
The port and harbor construction industry builds and maintains maritime infrastructure, such as wharves, docks, breakwaters, and jetties. Dredging and land reclamation are also important activities in this industry for improving navigation channels and harbor depths. The industry plays a critical role in supporting global trade and economic growth, particularly in coastal regions. GAO RFID Inc., a global top 10 RFID leader based in the cities of New York and Toronto, has served many companies in the port and harbor construction industry.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for the Port and Harbor Construction
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including the port and harbor construction industry.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humidity, vibration, and panic button:
- IP67 Rated BLE 2.45GHz Active RFID Wristband Tag w/ Panic Button
- BLE 2.45GHz Ultra Rugged Active RFID Pallet Tag/Beacon
- BLE 2.45GHz Active RFID Asset Tag/Beacon
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for all kinds of industries, including the port and harbor construction industry
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including the port and harbor construction industry:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including the port and harbor construction industry:
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including the port and harbor construction industry:
- 134.2KHz ISO11784/5 FDX RFID Plug and Play Portable Reader
- 134.2 kHz LF Long Range Fixed RFID Reader
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including the port and harbor construction industry
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers, Digital I/O adapters and relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
- UHF 860 – 960 MHz RFID Modules
- 13.56 MHz High Frequency RFID Modules
- 125 kHz Low Frequency RFID Modules
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in the port and harbor construction industry:
People or workers tracking system:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
- GAO RFID Heavy Duty Machinery Asset Management System
- GAO RFID Construction and Industrial Machinery Rental Asset Management System
- Tool & Industrial Equipment Tracking System
- Asset Tracking Software
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
There are two versions of GAO’s software, one is running on a local server, and another running in the cloud.
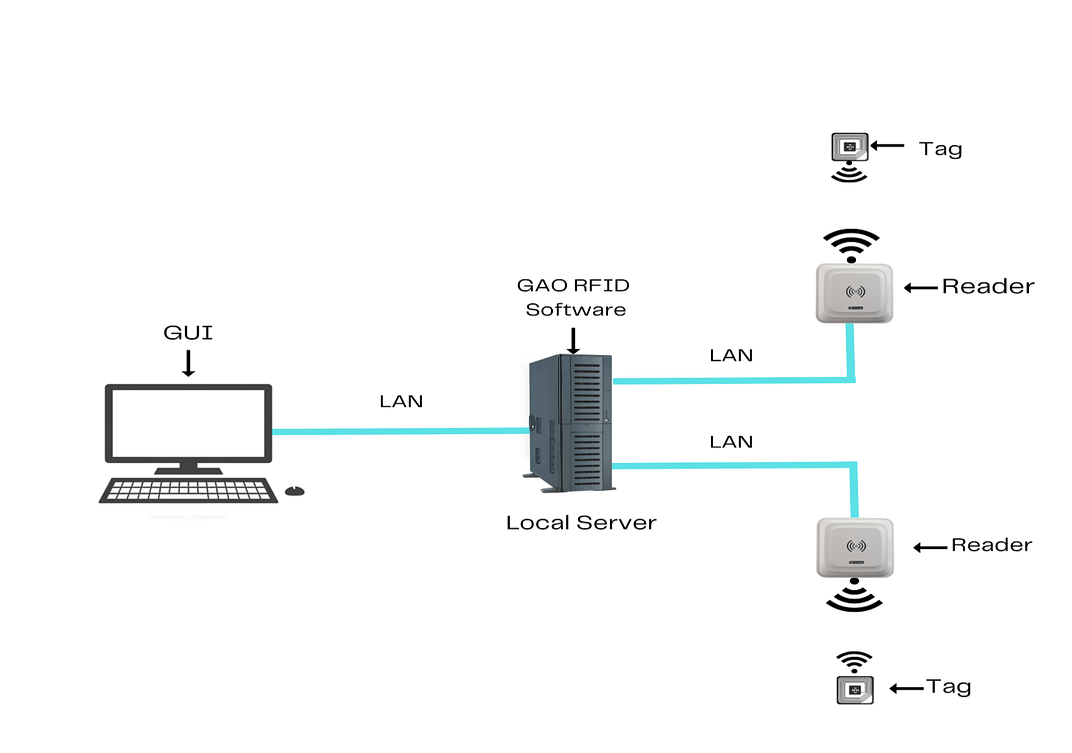 GAO’s software runs on a local server
GAO’s software runs on a local server
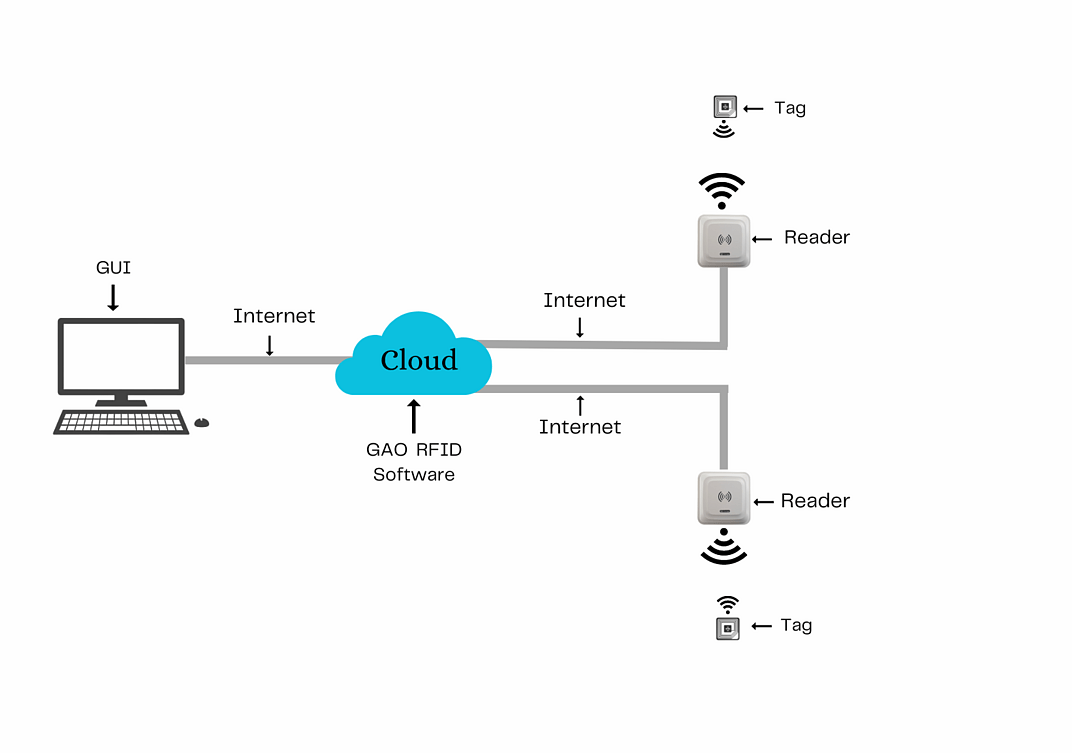 GAO’s software runs in the cloud
GAO’s software runs in the cloud
GAO offers free samples of its RFID tags, labels, badges, and wristbands.
GAO offers a free trial for all of its software available.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Port and Harbor Construction
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drones technologies provide many benefits for port and harbor construction:
Applications & Benefits of applying RFID to port and harbor construction:
- Improved Inventory Management: GAO RFID products can enable port operators to track and manage inventory more efficiently. It can help automate the tracking of cargo and containers, reducing the need for manual data entry, minimizing errors, and ensuring the accurate and timely delivery of cargo.
- Enhanced Safety: Our RFID tags can help improve safety by monitoring the movement of the stevedore, dockworkers, crane operators, marine engineers, and harbor pilots within the port.
- Reduced Costs: RFID technology can help reduce costs by increasing efficiency and reducing errors. By automating the tracking of cargo and inventory, port operators can save time and resources, reducing costs and increasing profitability.
Applications & Benefits of applying BLE to port and harbor construction
- Real-time Asset Tracking: Our BLE beacons can be attached to equipment and machinery like cranes, forklifts, straddle carriers, and terminal tractors, allowing port operators to track the location of these assets in real-time.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: GAO’s BLE can be used to monitor energy consumption and optimize resource usage. For example, sensors can be used to automatically turn off lights and HVAC systems in unoccupied areas, reducing energy consumption and costs.
Applications & Benefits of applying a combination of RFID and drones to port and harbor construction
- Construction Monitoring: Drones can be used to monitor the progress of construction and ensure that it is proceeding according to plan. By using our RFID tags to track materials and equipment like excavators, loaders, dump trucks, bulldozers, and graders, drones can be programmed to fly over specific areas and check that everything is in the right place.
- Maintenance and Repairs: By using GAO’s RFID tags to track assets and maintenance and repair work can be scheduled more efficiently. Drones can also be used to inspect equipment and identify issues before they become more serious.
Applications & Benefits of applying a combination of RFID and IoT to port and harbor construction:
- Predictive Maintenance: By combining IoT sensors with our RFID tags, it becomes possible to track when the equipment was last serviced, ensuring that maintenance is performed on schedule and reducing the risk of downtime due to unexpected breakdowns.
- Environmental Monitoring: IoT sensors can be used to monitor environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and air quality. This information can be combined with RFID data to track the movement of materials, such as spreaders, pavers, backhoes, and compactors, and ensure that they are stored in the appropriate conditions.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Port and Harbor Construction
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in the port and harbor construction industry to deploy RFID systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates and regulations:
- ISO 18185: This standard specifies the requirements for the design, manufacture, and testing of electronic seals for containers.
- US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) Container Security Initiative (CSI): This initiative requires RFID tracking and monitoring of high-risk containers entering the United States.
- International Maritime Organization (IMO) International Ship and Port Facility Security (ISPS) Code: This code requires ports and harbors to implement security measures to prevent terrorist attacks, including the use of RFID technology to monitor the movement of people, vehicles, and cargo.
- National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA): NEPA requires federal agencies to consider the environmental impacts of their actions, including the construction and operation of ports and harbors.
- Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA): OSHA regulates occupational health and safety in the Port and Harbor Construction Industry, including the use of equipment and machinery.
- Canada Shipping Act, 2001: This act governs the safety and security of ships, marine personnel, and marine infrastructure in Canadian waters.
- Canada Marine Act: This act provides the framework for the governance and management of Canadian ports, including their construction and operation.
- Canadian Energy Regulator Act: This act regulates the construction and operation of energy infrastructure, including pipelines and marine terminals.
 U.S. Customs and Border Protection
U.S. Customs and Border Protection
 Container Security Initiative
Container Security Initiative
 International Maritime Organization
International Maritime Organization
 International Organization for Standardization
International Organization for Standardization
 Occupational Safety and Health Act
Occupational Safety and Health Act
 National Environmental Policy Act
National Environmental Policy Act
GAO’s Software Provides API
GAO’s popular RFID software such as personnel tracking, asset tracking. access control, parking system control offers a free trial and offers an API to each of the common software in the port and harbor construction industry:
Personnel Management
- Recruitment and staffing: Identifying personnel like crewman, engineers, and labors needs and attracting suitable candidates to fill positions within the port and harbor construction industry.
- Succession planning: Developing strategies to identify and prepare employees for advancement within the organization.
Equipment Management
- Maintenance and repair management: Ensuring backhoes, cranes, pavers, etc is properly maintained and repaired to avoid downtime and maintain operational efficiency.
- Procurement and inventory management: Sourcing equipment and managing inventory levels to ensure that necessary equipment is available when needed.
- Obsolescence management: Developing plans to replace outdated or obsolete equipment to maintain operational efficiency.
Supply Chain Management
- Logistics and transportation management: Managing the movement of goods and materials to and from the construction site.
- Supplier management: Developing and maintaining relationships with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of materials and supplies.
- Risk management: Identifying and managing risks that may impact the supply chain, such as delays or disruptions.
Other Applications
- Project management and scheduling: Planning, coordinating, and managing construction projects to ensure that they are completed on time, within budget, and to specifications.
- Financial management and accounting: Managing project finances, including budgeting, forecasting, and financial reporting.
- Quality control and assurance: Ensuring that construction projects meet quality standards and specifications.
Case Studies of RFID Applications
A case study of RFID application in the port and harbor construction industry
The Port of Los Angeles, one of the largest ports in the United States, implemented an RFID system to improve the tracking and monitoring of cargo containers. The system uses RFID tags that are attached to each container, which are read by RFID readers at various points throughout the port. The RFID system provides real-time visibility into the movement and location of containers, enabling port officials to optimize the flow of cargo through the port and reduce congestion and delays. It also helps to improve security by enabling more accurate tracking and monitoring of the movement of containers. In addition, the RFID system has enabled the Port of Los Angeles to improve its inventory management processes. By providing real-time information on the location and status of containers, the port is better able to manage its resources and storage capacity, and reduce the risk of loss or damage to cargo.
Another case study of RFID application in the port and harbor construction industry.
In 2017, the Port of Virginia implemented an RFID-based inventory management system to improve the accuracy and efficiency of its container inventory management. The system was developed in partnership with Radiant RFID, a provider of RFID solutions. The RFID system involved the installation of RFID readers at various locations in the port, including the gate entrances, terminals, and rail yards. RFID tags were also placed on containers and chassis that entered and exited the port. The RFID system was used to track the location and movement of containers and chassis throughout the port, and the data was transmitted to a central database in real-time. The system provided port personnel with real-time visibility into the location and status of containers and chassis, which allowed them to quickly identify and resolve any issues or delays in container movements. Prior to the implementation of the RFID system, container inventory management was largely manual and prone to errors. With the RFID system, container inventory data was automatically recorded and updated in real-time, which helped to reduce errors and improve the accuracy of container inventory management.
GAO Has Served Port and Harbor Construction Extensively
GAO RFID Inc., a global top 10 leader in RFID, has served many leading companies in port and harbor construction, including its various divisions such as:
- Marine construction: This division includes the construction of piers, wharves, jetties, breakwaters, seawalls, and other marine infrastructure.
- Dredging: This division involves the removal of sediment and debris from waterways and harbor areas to maintain or improve navigability and safety.
- Land reclamation: This division involves the creation of new land by filling in coastal areas, creating artificial islands or reclaiming land from the sea.
- Harbor maintenance: This division involves the maintenance and repair of existing harbor infrastructure, including dredging, repair of breakwaters and seawalls, and maintenance of navigational aids.
- Port management: This division involves the management and operation of ports and harbors, including the provision of port services such as cargo handling, storage, and transportation.
- Environmental services: This division involves the management and mitigation of environmental impacts associated with port and harbor construction and operation, including the management of waste, pollution control, and habitat restoration.
- Design and engineering: This division involves the design and engineering of harbor infrastructure, including planning, design, and construction supervision services.
The Leading Companies in Port and Harbor Construction in The U.S.:
 Manson Construction Company
Manson Construction Company
 Cashman Dredging & Marine Contracting Company, LLC
Cashman Dredging & Marine Contracting Company, LLC
 Weeks Marine, Inc.
Weeks Marine, Inc.
 Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Company, LLC
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Company, LLC
 Kiewit Corporation
Kiewit Corporation
 Moffatt & Nichol, Inc.
Moffatt & Nichol, Inc.
 Triton Marine Construction Corporation
Triton Marine Construction Corporation
 Southwind Construction Services, LLC
Southwind Construction Services, LLC
 Pacific Pile & Marine Company
Pacific Pile & Marine Company
 Gulf Island Fabrication, Inc.
Gulf Island Fabrication, Inc.
 Massman Construction Company
Massman Construction Company
 Marinex Construction, Inc.
Marinex Construction, Inc.
 British Aerospace Engineering
British Aerospace Engineering
 Luedtke Engineering Company
Luedtke Engineering Company
 Callan Marine, LTD.
Callan Marine, LTD.
 Sterling Construction Company, Inc.
Sterling Construction Company, Inc.
 Corman Kokosing Construction Company
Corman Kokosing Construction Company
 GLF Construction Corporation
GLF Construction Corporation
The Leading Companies in Port and Harbor Construction in Canada:
 Pomerleau, Inc.
Pomerleau, Inc.
 McAsphalt Marine Transportation, Ltd.
McAsphalt Marine Transportation, Ltd.
 PCL Construction, Inc.
PCL Construction, Inc.
 McKeil Marine Ltd.
McKeil Marine Ltd.
 Dragados Canada, Inc
Dragados Canada, Inc
 Fraser River Pile & Dredge (GP), Inc.
Fraser River Pile & Dredge (GP), Inc.
