
Index
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for, Urban Transit Systems Industry
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Urban Transit Systems Industry:
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
Case Studies Of RFID,Iot&Drones
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Urban Transit Systems Industry
Overview
The urban transit systems industry encompasses a wide range of public transportation services and infrastructure designed to facilitate the movement of people within urban and metropolitan areas. It plays a crucial role in addressing the transportation needs of densely populated cities and reducing congestion, pollution, and reliance on personal vehicles. Here’s a brief description of the urban transit systems industry. urban transit systems include various modes of transportation, such as buses, trams, subways, commuter trains, light rail, and even innovative solutions like bike-sharing and electric scooters. The industry involves the construction, maintenance, and operation of infrastructure like bus stops, train stations, subway tunnels, tracks, depots, and maintenance facilities. These are essential for the efficient functioning of transit systems. Transit systems can be owned and operated by public entities like city governments, regional authorities, or private companies through public-private partnerships. Public transit agencies are often responsible for planning, funding, and overseeing transit services.GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in urban transit systems industry to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials and operational equipment such as buses, trams, subways, commuter trains, light rail vehicles, electric buses, trolleybuses, bus shelters, train stations, subway tunnels, tracks and rails, track inspection vehicles, transit vehicles maintenance equipment, traffic management systems, signage and wayfinding infrastructure, passenger information displays, automated people movers, wheelchair-accessible ramps and lifts, mobile apps for real-time transit information, transit route planning software, electric charging infrastructure for buses, automatic train control systems, ticket inspection devices (e.g., handheld validators). Ranked as one of the top 10 global RFID suppliers, GAO RFID Inc. is based in New York City, U.S. and Toronto, Canada. GAO offers a comprehensive selection of UHF, HF (including NFC) and LF RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags, BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. Such RFID and BLE products and systems, as well as its IoT and drone technologies, have been successfully deployed for urban transit systems industry. Its sister company, GAO Tek Inc. https://gaotek.com, is a leading supplier of industrial or commercial testers and analyzers, drones, and network products. The targeted markets of both GAO RFID Inc. and GAO Tek Inc. are North America, particularly the U.S., Canada, Mexico, and Europe. As a result, this website gaorfid.com is offered in English and other major languages of North America and Europe such as Spanish, French, German, Italian, Polish, Ukrainian, Romanian, Russian, Dutch, Turkish, Greek, Hungarian, Swedish, Czech, Portuguese, Serbian, Bulgarian, Croatian, Danish, Finnish, Norwegian, Slovak, Catalan, Lithuanian, Bosnian, Galician, Slovene, Latvian, Estonian, Welsh, Icelandic, and Irish.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for, Urban Transit Systems Industry
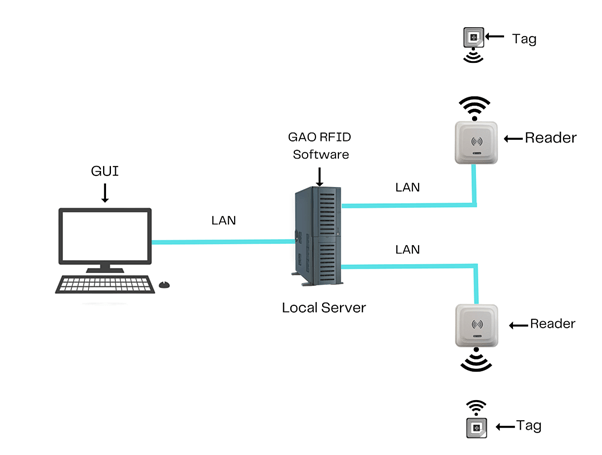
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for urban transit systems industry are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server that normally is on our client’s premises, and another version runs in the cloud. The cloud server could be GAO’s cloud server, client’s own cloud server or a cloud server from one of the leading cloud server providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud (formerly SoftLayer), Oracle Cloud, RedHat, Heroku, Digital Ocean, Cloudflare and Rackspace. The above illustrates GAO system for urban transit systems industry software running on a local server
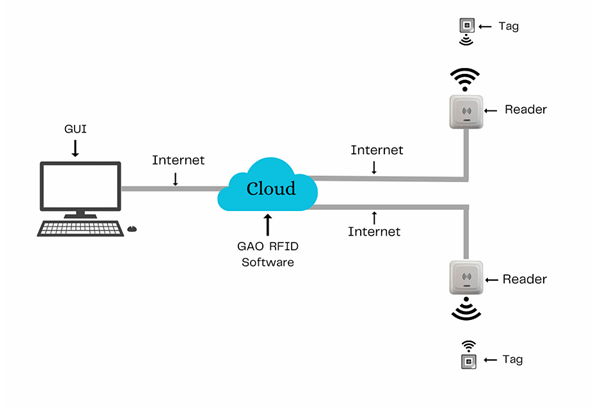
The above illustrates GAO system for urban transit systems industry with its software running in cloud.
GAO’s RFID and BLE technologies, consisting of RFID readers, RFID tags, BLE gateways, BLE beacons, software, cloud services and their systems, have the following applications in urban transit systems industry:
- Contactless Fare Payment: GAO’s RFID cards or NFC-enabled smartphones can be used as contactless payment methods for public transportation, allowing passengers to easily tap their cards or phones on readers to pay for rides.
- Smart Ticketing: GAO’s RFID-enabled smart cards can serve as reusable tickets for various modes of transportation, such as buses, subways, trams, and trains, reducing the need for paper tickets and improving convenience.
- Automated Fare Collection (AFC): GAO’s RFID technology is integral in AFC systems, which automate the process of fare collection and reduce the reliance on manual ticketing and cash handling.
- Access Control: GAO’s RFID cards or tokens can be used for access control in transit systems, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to restricted areas like maintenance depots, control rooms, and secure facilities.
- Passenger Tracking: GAO’s RFID technology can be used to track passenger movements, providing real-time data on passenger counts, boarding and alighting points, and helping transit agencies optimize routes and schedules.
- Security and Authentication: GAO’s RFID cards or badges can be used for secure identification of transit employees and contractors, helping to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive areas and equipment.
- Asset Tracking: GAO’s RFID tags can be attached to transit vehicles, equipment, and infrastructure to monitor their location, maintenance history, and performance, facilitating maintenance and inventory management.
- Maintenance and Inventory Management: GAO’s RFID technology can streamline maintenance processes by tracking the usage and maintenance needs of transit vehicles, tools, and spare parts.
- Lost and Found Systems: GAO’s RFID tags can be used to label personal belongings, such as bags or wallets, helping passengers and transit agencies reunite lost items with their owners.
- Passenger Information Systems: GAO’s RFID cards can store personalized information about passengers, allowing for customized information displays and notifications regarding transit services and updates.
GAO’s drone technologies find the following applications in the urban transit systems industry:
- Infrastructure Inspection: GAO’s Drones can be used to inspect bridges, tunnels, railways, and other transit infrastructure for signs of wear and tear, damage, or potential hazards. They can capture high-resolution images and videos for analysis.
- Track and Right-of-Way Inspection: GAO’s Drones equipped with specialized sensors can monitor the condition of railroad tracks, overhead wires, and rights-of-way, helping detect issues like obstructions, vegetation encroachment, or damaged components.
- Aerial Mapping and Surveying: GAO’s Drones equipped with LiDAR or photogrammetry equipment can create accurate 3D maps and surveys of transit routes, aiding in the planning and maintenance of transportation networks.
- Traffic Monitoring: GAO’s Drones can provide real-time traffic monitoring and data collection for roadways and transit hubs. This information can be used to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
- Emergency Response: GAO’s Drones can be rapidly deployed in emergency situations to assess damage, locate stranded passengers, and provide situational awareness to first responders during accidents or natural disasters.
- Security Patrols: GAO’s Drones equipped with cameras and sensors can patrol transit facilities, providing surveillance and security monitoring, especially in remote or high-risk areas.
- Maintenance and Repairs: GAO’s Drones can be used to carry out minor maintenance tasks, such as cleaning and painting, on hard-to-reach transit infrastructure like bridges or elevated structures.
- Asset Management: GAO’s Drones can help track the location and condition of transit assets such as buses, trains, and maintenance equipment, aiding in maintenance scheduling and asset management.
- Environmental Monitoring: GAO’s Drones can be equipped with sensors to monitor air quality, noise levels, and other environmental factors in and around transit systems, ensuring a healthy and safe environment for passengers.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GAO’s Drones can be used to update and maintain GIS databases by collecting geospatial data for urban transit systems, facilitating better planning and decision-making.
GAO’s IoT technologies, consisting of IoT sensors, sensors networks and systems, find the following applications in the urban transit systems industry:
- Real-Time Passenger Information: GAO’s IoT sensors and devices can provide passengers with real-time information about transit schedules, delays, and estimated arrival times through smartphone apps, digital signs, and public kiosks.
- Smart Ticketing and Fare Collection: GAO’s IoT-enabled smart cards and ticketing systems allow passengers to pay fares seamlessly using contactless methods, reducing the reliance on paper tickets and cash.
- Predictive Maintenance: GAO’s IoT sensors installed on transit vehicles and infrastructure can monitor their condition in real-time, predicting maintenance needs and reducing downtime by scheduling repairs proactively.
- Fleet Management: GAO’s IoT devices in buses, trains, and trams help transit agencies monitor the location, speed, and performance of their vehicles, optimizing routes and schedules for improved efficiency.
- Energy Management: GAO’s IoT can be used to monitor and control energy consumption in transit facilities, such as stations and maintenance depots, to reduce energy costs and environmental impact.
- Passenger Counting and Load Balancing: GAO’s IoT sensors and cameras can count passengers boarding and alighting, helping transit operators optimize vehicle loads and schedule additional services during peak hours.
- Environmental Monitoring: GAO’s IoT sensors can monitor air quality, noise levels, and other environmental factors within transit systems, ensuring passenger safety and compliance with environmental regulations.
- Security and Surveillance: GAO’s IoT-connected cameras and sensors can enhance security by providing real-time surveillance of transit stations, vehicles, and critical infrastructure.
- Asset Tracking: GAO’s IoT can track the location and condition of transit assets, such as buses, trains, and maintenance equipment, preventing theft and improving asset management.
- Traffic Management: GAO’s IoT sensors and traffic lights can communicate with transit vehicles to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion, improving on-time performance.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Urban Transit Systems Industry:
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in urban transit systems industry to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates and government regulations
RFID, BLE, IoT, & Drone Standards & Mandates
- ISO 14443
- ISO 15693
- ISO 18000
- ISO 29143
- Bluetooth 5.0
- Bluetooth 5.1
- Bluetooth Mesh
- IEEE 802.11
- MQTT
- CoAP
- Lora WAN
- Zigbee (IEEE 802.15.4-based)
- Thread (IPv6-based)
- OPC UA
- OneM2M
- ANSI/CTA-2063
- ISO 21384
- FAA Part 107 (U.S.)
- JARUS
Us Government Regulations
- Federal Transit Administration (FTA) Title 49 Part 604 – Charter Service
- FTA Title 49 Part 670 – Public Transportation Agency Safety Plans
- FTA Title 49 Part 672 – Public Transportation Safety Certification Training Program
- FTA Title 49 Part 673 – Public Transportation Safety Program
- FTA Title 49 Part 674 – Transit Asset Management
- FTA Title 49 Part 675 – State Safety Oversight
- FTA Title 49 Part 676 – Public Transportation Safety Certification of Transit Agencies
- FTA Title 49 Part 677 – Transit Asset Management
- FTA Title 49 Part 678 – Capital Investment Program
- FTA Title 49 Part 679 – Transit Asset Management for Urbanized Areas
- FTA Title 49 Part 682 – Public Transportation Agency Safety Plans
- FTA Title 49 Part 685 – Implementation of National Environmental Policy Act
- FTA Title 49 Part 722 – New Freedom Program
- FTA Title 49 Part 750 – Clean Fuels Grant Program
- FTA Title 49 Part 752 – Buses and Bus Facilities Infrastructure Investment Program
Canadian Government Regulations
- Canada Transportation Act, S.C. 1996, c. 10
- Canadian Environmental Assessment Act, 2012, S.C. 2012, c. 19
- Canadian Transportation Agency Designated Provisions Regulations, SOR/2020-182
- National Energy Board Act, R.S.C., 1985, c. N-4
- Transport Canada Aviation Security Regulations, SOR/2002-87
- Transport Canada Security Measures Regulations, SOR/2004-280
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods Act, 1992, S.C. 1992, c. 34
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations, SOR/2001-286
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods Safety Marks Regulations, SOR/2001-286
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods (Clear Language, SOR/2017-137
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods (General) Regulations, SOR/2019-101
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods (Interim Order Respecting), SOR/2020-52
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods (Shipping Documents) Regulations, SOR/2017-137
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods (Training) Regulations, SOR/2002-306
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods (United Nations Recommendations, IBC Code and IGC Code), SOR/2008-34.
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in urban transit systems industry such as:
Personnel Management:
- Employee Scheduling and Shift Management
- Training and Certification Tracking
- Employee Performance Evaluation
Equipment Management:
- Asset Tracking and Inventory Control
- Predictive Maintenance for Vehicles and Infrastructure
Access Control:
- Fare Gate Control
- Vehicle Depot Access Control
Warehouse Management:
- Stock Replenishment and Ordering
- Vendor and Supplier Management
Supply Chain Management:
- Logistics and Route Optimization
- Vendor Performance Evaluation
Other Applications:
- Automated Fare Collection
- Passenger Counting and Load Balancing
- Environmental Monitoring and Sustainability Tracking
- Incident Reporting and Management
- Emergency Response and Evacuation Planning
- Vehicle Monitoring and Telematics
- Traffic Management and Congestion Reduction
- Accessibility and Inclusivity Services
- Passenger Feedback and Customer Service Management
GAO has enabled its customers to make use of some of the leading software and cloud services in the urban transit systems industry. Below are some of popular software and cloud services in urban transit systems industry Workday, SAP SuccessFactors, Oracle Cloud HCM, BambooHR, Zenefits, Infor EAM, Asset Works, Up-Keep, Fiix, HID Global, Brivo, Kisi, Paxton, HighJump WMS, Manhattan Associates, JDA Warehouse Management, 3PL Central, Oracle SCM Cloud, Kinaxis RapidResponse, Blue Yonder (formerly JDA Software), Infor Supply Chain Planning.
GAO has worked with some of the leading technology companies in urban transit systems industry to provide integrated RFID, BLE, IoT and drone solutions to customers. Here are some of the technology leaders in urban transit systems industry IBM, Cisco Systems, Siemens Mobility, Cubic Transportation Systems, Thales Group, Alstom, Bombardier Transportation, Hitachi Rail, Hyundai Rotem, Stadler Rail, Siemens Mobility, Hyundai Rotem, Mitsubishi Electric, Wabtec Corporation, Toshiba Infrastructure Systems & Solutions Corporation
Case Studies of RFID, IoT & Drone Applications
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Below are some RFID application cases in urban transit systems industry.
The Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) in New York City uses RFID technology for its contactless fare payment system, known as OMNY (One Metro New York). Passengers can use contactless payment methods, such as NFC-enabled smartphones and contactless credit/debit cards, to access the subway and buses. The Washington Metropolitan Area Transit Authority (WMATA) implemented an RFID-based Smart Trip card system for fare collection. Passengers can load funds onto the RFID cards and use them for fare payment across the metro system. The TTC uses RFID-based Presto cards for contactless fare payments on buses, streetcars, and subways in Toronto. Passengers can load funds onto their Presto cards and use them for seamless transit access. The Société de transport de Montréal (STM) introduced the Opus card, which utilizes RFID technology for fare collection. Opus cards allow passengers to travel on the Montreal Metro, buses, and commuter trains. The Mexico City Metro introduced an RFID-based contactless fare payment system known as “Tarjeta de Movilidad Integrada” (Integrated Mobility Card). Passengers can use these cards to access the metro and other public transit services. The London Underground uses the Oyster card, an RFID-based smart card, for fare payment. Passengers can tap their Oyster cards on RFID readers to access the Tube, buses, trams, the Docklands Light Railway, London Overground, and other transit services. The Paris Metro system uses Navigo cards, which incorporate RFID technology, for fare payment. These cards allow passengers to travel on the Paris Metro, buses, trams, and commuter trains within the Île-de-France region. The Berliner Verkehrsbetriebe (BVG) uses the “Berliner Verkehrsbezahlkarte” (BVG Card) with RFID technology for contactless fare payment on buses, trams, subways, and commuter trains in Berlin.
Many applications of RFID by GAO can be found here.
Case Studies of IoT Applications
Below are some IoT application cases in urban transit systems industry. The Chicago Transit Authority has implemented IoT sensors and real-time data analytics to monitor the performance and condition of its buses and trains. This helps in predictive maintenance, reducing downtime, and ensuring reliable service. BART has deployed IoT sensors and data analytics to monitor track conditions, switches, and infrastructure. This information is used to optimize maintenance schedules and improve system reliability. TransLink uses IoT technology to provide real-time information to passengers. This includes bus location tracking, estimated arrival times, and service alerts, which are accessible through mobile apps and digital signage. The Mexico City Metro uses IoT sensors to monitor air quality in stations and tunnels. If air quality falls below acceptable levels, alerts are triggered to take corrective actions, ensuring passenger safety. The London Underground uses IoT sensors to monitor the temperature of its tunnels. This helps ensure passenger comfort and allows for preemptive maintenance in case of overheating. Amsterdam’s public transport system uses IoT-connected vehicles and infrastructure to optimize traffic signal timing, reducing congestion and improving the flow of buses and trams. The Copenhagen Metro employs IoT sensors to monitor passenger flow and optimize service frequency during peak hours. This improves passenger experience and reduces overcrowding. Vienna’s public transport system uses IoT sensors to monitor vehicle health and schedule maintenance tasks proactively. This helps prevent breakdowns and service disruptions.
Case Studies of Drone Applications
Below are some drone application cases in the urban transit systems industry. The Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (LACMTA) has used drones for aerial inspections of rail lines and infrastructure. Drones help identify potential issues quickly and efficiently, ensuring the safety of passengers. MBTA has employed drones for tunnel inspections, which are otherwise challenging to access. Drones equipped with cameras and sensors help inspect the condition of tunnels, tracks, and electrical systems. TTC has used drones for infrastructure inspection and maintenance. Drones help monitor elevated tracks, stations, and other critical transit infrastructure for signs of wear, damage, or unauthorized access. The Mexico City Metro has employed drones for aerial surveys of construction and maintenance projects. Drones assist in assessing the progress of projects, safety conditions, and compliance with construction standards. London Underground has utilized drones to inspect hard-to-reach areas within its extensive network, such as tunnels and viaducts. Drones help identify maintenance needs and reduce service disruptions. The Berliner Verkehrsbetriebe (BVG) has implemented drones for surveillance and security purposes. Drones equipped with cameras help monitor station premises, tracks, and infrastructure for potential security threats. The Paris Metro has used drones for environmental monitoring. Drones equipped with sensors assess air quality, noise levels, and other environmental factors within and around the transit system, ensuring a safe and comfortable environment for passengers. Vienna’s public transport system has employed drones for traffic monitoring and management. Drones help assess traffic conditions, optimize traffic signal timing, and ensure efficient bus and tram operations during peak hours.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Urban Transit Systems Industry
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including urban transit systems industry
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including urban transit systems industry.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including urban transit systems industry:
- GEN 2 UHF 902-928 MHz RFID RRADERS
- GEN 2 UHF 865-868 MHz PASSIVE RFID READERS
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including urban transit systems industry
- GEN 2 UHF 902-928 MHz RFID TAGS
- GEN 2 UHF 865-868 MHz RFID TAGS
- SEMI PASSIVE UHF GEN2 RFID TAGS
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including urban transit systems industry:
- HIGH FREQUENCY 13.56 MHz PASSIVE RFID READERS
- LOW FREQUENCY 134 kHz PASSIVE RFID READERS
- LOW FREQUENCY 125 kHz PASSIVE RFID READERS
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including urban transit systems industry:
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
and relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
- UHF 860 – 960 MHz RFID MODULES
- 13.56 MHz HIGH FREQUENCY RFID MODULES
- 25 kHz LOW FREQUNCY RFID MODULES
In collaboration with its sister company GAO Tek Inc, a wide selection of high-quality drones is offered:
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in urban transit systems industry:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include Point of Sale (POS) Systems, Cash Registers, Pricing Guns, Barcode Scanners, Shopping Carts, Shopping Baskets, Clothing Racks, Shelving Units, Security Cameras, Electronic Article Surveillance (EAS) Systems, Mannequins and Display Forms, Mirrors, Hangers, Price Tags and Labels, Security Tags and Detachers, Slatwall Displays, Gridwall Displays, Security Mirrors, Lockers for Customer Use, Price Check Stations.
People or workers tracking system:
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
Furthermore, GAO provides the customization of RFID tags, RFID readers, BLE beacons and BLE gateways, IoT, drones, and systems and consulting services for urban transit systems industry and for various industries in all metropolitans in North America, particularly the U.S., Canada and Mexico, and Europe:
GAO Makes Efforts to Satisfy Customers
Large Choice of Products
In order to satisfy the diversified needs of their corporate customers, GAO RFID Inc. and its sister company GAO Tek Inc. together offer a wide choice of RFID, BLE, IoT, drones, testing and measurement devices, and network products.
Overnight Delivery
In order to shorten the delivery to our customers, GAO has maintained a large stock of its products and is able to ship overnight within continental U.S. and Canada, and fast delivery to anywhere in Mexico and Europe from the nearest warehouse.
Local to Our Customers
We are located in both the U.S. and Canada. We travel to customers’ premises if necessary. Hence, we provide a very strong local support to our customers in North America, particularly the U.S., Canada and Mexico, and Europe. Furthermore, we have built partnerships with some integrators, consulting firms and other service providers in different cities to further strengthen our services. Here are some of the service providers in urban transit systems industry we have worked with to serve our joint customers Cubic Transportation Systems, Siemens Mobility, Accenture, TransLoc, Thales Group, Trapeze Group, Televic Rail, Indra, Siemens Mobility, Alstom, Siemens Mobility, Kapsch Traffic Com, Init
GAO Has Served Urban Transit Systems Industry Extensively
GAO RFID Inc. and its sister company GAO Tek Inc. together offer a wide choice of RFID, BLE, IoT, drone, testing and measurement devices, and network products.
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in urban transit systems industry to achieve success in Mobility as a Service (Maas), Electrification, Autonomous Vehicles, Contactless Payments, Smart Cities, Sustainable Transportation, Transit-Oriented Development (TOD), Last-Mile Solutions, Micro-Mobility, Data Analytics, Predictive Maintenance, Integrated Fare Systems, Digital Twins, On-Demand Transit, 5G Connectivity, Artificial Intelligence (AI).
GAO RFID Inc. has deployed RFID, BLE and IoT projects for many companies in urban transit systems industry, including many in its various divisions such as
- Mass Transit Rail Systems: This division includes subways, metro systems, light rail, and commuter rail networks. These systems typically run on dedicated tracks, providing fast and efficient transportation within cities and their suburbs.
- Bus Transit Systems: Bus transit systems involve a network of bus routes and stops within a city or metropolitan area. They can include regular city buses, bus rapid transit (BRT) systems with dedicated lanes, and shuttle services.
- Tram and Streetcar Systems: Trams and streetcars are often used for urban transit in some cities. These systems typically run on tracks embedded in city streets and provide transportation within specific areas or along designated routes.
- Trolleybuses: Trolleybuses are electric buses that draw power from overhead wires. They are often used in cities to provide clean and efficient public transportation.
- Paratransit Services: Paratransit services are designed to meet the needs of individuals with disabilities or other mobility challenges. They include door-to-door or curb-to-curb transportation options, such as dial-a-ride programs.
- Ferries and Water-Based Transit: In cities located near bodies of water, ferry services and water-based transit systems can be crucial for commuters. These services include passenger ferries, water taxis, and other vessels that transport people across rivers, lakes, or coastal areas.
- Cycling and Pedestrian Infrastructure: Part of the urban transit system includes cycling lanes, pedestrian pathways, and bike-sharing programs that encourage non-motorized transportation options.
- Integrated Fare and Payment Systems: This division focuses on fare collection methods and integrated payment systems that allow passengers to use various modes of transit seamlessly using a single payment method or card.
- Transit Operations and Maintenance: This segment involves the day-to-day operations, maintenance, and management of transit vehicles, infrastructure, and services to ensure safe and reliable transit operations.
- Transit Planning and Development: Transit planning experts and agencies are responsible for designing and expanding urban transit systems, considering factors like population growth, traffic patterns, and environmental sustainability.
GAO’s technologies enable its customers in urban transit systems industry to effectively track their workforces such as Bus Driver, Train Operator, Conductor, Station Agent, Dispatcher, Transit Police Officer, Maintenance Technician, Fare Inspector, Mechanic, Customer Service Representative, Transit Supervisor, Transit Administrator, Safety Inspector, Transit Manager, Environmental Specialist, Ticket Sales Agent, Transit Analyst and effectively track operational assets such as Light Rail Vehicle, Commuter Train, Trolleybus, Ferries, Transit Van, Paratransit Vehicle, Bicycle Sharing Station, Ticket Vending Machine, Farebox, Faregate, Bus Shelter, Tram Stop, Train Platform, Transit Terminal.
Here are some of the leading companies in urban transit systems industry GAO has served:
- Gillig Corporation
- Cubic Transportation Systems Inc.
- Vossloh Group
- Alstom USA
- AECOM
- Stadler Rail Group
- Wabtec Corporation
- BYD North America
- First Transit Inc.
- Keolis North America
- MV Transportation Inc.
- CRRC Corporation
- BAE Systems Inc.
- Bombardier Transportation Canada Inc.
- Nova Bus (A Division of Volvo Group Canada Inc.)
- New Flyer Industries Canada ULC
- Siemens Mobility Limited (Canada)
- Proterra Canada Inc.
- Transdev Canada Inc.
























You Are Invited to Contact Us!
If you are interested in our products, services or partnering with us, please feel free to contact us by filling out this form:
or email us at sales@gaorfid.com
