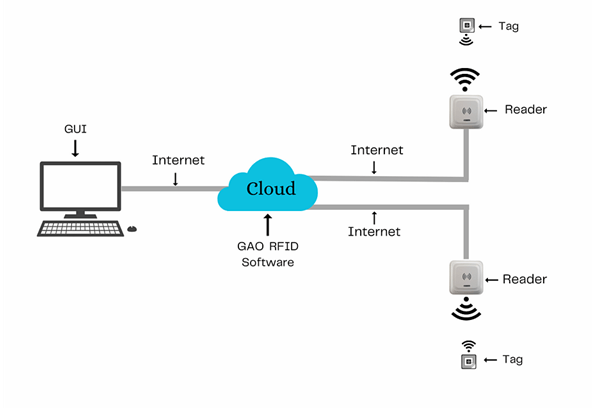
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including the automation and control system manufacturing.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with important functions such as temperature, humidity, vibration, and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for all kinds of industries, including the automation and control system manufacturing.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including the automation and control system manufacturing:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, and wristbands for various industries, including the automation and control system manufacturing:
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications), and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including the automation and control system manufacturing:
- High Frequency 13.56 MHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 134 kHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 125 kHz Passive RFID Readers
HF, NFC, and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, and wristbands for various industries, including the automation and control system manufacturing:
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
Digital I/O adapters:
and relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules suitable for use in the automation and control system manufacturing:
UHF 860-960 MHz RFID modules:
13.56 MHz high-frequency RFID modules:
125 kHz low-frequency RFID modules:
The RFID systems provided by GAO are highly popular among clients in the automation and control system manufacturing for various purposes:
Personnel or worker tracking system:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
GAO offers free samples of its RFID tags, labels, badges, and wristbands.
GAO offers a free trial for all of its software available.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Automation and Control System Manufacturing
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drones technologies provide many benefits for automation and control system manufacturing:
Applications & Benefits of applying RFID:
- Process Automation: GAO RFID products can be used to automate various processes, such as identifying and routing products like programmable logic controllers (PLCs), actuators, control panels, and power supplies, to specific areas of the production line, reducing manual labor and increasing efficiency.
- Increased Data Collection: Our RFID systems can collect data in real-time, providing valuable insights into the production process, such as cycle time, throughput, and bottlenecks.
- Improved Traceability: GAO’s RFID tags can be used to track products like human machine interfaces (HMIs), industrial robots, and sensors, from the raw material stage through to the finished product, making it easier to trace any quality issues or defects back to their source.
Applications & Benefits of applying BLE:
- Process Optimization: GAO’s BLE sensors can be used to collect data on various process parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and pressure, enabling operators to optimize production processes and improve product quality.
- Energy Management: Our BLE sensors can be used to monitor energy usage and identify areas for improvement, reducing energy costs and improving sustainability.
Applications & Benefits of applying a combination of RFID and drones:
- Equipment Monitoring: Drones can be used to monitor equipment like CNC machines, chillers and HVAC systems, and material handling equipment, and identify issues before they become more serious. GAO’s RFID tags can be used to track equipment location and maintenance history, allowing for more effective management and scheduling of maintenance.
- Logistics: GAO’s RFID tags can be used to track the movement of products like conveyors, robots, and test equipment, throughout the supply chain, from raw materials to finished products. Drones can be used to monitor transportation routes and identify areas where delays or other issues are likely to occur.
Applications & Benefits of applying a combination of RFID and IoT:
- Asset Management: GAO’s RFID tags can be used to track and manage assets such as machinery, tools, and equipment, like lighting and electrical systems, pumps and valves, and filtration systems. IoT sensors can provide additional data such as usage patterns and maintenance requirements, allowing for more effective management and scheduling of equipment.
- Quality Control: IoT sensors can be used to monitor production lines and identify areas where quality issues are likely to occur. GAO’s RFID tags can be used to track the movement of materials like SCADA systems and variable frequency drives (VFDs), throughout the manufacturing process, allowing for more effective quality control and defect prevention.
- Safety: IoT sensors can be used to monitor safety conditions on the factory floor, such as temperature, noise levels, and air quality. RFID tags can be used to track the location of workers like PLC programmers, control engineers, maintenance technicians, electricians, and machine operators, and ensure that they are not exposed to hazardous conditions.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Automation and Control System Manufacturing
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in the automation and control system manufacturing to deploy RFID systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates and regulations:
- EPCglobal: This is a global organization that develops standards for RFID technology in supply chain management. The EPCglobal Network is a set of standards that enables companies to share RFID data across their supply chains. EPCglobal has developed the Electronic Product Code (EPC), which is a unique identifier for products that can be read by RFID readers.
- FDA: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued guidelines for the use of RFID technology in the pharmaceutical industry. These guidelines provide recommendations for the use of RFID technology in drug supply chain management, including the use of unique identification codes for individual drug products.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): OSHA is responsible for ensuring safe and healthy working conditions in the workplace. OSHA has established regulations and standards that apply to automation and control systems manufacturing, including electrical safety, machine guarding, and hazardous materials handling.
- National Electrical Code (NEC): The NEC is a set of standards for electrical installation and safety in the United States. The NEC covers topics such as wiring methods, grounding and bonding, and electrical system design. Compliance with the NEC is required by law in many jurisdictions in the United States.
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): NIST is responsible for developing and maintaining standards for a wide range of industries and technologies, including automation and control systems manufacturing. NIST has developed the Cybersecurity Framework, which provides guidance on how to manage and reduce cybersecurity risk in industrial control systems.
- Department of Energy (DOE): The DOE is responsible for overseeing the development and implementation of energy policies and programs in the United States. The DOE has established regulations and standards for energy efficiency and conservation in industrial processes, which apply to automation and control systems manufacturing.
- Canadian Electrical Code (CEC): The CEC is a set of standards for electrical installation and safety in Canada. The CEC covers topics such as wiring methods, grounding and bonding, and electrical system design. Compliance with the CEC is required by law in many jurisdictions in Canada.
- Canadian Standards Association (CSA): The CSA is responsible for developing and maintaining standards for a wide range of industries and technologies, including automation and control systems manufacturing. The CSA has developed standards for electrical safety, hazardous materials handling, and other topics that apply to automation and control systems manufacturing.
- Occupational Health and Safety Regulations (OHSR): The OHSR is a set of regulations established by the Canadian government to ensure safe and healthy working conditions in the workplace. The OHSR covers topics such as electrical safety, machine guarding, and hazardous materials handling.
- Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC): ECCC is responsible for protecting the environment and the health of Canadians. ECCC has established regulations and standards for managing hazardous waste and hazardous materials in the workplace, which apply to automation and control systems manufacturing.
- Natural Resources Canada (NRCan): NRCan is responsible for developing and implementing policies and programs related to natural resources in Canada. NRCan has established regulations and standards for energy efficiency and conservation in industrial processes, which apply to automation and control systems manufacturing.
GAO’s Software Provides API
GAO’s popular RFID software such as personnel tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking system control offers a free trial and offers and API to each of the common software in automation and control system manufacturing:
Personnel management:
- Payroll processing – involves calculating and distributing employee salaries and benefits accurately and efficiently.
- Employee benefits management – involves managing employee benefits, such as healthcare, retirement plans, and insurance.
- Employee training and development – involves creating and managing employee training programs to develop and enhance employee skills and knowledge.
Equipment management:
- Asset tracking and management – involves tracking and managing the location, status, and maintenance history of company assets, including equipment, vehicles, and tools.
- Condition monitoring and diagnostics – involves monitoring equipment performance and diagnosing issues to prevent unexpected downtime.
- Inventory management of spare parts and consumables – involves managing inventory levels of spare parts and consumables to ensure that they are available when needed.
Supply chain management:
- Purchase order processing and management – involves creating and managing purchase orders for raw materials and other supplies.
- Order management and fulfillment – involves managing customer orders and ensuring timely and accurate order fulfillment.
- Logistics and transportation management – involves managing the transportation of raw materials, finished goods, and other supplies.
Other applications:
- Data analytics and reporting – involves collecting and analyzing data to identify trends, optimize processes, and inform decision-making.
- Research and development management – involves managing research and development projects to develop new products and improve existing ones.
- Customer relationship management – involves managing relationships with customers to ensure customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Here are two cases of applying RFID in automation and control system manufacturing
Rockwell Automation implemented an RFID-based inventory management system for their line of electrical control products. The system was designed to automate the process of inventory tracking and management, while improving accuracy and efficiency. RFID tags were attached to each electrical control product and were used to identify and track the movement of products through the manufacturing process. The RFID tags were read by a series of RFID readers placed at strategic locations throughout the manufacturing plant. The RFID-based inventory management system allowed Rockwell Automation to track inventory in real-time, which improved inventory accuracy and enabled better inventory forecasting. This helped the company to optimize inventory levels and reduce carrying costs. The RFID system also helped to streamline the manufacturing process by automating the tracking and movement of products. This reduced manual labor and increased production efficiency. In addition, the RFID data was used to generate reports and analytics on inventory levels, production flow, and other key metrics. This allowed Rockwell Automation to gain insights into their operations and make data-driven decisions to optimize their processes.
Honeywell implemented an RFID-based asset tracking system for their aerospace division, which produces aircraft engines and components. The system was designed to improve inventory accuracy and reduce manual labor in the tracking and management of assets. RFID tags were attached to each asset, including engines, components, and tooling equipment. RFID readers were installed at strategic locations throughout the manufacturing plant, including the receiving area, workstations, and final assembly area. The RFID-based asset tracking system allowed Honeywell to track the location and movement of assets in real-time, which improved inventory accuracy and reduced the time and effort required for manual tracking. The system also allowed Honeywell to optimize the use of assets by identifying underutilized equipment and improving overall asset utilization. In addition, the RFID data was used to generate reports and analytics on asset utilization, maintenance schedules, and other key metrics. This allowed Honeywell to make data-driven decisions to optimize their operations and improve asset management.
GAO Has Served Automation and Control System Manufacturing Extensively
GAO RFID Inc., a global top 10 leader in RFID, has served many leading companies in automation and control system manufacturing, including its various divisions such as:
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): These are computer-based industrial controllers that are used to automate machinery and processes in manufacturing and other industries.
- Human Machine Interface (HMI): HMIs are used to provide operators with a graphical user interface (GUI) to interact with industrial automation systems.
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA): SCADA systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes and equipment from a central location.
- Distributed Control Systems (DCS): DCSs are used to automate and control complex processes in industries such as chemical, petrochemical, and power generation.
- Industrial Robots: Industrial robots are used to automate manufacturing processes, such as welding, painting, and assembly.
- Motion Control: Motion control systems are used to control the movement of industrial machinery, such as motors, actuators, and positioning systems.
- Instrumentation: Instrumentation refers to the sensors, transmitters, and other devices used to measure and control various parameters in industrial processes, such as temperature, pressure, and flow.
- Industrial Networks: Industrial networks are used to connect industrial devices and systems together for communication and data exchange.
List Of the Leading Companies in automation and control system manufacturing in The U.S.:
List Of the Leading Companies in automation and control system manufacturing in Canada: