
Related Products & Systems on Other Pages on This Website
People Tracking System for Manufacturing Facilities
Employee & Attendance Access Control System
Return & Pallet Asset Tracking – GAO RFID
Work In Process WIP Asset Tracking System
BLE | Bluetooth Low Energy | BLE Gateways & Beacons – GAO RFID
RFID Readers | Buy RFID Readers | RFID Reader Writers – GAO RFID
RFID Tags | Buy RFID Tags – GAO RFID
Overview
Crop Production industry involves the cultivation and harvesting of crops for various purposes, such as food production, animal feed, fiber, and industrial uses. Farmers use a combination of traditional and modern farming techniques to maximize yields and ensure crop health. It is influenced by factors such as climate, soil type, market demand, government policies, and technological advancements, making it a dynamic and challenging sector to operate in.
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in Crop Production to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials and operational equipment such abstractors, seeders and planters, harvesters, sprayers, irrigation systems, tillage equipment, fertilizer spreaders, crop monitoring technology, grain dryers, storage facilities, livestock equipment, miscellaneous tools.
Ranked as a top 10 global RFID supplier and based in New York City and Toronto, GAO RFID Inc offers a wide choice of RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags at ultra-high frequency (UHF), high frequency (HF, including NFC) and low frequency (LF), BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. Such RFID and BLE products and systems, together with its IoT and drone technologies, have been widely used in Crop Production.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Crop Production
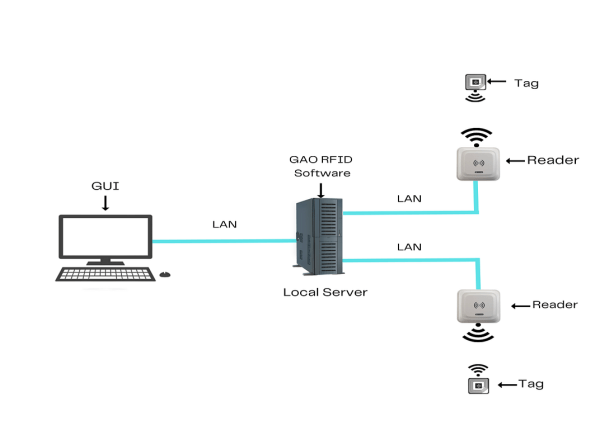
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for crop production are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server, and another version is that its software runs in the cloud. The above illustrates GAO system for crop Production with its software running on a local server.
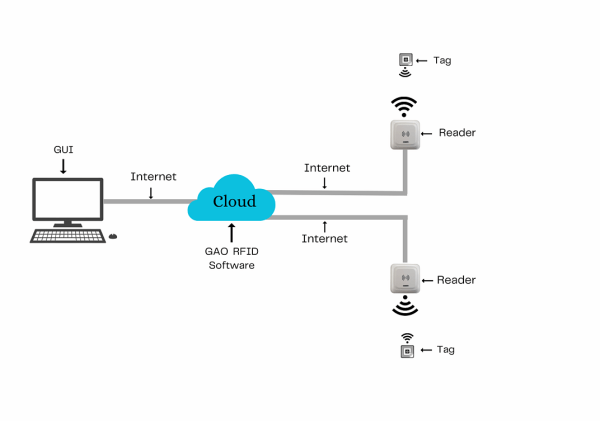
The above illustrates GAO system for crop production industry with its software running in cloud.
GAO’s RFID technologies bring the many benefits to crop production industry:
- Enhanced Inventory Management: GAO’S RFID tags enable accurate tracking of inventory levels, allowing farmers to maintain optimal stock levels and streamline procurement processes.
- Efficient Supply Chain Management: Agriculture-related items may be tracked and traced using GAO’S RFID, which enhances logistics, lowers losses, and guarantees product quality and safety.
- Improved Traceability and Quality Control: Our RFID tags enable precise traceability, enhancing quality control, product recalls, and assurance of food origin and safety.
- Better Farm Asset Management: GAO’SRFID can aid farmers in optimizing asset utilization, minimizing losses, and boosting productivity.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: GAO’S RFID systems automate data collection, saving time and improving efficiency.
- Precision Agriculture: Farmers may get real-time data using GAO’S RFID technology to make accurate decisions.
- Theft and Loss Prevention: Our RFID tags can help find missing property or animals as well as prevent theft.
- Data Analytics and Decision Support: By combining RFID-generated data enables data-driven decision-making for farmers.
GAO’s BLE technologies offer longer reading range and particularly attractive for applications with larger work spaces within crop production industry:
- Real-time Monitoring: GAO’SBLE devices enable farmers to monitor crop conditions and adjust management practices.
- Remote Control and Automation: Remote control and automation of farm equipment improves efficiency.
- Precision Farming: GAO’SBLE sensors enable targeted interventions tooptimize resource usage and yields.
- Improved Equipment Management: Our BLE tags can be used to track and manage assets, reduce theft, and improve efficiency.
- Safety and Security: By installing proximity sensors and alerts, GAO’S BLE devices may improve farm security and safety.
- Data-driven Decision Making: Data-driven approach helps farmers make informed decisions to improve productivity and profitability.
- Mobile Connectivity and Farm Management Apps: Farmers can access real-time data, receive alerts, and control operations.
- Cost and Energy Efficiency: GAO’S BLE devices are energy-efficient and affordable, making them accessible to farmers.
GAO’s RFID and drone technologies are often combined and such solutions offer the following benefits to crop production industry:
- Crop Monitoring and Precision Agriculture: Drones and GAO’S RFID technology enable precise monitoring and targeted interventions.
- Efficient Inventory Management: GAO’S RFID tags can be used to track and manage agricultural inputs.
- Automated Plant Identification and Mapping: Drones use RFID readers to map crop distribution, density, and growth stages.
- Enhanced Crop Tracking and Traceability: GAO’S RFID technology enables accurate traceability and improved supply chain transparency.
- Improved Pest and Disease Management: Drones detect early signs of pest infestations, enabling targeted interventions.
- Optimal Resource Management: Farmers can use drone imagery and RFID data to optimize resource allocation.
- Timely Harvesting and Yield Estimation: Drones can help farmers assess crop maturity and yield potential.
- Safety and Monitoring: Drones with RFID technology help monitor livestock and prevent theft.
- Efficient Field Mapping and Planning: Better analysis and decision-making are made possible by RFID data and drones.
Here are the benefits of GAO’s IoT technologies to crop production industry:
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Farmers can remotely monitor and control farm operations to optimize crop growth.
- Precision Agriculture: IoT devices and data analytics enable precise and targeted interventions to improve crop yields.
- Efficient Resource Management: GAO’S IoT technology helps farmers optimize irrigation schedules, reduce water waste, and conserve energy.
- Predictive Analytics and Decision Support: Farmers can use predictive models to make informed decisions.
- Automated Monitoring and Alerts: IoT sensors provide automated monitoring and alerts to prevent crop damage.
- Enhanced Traceability and Quality Control: By enabling agricultural traceability, IoT devices give consumers comprehensive information.
- Remote Surveillance and Security: IoT-enabled cameras and security systems enhance farm security.
- Integration with Other Technologies: Data interchange, optimization, and increased production are made possible by IoT technology.
- Data-driven Insights and Farm Management: IoT-generated data enables farmers to make data-driven decisions.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Crop Production
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in crop production to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates and government regulations.
RFID, BLE, IoT, &Drone Standards& Mandates:
- Electronic Product Code Generation 2 (EPC Gen2): EPC Gen2 is a global RFID standard that provides a common framework for RFID systems, used for item-level tagging and supply chain applications.
- OMA LWM2M (Open Mobile Alliance Lightweight M2M): LWM2M provides a standard framework for managing and controlling IoT devices, such as sensors and actuators in agricultural applications.
- Proprietary Protocols and APIs: Agricultural technology providers develop proprietary protocols and APIs to integrate BLE-enabled devices into their solutions.
- Message Queuing Telemetry Transport(MQTT):MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol used in the agriculture sector to exchange data between IoT devices.
- Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP): CoAP is a protocol designed for resource-constrained devices and networks, enabling efficient communication and lightweight RESTful interactions.
- OPC Unified Architecture(OPC UA): OPC UA is a platform-independent standard for secure and reliable data exchange between industrial automation systems.
- OGC (Open Geospatial Consortium) SensorThings API: The SensorThings API is an OGC standard for accessing and managing IoT sensor data in a spatial context, particularly useful in Crop Production industry.
- Zigbee: Zigbee is a low-power, wireless communication protocol used in agriculture to connect sensors, actuators, and control systems.
- Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN): LoRaWAN is a WAN protocol that enables long-range, low-power communication between IoT devices in rural or remote areas.
- OneM2M: OneM2M is a global standard for interoperability and management of IoT devices and services, particularly relevant in Crop Production industry.
- FAA Part 107: The FAA has established regulations for the commercial operation of drones, including pilot certification, aircraft registration, operational limitations, and safety considerations.
- European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) Regulations: EASA has established regulations for drone operations in agriculture, covering categories, pilot qualifications, operational limitations, and safety requirements.
- ASTM International: ASTM has developed standards related to drone design, performance, and operations, including flight operations, crew qualifications, maintenance, and safety management.
- IEC 62443: This International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard provides guidelines for securing drone systems and networks against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Remote Identification Standards: Remote identification standards are being developed to enable the identification and tracking of drones in real-time, enhancing safety and security.
US. Government Regulations for Crop Production:
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Regulations:
- Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA): Regulates the registration, distribution, sale, and use of pesticides.
- Clean Water Act (CWA): Regulates the discharge of pollutants into navigable waters, including agricultural runoff.
- Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA): Regulates the management and disposal of hazardous waste generated by agricultural operations.
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Regulations:
-
- Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA): Implement preventive controls, inspections, and compliance requirements to prevent foodborne illnesses.
- Produce Safety Rule: Sets standards for the growing, harvesting, packing, and holding of produce to minimize the risk of contamination.
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Regulations:
-
- Agricultural Marketing Agreement Act (AMAA): Establishing marketing orders and agreements to stabilize markets and ensure fair trade practices.
- National Organic Program (NOP): Establishes standards for the production, handling, labeling, and certification of organic agricultural products.
- Conservation Reserve Program (CRP): Provides financial incentives to farmers for the conservation and restoration of environmentally sensitive land.
- Farm Bill Programs: The Farm Bill provides programs and regulations for crop insurance, subsidies, conservation, research, and rural development.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Regulations:
- General Industry Standards: Establishes workplace safety and health standards for agricultural operations.
- State and Local Regulations: State and local jurisdictions may require additional regulations and requirements for agriculture.
Canadian Government Regulations for Crop Production:
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) Regulations: The CFIA regulates the import, export, and domestic movement of plants, plant products, and pests to prevent the spread of pests and diseases. It also regulates the quality, labeling, and certification of seeds, fertilizers, and health of animals.
- Pest Control Products Act (PCPA): Regulates the registration, sale, and use of pesticides in Canada, including those used in crop production, to protect human health and the environment.
- Canadian Environmental Protection Act (CEPA): Regulation of hazardous substances to protect human health and environment.
- Safe Food for Canadians Act (SFCA): Regulations for food safety in Canada, including production, processing, labeling, and import/export activities.
- Canadian Agricultural Loans Act (CALA): Provides loan guarantees to agricultural producers, including those in the crop production sector, to support their financial needs.
- Canadian Grain Commission (CGC) Regulations: Grain regulations in Canada are administered through standards, licensing, grading, and inspection.
- Employment Standards Legislation: Canada’s employment standards legislation sets minimum wages, working hours, conditions, and worker safety for agricultural workers.
- Provincial and Territorial Environmental Regulations: Regulations related to environmental protection, water usage, land use planning, and pesticide control are specific to agricultural activities.

Electronic Product Code Generation 2

International Organization for Standardization

General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade

IEC

OPC Unified Architecture

Occupational Safety and Health Administration

Canadian Food Inspection Agency

EASA
GAO’s Software Provides API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in crop production such as:
Personnel Management:
- Workforce Planning and Scheduling: Managing and scheduling farm labor and staff activities efficiently.
- Employee Tracking and Attendance: Tracking and recording employee attendance and work hours.
- Training and Certification Management: Managing training programs and certifications for agricultural workers.
- Performance Evaluation: Assessing and evaluating employee performance and productivity.
Equipment Management:
- Equipment Tracking and Maintenance: Tracking the location, usage, and maintenance schedules of agricultural machinery and equipment.
- Asset Management: Managing and maintaining a record of farm assets, including equipment, vehicles, and infrastructure.
- Equipment Utilization and Optimization: Analyzing equipment usage and performance to optimize operations and reduce downtime.
Access Control:
- Farm Access Management: Controlling access to farm premises and restricted areas to ensure security and safety.
- Visitor Management: Tracking and managing visitor access to the farm, including contractors, suppliers, and other personnel.
Warehouse Management:
- Inventory Tracking: Monitoring and tracking the inventory of harvested crops, seeds, fertilizers, and other agricultural inputs.
- Quality Control: Implementing processes and systems to ensure the quality and integrity of stored crops and products.
- Stock Rotation and Shelf-Life Management: Managing the rotation and storage of crops based on their shelf life and expiry dates.
Supply Chain Management:
- Traceability and Certification: Tracking and documenting the origin, production processes, and certifications of crops for regulatory compliance and consumer trust.
- Logistics and Transportation Management: Optimizing transportation routes, coordinating shipments and managing logistics for crop distribution.
- Demand Forecasting and Planning: Analyzing market trends and data to forecast demand and plan crop production accordingly.
- Supplier Management: Managing relationships with suppliers of inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides.
- Contract and Pricing Management: Managing contracts, pricing agreements, and negotiations with buyers and suppliers.
Other Applications:
- Crop Monitoring and Precision Agriculture: Using sensors, drones, and other technologies for real-time crop monitoring, yield prediction, and precision farming practices.
- Irrigation and Water Management: Monitoring soil moisture levels and implementing efficient irrigation systems to optimize water usage.
- Pest and Disease Management: Implementing monitoring systems and adopting integrated pest management strategies to minimize crop damage.
- Environmental Monitoring and Sustainability: Tracking and managing environmental factors, such as weather conditions, soil health, and water quality, to ensure sustainable farming practices.
GAO has enabled its customers to make use of some of leading software and cloud services in crop production industry. Below are some of popular software and cloud services in crop production industry.
- AgSquared: A comprehensive farm management software that includes features for personnel management, task scheduling, equipment tracking, and record keeping.
- FarmLogs: It provides personnel and equipment management tools to track labor activities, work hours, and performance.
- Granular: Provides personnel management solutions for labor tracking, scheduling, and performance evaluation. It also offers equipment management features for tracking equipment location, usage, and maintenance.
- Farmers Edge: Offers cloud-based solutions for personnel management, including workforce planning and scheduling. It also provides equipment management tools for tracking equipment usage, maintenance, and optimization.
- Cropio: Cropio provides cloud-based personnel and equipment management solutions, allowing users to schedule tasks, track labor activities, and manage equipment usage and maintenance.
- AgriChain: A comprehensive platform for access control, warehouse management, supply chain management, inventory tracking, traceability, quality control, and logistics management.
- Croptracker: Croptracker is a software solution designed specifically for Crop Production industry, offering features for personnel management, access control, inventory tracking, and supply chain management.
- FarmSoft: Provides cloud-based solutions for access control, warehouse management, and supply chain management. It offers features for inventory tracking, order management, traceability, and reporting.
- FarmERP: A comprehensive farm management software that covers personnel, equipment, inventory, supply chain, and financial management.
- Conservis: Offers a farm management software platform that includes features for personnel management, equipment management, financial management, and crop planning.
- Agrian: Offers a cloud-based platform for farm management, providing features for personnel management, equipment management, compliance management and crop planning.
- Microsoft Azure: Microsoft Azure provides a cloud platform for Crop Production businesses to leverage cloud computing for applications, data storage, analytics and machine learning.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS provides scalable and flexible cloud computing resources, storage solutions, data analytics, and machine learning capabilities to help businesses optimize operations and streamline workflows.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP provides scalable infrastructure, data storage, analytics, machine learning and IoT services to help businesses manage and analyze agricultural data, implement precision farming techniques, and enhance decision-making processes.
- IBM Cloud: IBM Cloud provides advanced cloud services for Crop Production industry, enabling businesses to optimize operations, improve yield, and enhance supply chain management.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI): OCI provides cloud services designed for Crop Production industry, enabling businesses to manage and analyze agricultural data, improve resource allocation, and make data-driven decisions.

AgSquared

FarmLogs
Granular

Farmers Edge

Cropio

AgriChain
![]()
Croptracker

FarmSoft

FarmERP

Conservis

Agrian

Microsoft Azur0e
GAO has worked with some of the leading technology companies in crop production industry in to provide integrated its RFID, BLE, IoT and drone solutions to customers. Here are some of the technology leaders in crop production industry:
- John Deere: John Deere provides agricultural machinery, equipment, and precision farming technologies to enhance productivity and efficiency in crop production.
- Trimble: Trimble provides advanced GPS, guidance, and telematics systems to optimize farm operations, manage resources, and increase yield.
- AGCO Corporation: AGCO Corporation is a global leader in agricultural machinery and solutions to support efficient and sustainable crop production.
- Raven Industries: Raven Industries provides precision agriculture solutions to help farmers optimize operations and make informed decisions.
- Climate Corporation: Climate Corporation provides digital agriculture solutions to help farmers optimize planting, fertilization, and irrigation practices.
- AG Leader Technology: AG Leader Technology provides precision agriculture solutions to help farmers improve productivity and profitability.
- Lindsay Corporation: Lindsay Corporation provides innovative irrigation solutions for Crop Production industry, including pivot and lateral move systems.
- Yara International: Yara International provides sustainable fertilizers and agronomic solutions to optimize nutrient management and maximize yield.
- SST Software: SST Software provides precision agriculture software solutions to help farmers make data-driven decisions and optimize resource allocation.
- Topcon Positioning Systems: Topcon Positioning Systems provides precision guidance, machine control, and site management to facilitate efficient agricultural operations.
- MTS Systems Corporation: MTS Systems Corporation provides testing and simulation systems to evaluate agricultural machinery performance and durability, ensuring quality and reliability.
- AGJunction: AGJunction provides GPS-based systems for precision guidance and automation solutions for Crop Production industry.

John Deere

Trimble

AGCO

Raven Industries

Climate Corporation

AG Leader Technology

Lindsay Corporation

Yara International

SST Software

Topcon

MTS Systems Corporation

AGJunction
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Below are some RFID application cases in Crop Production industry:
Driscoll’s Berry Farms is a leading berry producer, implemented RFID technology to improve traceability and inventory management. RFID tags were placed on each container of berries, allowing real-time tracking of their movement from farm to distribution centers. The system enabled efficient inventory management, reduced shrinkage, and enhanced traceability for quality control and compliance purposes.
A Canadian seed supplier implemented RFID technology to enhance their seed inventory management and distribution processes. RFID tags were applied to seed packets, enabling real-time tracking and inventory visibility. This helped the supplier optimize seed distribution, reduce stockouts, and improve customer service.
Chico State Organic Dairy Farm RFID technology was implemented to track and monitor individual cows in the Chico State Organic Dairy Farm. Each cow was fitted with an RFID ear tag, enabling real-time monitoring of their health, milk production, and feeding habits. The system allowed the farm to automate data collection, optimize feeding schedules, and improve overall herd management.
HarvestCo, a crop harvesting and processing company, implemented UFH RFID technology to improve their supply chain management. UFH RFID tags were applied to bins of harvested crops, enabling automated tracking and inventory management. This allowed HarvestCo to optimize logistics, reduce manual errors, and enhance traceability throughout the supply chain.
G Farms, a large-scale vegetable producer, implemented UFH RFID technology to improve their inventory management and traceability. UFH RFID tags were attached to crates of produce, enabling real-time tracking and monitoring of the movement and location of each crate. This allowed the farm to streamline their inventory processes, reduce losses, and ensure accurate traceability for quality control and compliance purposes.
Many applications of RFID by GAO can be found here:
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Crop Production
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including crop production.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
As well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including crop production.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including crop production:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including crop production:
And an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including crop production:
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including crop production:
And antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
Digital I/O adapters:
And relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
- Find Your 860-960 MHz RFID Module
- Find Your 13.56 MHz High Frequency RFID Module
- Find Your 125 kHz RFID Reader Modules
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in crop production:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include:
- Tractors: Tractors are used to plough, plant, cultivate, and harvest crops, with different sizes and power capacities.
- Harvesters: Harvesters are used to efficiently harvest crops such as grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Planters and Seeders: Equipment used for precise planting of seeds or seedlings. They ensure proper seed spacing and depth, contributing to optimal crop growth and yield.
- Sprayers: Sprayers are used to apply fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, and other crop protection products.
- Irrigation Systems: Irrigation equipment is essential for providing water to crops in insufficient rainfall.
- Precision Agriculture Tools: Advanced technologies are used to optimize crop production, such as GPS, yield monitors, and variable rate application systems.
- Greenhouse Equipment: Controlled environment agriculture uses climate control, hydroponic systems and lighting to grow crops.
- Grain Dryers: Used to remove excess moisture from harvested grains to prevent spoilage and maintain quality.
- Silos and Grain Storage Systems: Designed for safe storage of harvested grains, protecting them from moisture, pests, and spoilage.
- Livestock Handling Equipment: Equipment is used to manage livestock effectively for crop-livestock integration.
- Mulchers and Chippers: Used to clear vegetation, control weeds, and manage crop residues. Mulchers and chippers help maintain clean fields and improve soil health.
- Soil Testing Equipment: Instruments used to assess soil fertility, nutrient levels, pH, and other important parameters. Soil testing equipment helps farmers make informed decisions regarding fertilization and soil management.
- Crop Storage and Packaging Equipment: Equipment such as conveyors, sorters, and packaging machinery used for efficient post-harvest handling, storage, and packaging of crops.
- Crop Monitoring Systems: Technologies like drones, sensors, and remote sensing equipment used for monitoring crop health, growth, and pest/disease detection.
- Animal Feed Equipment: Machinery used for processing and mixing animal feed, including feed mills, grinders, and mixers.
- Hay and Forage Equipment: Equipment used for harvesting, baling, and storing hay and forage crops, including mowers, balers, and hay rakes.
- Agricultural Robotics: Advanced robotic systems designed for various tasks, such as autonomous weeding, precision spraying, and selective harvesting.
- Farm Management Software: Software applications help streamline farm operations and improve decision-making.
People or workers tracking system:
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
GAO Has Served Crop Production Extensively
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in crop production industry to achieve success imprecision agriculture, sustainable farming, digital farming, vertical farming, crop health monitoring, robotics and automation, blockchain in agriculture, farm management software, climate-smart agriculture, climate-smart agriculture, regenerative agriculture, food traceability.
GAO RFID Inc. has served many customers in crop production, including its various divisions such as:
- Field Crops: This division includes the cultivation of crops like grains (wheat, corn, rice, barley), oilseeds (soybeans, canola, sunflower), fiber crops (cotton, flax), and forage crops (alfalfa, clover) grown in open fields on a large scale.
- Horticulture: This division encompasses the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, herbs, and ornamental plants. It includes practices like greenhouse production, nursery operations, fruit orchards, vegetable farms and floriculture.
- Livestock Feed Crops: Animal feed crops are essential for livestock and poultry industry.
- Specialty Crops: Niche crops are crops with unique characteristics or grown in specific regions for specific markets.
- Organic Crop Production: Organic farming practices are becoming increasingly popular due to demand for organic products.
- Agroforestry: Tree crops are integrated into farming systems to provide benefits such as soil conservation, shade, and timber.
- Hydroponics and Vertical Farming: Hydroponics, aeroponics, and vertical farming use nutrient-rich water and artificial lighting to grow crops in controlled environments.
- Seed Production: The division of agricultural seeds involves breeding, testing, hybridization, and seed conditioning to provide high-quality seeds.
- Integrated Crop Management: IPM, crop rotation, soil conservation, and sustainable farming techniques are used to optimize crop productivity while minimizing environmental impact.
Here are some of the leading companies in crop production industry:

Cargill incorporated

Archer Daniels Midland

John Deere

Bayer Crop Science

Syngenta AG0

Monsanto Company

ADM Crop Risk Services

DuPont Pioneer

Nutrien Limited

Agrium incorporated

BASF Corporation

Corteva Agriscience

FMC Corporation

Dow AgroSciences

Valent U.S.A. Corporation

Simplot Company

Wilbur-Ellis Company

Mosaic Company

La Coop fédérée

CANTERRA SEEDS

Parrish &Heimbecker, Limited

AGT Food and Ingredients incorporated

NutrienLimited

Richardson International
