Related Products & Systems on Other Pages on This Website
People Tracking System for Manufacturing Facilities
Employee & Attendance Access Control System
Return & Pallet Asset Tracking – GAO RFID
Work In Process WIP Asset Tracking System
BLE | Bluetooth Low Energy | BLE Gateways & Beacons – GAO RFID
RFID Readers | Buy RFID Readers | RFID Reader Writers – GAO RFID
RFID Tags | Buy RFID Tags – GAO RFID
People Tracking RFID Tags and Wristbands
Overview
The Communications Equipment Manufacturing Industry is responsible for designing, producing, and distributing a wide range of devices and equipment used for communication purposes. This industry encompasses the manufacturing of various products, including telecommunication hardware, networking equipment, mobile devices, and other communication devices.
Companies in this industry are involved in the development and production of communication infrastructure, such as routers, switches, modems, antennas, and satellite systems. They also manufacture consumer electronics like smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices that enable wireless communication.
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in the Sub-Industry Industry to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials and operational equipment such as printed circuit board (pcb) manufacturing equipment, surface mount technology (smt) equipment, test and measurement equipment, assembly line equipment, cnc machines, wire bonding machines, environmental test chambers, antenna testing equipment, cleanrooms, software and design tools, and material handling equipment.
Ranked as one of the top 10 global RFID suppliers, GAO RFID Inc. is based in New York City, U.S. and Toronto, Canada. GAO offers a comprehensive selection of UHF, HF (including NFC) and LF RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags, BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. Such RFID and BLE products and systems, as well as its IoT and drone technologies, have been successfully deployed for Communications Equipment Manufacturing.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Communications Equipment Manufacturing
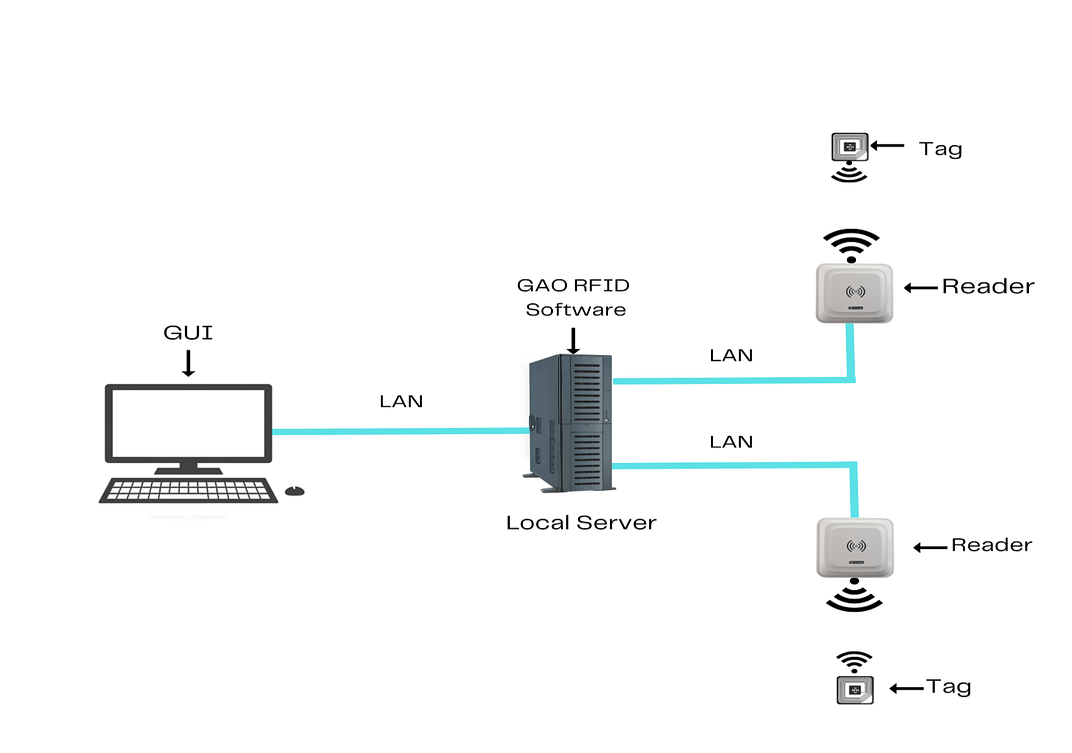 To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for the communications equipment manufacturing industry are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server, and another version is that its software runs in the cloud. The above illustrates GAO system for the communications equipment manufacturing industry with its software running on a local server.
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for the communications equipment manufacturing industry are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server, and another version is that its software runs in the cloud. The above illustrates GAO system for the communications equipment manufacturing industry with its software running on a local server.
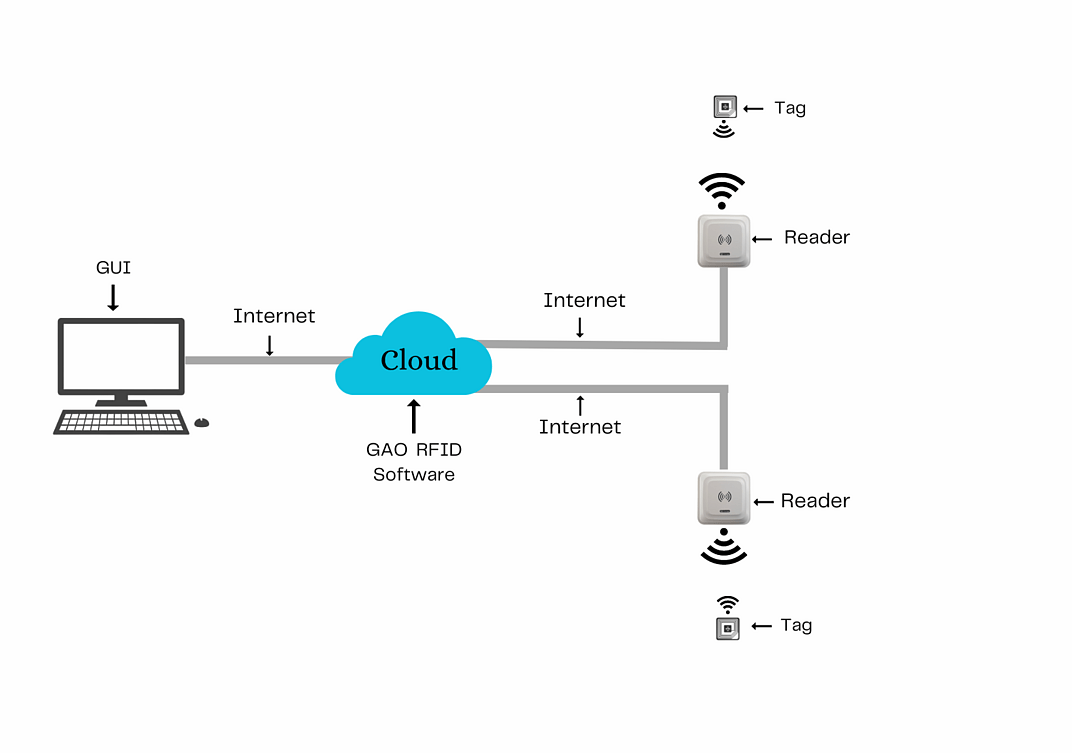 The above illustrates GAO system for the communications equipment manufacturing industry with its software running in cloud.
The above illustrates GAO system for the communications equipment manufacturing industry with its software running in cloud.
GAO’s RFID technologies bring the many benefits to the communications equipment manufacturing industry:
- Improved Inventory Management: GAO’s RFID tags can be attached to communication equipment, enabling real-time tracking and monitoring of inventory. This helps in accurately identifying and locating items, reducing inventory errors, and improving overall supply chain efficiency.
- Enhanced Traceability: GAO’s RFID technology enables detailed tracking of communication equipment throughout the manufacturing process and distribution chain. This improves traceability, making it easier to identify and address any issues or defects, leading to better quality control.
- Theft Prevention and Security: Our RFID tags can be used to deter theft and unauthorized access to communication equipment. If an item is moved without proper authorization, the RFID system can trigger alerts, enabling quick response and prevention of potential losses.
- Improved Customer Service: GAO’s RFID-enabled systems allow for accurate and timely order fulfillment, reducing order errors and ensuring on-time delivery. This improves customer satisfaction and strengthens relationships with customers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Our RFID technology can help ensure compliance with regulatory requirements by providing accurate records and documentation of equipment movements, inspections, and certifications.
GAO’s BLE technologies offer longer reading range and particularly attractive for applications with larger work spaces within the communications equipment manufacturing industry:
- Device Connectivity and Interoperability: Our BLE allows for easy and seamless connectivity between communication equipment and other BLE-enabled devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and computers. This promotes interoperability and enables efficient data transfer and communication.
- Efficient Asset Tracking: GAO’s BLE beacons can be installed on communication equipment, enabling precise and real-time asset tracking within manufacturing facilities. This improves inventory management, reduces loss or misplacement of assets, and streamlines asset retrieval.
- Location-Based Services: Our BLE technology enables the implementation of location-based services within manufacturing facilities. This can include features like indoor navigation, asset locating, and proximity-based notifications, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
- Improved User Experience: Our BLE technology allows for seamless and effortless pairing of communication equipment with user devices, reducing setup time and complexity. This enhances the overall user experience and promotes customer satisfaction.
- Future-Proofing: GAO’s BLE technology is widely adopted and supported by various device manufacturers and platforms. Implementing Our BLE in communication equipment ensures compatibility with current and future devices, providing long-term viability and flexibility.
GAO’s RFID and drone technologies are often combined and such solutions offer the following benefits to the communications equipment manufacturing industry:
- Rapid Asset Search and Retrieval: Drones equipped with GAO’s RFID readers can efficiently search for and locate communication equipment in large manufacturing facilities or warehouses. This reduces the time and effort required to manually search for specific items, ensuring quick retrieval and improving operational efficiency.
- Improved Warehouse and Storage Management: Drones integrated with our RFID technology can assist in optimizing warehouse layout and storage management. They can scan RFID tags on communication equipment to identify available storage space, monitor inventory levels, and suggest optimal placement for equipment. This helps in maximizing storage capacity and minimizing errors in inventory placement.
- Improved Safety and Accessibility: Drones integrated with our RFID technology can access hard-to-reach or hazardous areas within manufacturing facilities, enabling inspections and inventory checks in challenging environments. This improves worker safety by reducing the need for manual inspection in potentially risky locations.
- Real-time Data Capture and Analytics: GAO’s RFID-enabled drones can collect real-time data on communication equipment, such as location, condition, and usage patterns. This data can be integrated with analytics platforms to gain insights into equipment performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions for process optimization and product improvements.
- Time and Cost Savings: The combination of GAO’s RFID and drones can significantly reduce manual labor and time required for inventory management, asset tracking, and inspections. This leads to cost savings by improving operational efficiency, reducing errors, and optimizing resource allocation.
Here are the benefits of GAO’s IoT technologies to the communications equipment manufacturing industry:
- Enhanced Quality Control: IoT enables continuous monitoring and analysis of production data, facilitating real-time quality control. Connected sensors and devices can detect anomalies or deviations in manufacturing processes, allowing for immediate corrective actions and ensuring consistent product quality.
- Supply Chain Optimization: IoT enables end-to-end visibility and traceability across the supply chain. Manufacturers can track the movement of communication equipment, monitor inventory levels, optimize logistics, and respond quickly to changes in demand, improving supply chain efficiency and reducing costs.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: IoT enables remote monitoring and control of manufacturing processes and equipment. Manufacturers can access real-time data, perform remote diagnostics, and make adjustments or interventions as needed, reducing the need for physical presence and improving operational agility.
- Customization and Personalization: IoT enables customization and personalization of communication equipment. Connected devices can gather data on customer preferences and usage patterns, allowing for tailored products and services that meet individual needs and preferences.
- Data Analytics and Insights: IoT-generated data provides valuable insights for manufacturers. Advanced analytics can uncover patterns, trends, and customer behavior, helping in decision-making, product development, and identifying new business opportunities.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of the Communications Equipment Manufacturing
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in the communications equipment manufacturing industry to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates, and government regulations:
RFID, BLE, IoT, & Drone Standards & Mandates
- ASTM F38: ASTM F38 is a standard established by ASTM International that covers the design, construction, and testing of unmanned aircraft systems (UAS), including drones. It provides guidelines for various aspects, such as airworthiness, flight operations, and safety considerations.
- ISO 21384 (Part 3 and Part 4): ISO 21384 is an international standard that specifies the general requirements for unmanned aircraft systems and their applications. Part 3 focuses on operational procedures and requirements, while Part 4 covers the specifications for unmanned aircraft systems used for specific applications.
- ISO/IEC 30141: This international standard provides a framework for IoT systems, addressing aspects such as interoperability, security, and privacy considerations.
- Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Regulations: In the United States, the FAA regulates drone operations under Part 107, which covers requirements for drone pilots, airspace restrictions, and operational safety guidelines.
- International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO): The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) provides guidelines and recommendations for the operation of unmanned aircraft systems. These guidelines aim to ensure safety, security, and the integration of drones into global airspace.
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI): This standard, developed by Underwriters Laboratories (UL), focuses on the safety of batteries used in drones. It provides requirements for battery performance, reliability, and safety features to mitigate the risk of fire, explosion, or other hazards.
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) SP 800-183: Published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), this document provides cybersecurity guidance for IoT devices, systems, and applications.
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)11 Wi-Fi Standards: These standards define the protocols for wireless local area network (WLAN) technology, which can be utilized in drones for communication and control purposes.
- OPC UA (Unified Architecture): OPC UA is a machine-to-machine communication protocol for industrial automation. It provides a secure and reliable means of exchanging data between devices and systems, enabling interoperability and integration in the context of industrial IoT applications.
U.S. government regulations
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC): The FCC is the primary regulatory body governing the communications industry in the United States. They enforce regulations related to equipment authorization, radiofrequency emissions, spectrum allocation, and telecommunications services.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): OSHA sets occupational health and safety standards that apply to manufacturing facilities, ensuring a safe working environment for employees in the communications equipment manufacturing industry.
- The U.S. Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS): The administers export control regulations, including the Export Administration Regulations (EAR). These regulations control the export, re-export, and transfer of certain communications equipment and technologies for national security, foreign policy, and non-proliferation reasons.
Canadian government regulations
- Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED): ISED is responsible for regulating and overseeing the communications industry in Canada. They enforce regulations and standards related to telecommunications, radio frequency spectrum, and equipment certification.
- Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC): The CRTC is an independent regulatory agency that governs and regulates broadcasting and telecommunications in Canada. They establish rules related to licensing, content, competition, and consumer protection in the communications industry.
GAO’s Software Provides API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in the communications equipment manufacturing industry such as:
- Personnel Management: Personnel management encompasses workforce planning, employee recruitment and selection, training and development, performance management, and employee relations It involves strategic planning for staffing, talent acquisition, and succession planning. Additionally, it focuses on training programs, performance evaluations, and maintaining positive employee relations for a productive work environment.
- Equipment Management: Equipment management involves maintaining a comprehensive equipment inventory, implementing preventive maintenance schedules, and monitoring equipment calibration for accuracy and performance. It also includes managing equipment repairs, warranty claims, and identifying opportunities for replacement of obsolete or damaged equipment. Additionally, equipment tracking and utilization are monitored to optimize resource allocation and identify efficiencies in equipment usage.
- Access Control: Access control includes physical access control measures, network and data security protocols, user access management, visitor management procedures, and data privacy and confidentiality policies. This involves implementing surveillance systems, access cards, and biometric authentication for physical access control, as well as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and user authentication for network security. Additionally, procedures are established to manage visitor access and protect sensitive customer and business information from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Warehouse Management: Warehouse management involves order fulfillment, including picking, packing, and shipping processes, as well as receiving and inspecting incoming shipments to maintain accurate inventory records. It also includes optimizing warehouse layout and organization for efficient space utilization and implementing automation technologies like robotics and barcode scanners for improved operational efficiency. Additionally, managing return and reverse logistics processes for product returns and warranty claims is essential in maintaining effective warehouse operations.
- Supply Chain Management: Supply chain management involves demand planning and forecasting to optimize production and inventory levels based on historical data and market trends. It includes managing supplier relationships, from selection to performance monitoring, to ensure timely and high-quality deliveries. The procurement and purchasing process, logistics and transportation management, and quality control and assurance are crucial components to efficiently move goods from suppliers to manufacturing facilities and deliver products to customers while maintaining quality standards.
- Other Applications: In addition to the aforementioned areas include Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) for managing the entire lifecycle of products, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) for enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty through effective sales and support processes. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) integrates various business functions for streamlined operations, while Business Intelligence and Analytics provide insights for informed decision-making. Compliance and Regulatory Management ensures adherence to industry regulations, certifications, and quality standards. These applications contribute to efficient and customer-centric operations within the industry.
GAO has integrated its RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems with some of leading software and cloud services in the communications equipment manufacturing industry. Below are some of popular software and cloud services in the communications equipment manufacturing industry:
- Oracle Enterprise Resource Planning Cloud: Oracle ERP Cloud is a comprehensive enterprise resource planning (ERP) software that helps manage various aspects of business operations, including finance, procurement, inventory, and supply chain management.
- SAP (Systems, Application and Products) S/4HANA: SAP S/4HANA is an intelligent, integrated ERP software that enables efficient management of personnel, equipment, finance, logistics, and manufacturing processes for the communications equipment manufacturing industry.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a cloud-based business management solution that offers modules for personnel management, equipment tracking, finance, sales, and customer relationship management (CRM).
- IBM (International Business Machines) Maximo: IBM Maximo is an enterprise asset management (EAM) software that helps in equipment management, maintenance planning, and asset optimization, enabling efficient operations and minimizing downtime.
- JDA (James Donald Armstrong) Warehouse Management: JDA Warehouse Management is a comprehensive software solution for warehouse management, providing real-time visibility, optimization, and control over inventory, order fulfillment, and logistics operations.
- Blue Yonder: Blue Yonder (formerly JDA Software) is a supply chain management software that combines artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to optimize inventory, demand planning, and logistics processes.
- Honeywell Intelligrated: Honeywell Intelligrated offers warehouse automation and control systems, including software solutions for material handling, order fulfillment, and warehouse optimization.
- Epicor ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning): Epicor ERP is a robust software suite that covers personnel management, equipment tracking, supply chain management, and manufacturing operations for the communications equipment manufacturing industry.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: Salesforce Sales Cloud is a customer relationship management (CRM) software that helps manage sales processes, customer interactions, and lead tracking for communications equipment manufacturers.
- Plex Systems: Plex Systems provides a cloud-based manufacturing execution system (MES) software that covers production control, quality management, supply chain management, and traceability for communications equipment manufacturers.
- Infor CloudSuite Industrial: Infor CloudSuite Industrial (formerly SyteLine) is an industry-specific ERP software designed for manufacturers, offering features for personnel management, equipment tracking, supply chain management, and more.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides a comprehensive suite of cloud services, including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS) offerings, suitable for various applications in the communications equipment manufacturing industry.
GAO has worked with some of the leading technology companies in the communications equipment manufacturing industry to provide integrated RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone solutions to customers. Here are some of the technology leaders in the communications equipment manufacturing industry:
- Cisco Systems: Cisco Systems is a multinational technology company that provides networking hardware, software, and services for communication and information technology infrastructure.
- Huawei Technologies: Huawei Technologies is a global provider of telecommunications equipment and services, including networking products, smartphones, and cloud solutions.
- Nokia Corporation: Nokia Corporation is a telecommunications and information technology company that offers a wide range of products and services, including network infrastructure, software, and licensing.
- Ericsson: Ericsson is a multinational networking and telecommunications company that provides equipment and services for mobile and fixed networks.
- Qualcomm Incorporated: Qualcomm Incorporated is a global leader in wireless technology and semiconductor solutions, providing chips, processors, and wireless communication technologies for various communication equipment.
- Intel Corporation: Intel Corporation is a multinational technology company that designs and manufactures semiconductor chips, including processors and networking solutions, used in communications equipment.
- Broadcom Incorporated: Broadcom Inc. is a leading semiconductor company that specializes in designing and manufacturing a wide range of communication chips and components used in networking and wireless equipment.
- Texas Instruments Incorporated: Texas Instruments Incorporated is a semiconductor company that produces a diverse range of integrated circuits, including analog and digital signal processors used in communications equipment.
- Nokia Networks (formerly Alcatel-Lucent): Nokia Networks, previously Alcatel-Lucent, provides networking and communication solutions, including network infrastructure, software, and services for telecommunications companies.
- Juniper Networks: Juniper Networks is a leading provider of networking solutions, including routers, switches, security products, and software-defined networking (SDN) solutions.
- Analog Devices Incorporated: Analog Devices, Inc. is a multinational semiconductor company specializing in high-performance analog, mixed-signal, and digital signal processing integrated circuits used in communication systems.
- ZTE (Zhongxing Telecommunication Equipment) Corporation: ZTE Corporation is a global telecommunications equipment and systems company that offers a range of products for communication networks, including wireless, broadband, and optical transmission solutions.
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Below are some RFID application cases in the communications equipment manufacturing industry:
- Work-in-Progress (WIP) Tracking: RFID technology enables real-time tracking and monitoring of work-in-progress units during the manufacturing process. By attaching RFID tags to individual components or sub-assemblies, manufacturers can capture data on production stages, identify bottlenecks, and optimize workflow. This facilitates efficient production planning and resource allocation.
- Quality Control and Product Authentication: RFID can play a role in ensuring product quality and authenticity. By incorporating RFID tags into communications equipment, manufacturers can track and monitor key quality control checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. RFID can also be used to authenticate products, ensuring they are genuine and not counterfeit.
- Maintenance and Service Records: RFID technology can be utilized to track maintenance and service records of communications equipment. By associating RFID tags with specific devices, manufacturers can store and retrieve maintenance information, repair history, firmware updates, and performance data. This facilitates proactive maintenance, improves customer support, and aids in warranty management.
- Inventory and Supply Chain Management: UFH RFID can be used to track and manage inventory throughout the manufacturing and supply chain process. By attaching RFID tags to components, equipment, and products, manufacturers can automatically track and monitor their movement, ensuring accurate inventory counts, reducing manual errors, and improving overall supply chain efficiency.
- Equipment Tracking and Maintenance: Communications equipment manufacturers can utilize UFH RFID to track and manage their valuable assets, such as routers, switches, and other network devices. RFID tags can be attached to each equipment item, enabling real-time monitoring of their location and maintenance status. This helps in streamlining equipment audits, preventing loss or theft, and optimizing maintenance schedules.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for the Communications Equipment Manufacturing
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including the communications equipment manufacturing industry:
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including the communications equipment manufacturing industry;
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including the communications equipment manufacturing industry:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including the communications equipment manufacturing industry:
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including the communications equipment manufacturing industry:
- High Frequency 13.56 MHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 134 kHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 125 kHz Passive RFID Readers
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including the communications equipment manufacturing industry:
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
Digital I/O adapters:
and relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
- UHF 860 – 960 MHz RFID Modules
- 13.56 MHz High Frequency RFID Modules
- 125 kHz Low Frequency RFID Modules
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in the communications equipment manufacturing industry:
People or workers tracking system:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include:
Communication Protocols Analyzers
- SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor: A network monitoring tool that includes protocol analysis features for assessing the performance and behavior of communication protocols.
- Colasoft Capsa: A network analyzer with protocol decoding capabilities, enabling in-depth analysis of communication protocols.
- Wi-Fi Analyzer: A tool specifically designed for analyzing and troubleshooting wireless communication protocols in Wi-Fi networks.
- EtherApe: A graphical network monitor and protocol analyzer that displays network traffic in real-time, allowing analysis of communication protocols.
- Snort: An open-source intrusion detection and prevention system that can also function as a protocol analyzer, detecting and analyzing network traffic based on predefined rulesets.
Network Simulation and Emulation Systems
- Traffic Generators: Generate network traffic patterns and simulate various protocols to assess the performance and scalability of communication equipment.
- Protocol Analyzers: Capture, analyze, and decode network traffic to identify issues, monitor protocol compliance, and optimize communication equipment.
- Network Performance Monitoring Tools: Continuously monitor and measure the performance metrics of communication equipment, providing real-time insights and diagnostics.
- Traffic Shaping Tools: Control and shape network traffic patterns to simulate different network conditions and assess the impact on communication equipment.
- Network Simulators for IoT: Specialized simulators that emulate IoT networks, allowing the evaluation of communication equipment’s compatibility and performance in IoT environments.
Quality Control and Inspection Systems
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) Systems: Utilizes cameras and image recognition algorithms to inspect electronic components, PCBs, and assembled products for defects.
- X-ray Inspection Systems: Performs non-destructive testing to inspect internal structures and solder joints in communication equipment.
- In-Circuit Test (ICT) Systems: Conducts electrical tests on PCBs to check for shorts, opens, and other electrical parameters.
- Environmental Chambers: Simulates various environmental conditions to test the reliability and durability of communication equipment.
- Radio Frequency Testing Equipment: Measures and analyzes the performance of wireless communication devices and systems.
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
GAO Has Served the Communications Equipment Manufacturing Extensively
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in communications equipment manufacturing industry to achieve success in 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), edge computing, Artificial Intelligence (AI), digital transformation, industry 4.0, cybersecurity, cloud computing, virtualization, machine learning, sustainable manufacturing, agile manufacturing.
GAO RFID Inc. has deployed RFID, BLE and IoT projects for many companies in the communications equipment manufacturing industry, including many in its various divisions such as:
- Network Equipment Manufacturers: These companies specialize in designing, manufacturing, and providing network infrastructure equipment such as routers, switches, modems, and wireless access points.
- Telecommunications Equipment Manufacturers: This division focuses on producing equipment and devices used in telecommunication networks, including telephone systems, mobile devices, base stations, and satellite communication equipment.
- Broadcast Equipment Manufacturers: These companies specialize in developing and manufacturing equipment used in broadcast and media industries, such as television and radio broadcasting equipment, studio equipment, transmitters, and antennas.
- Optical Communication Equipment Manufacturers: This division focuses on producing optical networking equipment, fiber optic cables, transceivers, amplifiers, and other components used in high-speed data transmission and telecommunications.
- Wireless Communication Equipment Manufacturers: This segment specializes in designing and manufacturing equipment for wireless communication technologies, including mobile phones, wireless routers, access points, and wireless communication modules.
- Test and Measurement Equipment Manufacturers: These companies develop and manufacture specialized equipment used for testing, monitoring, and measuring various aspects of communications equipment, such as signal strength, quality, performance, and compliance with industry standards.
- Voice and Data Communication Equipment Manufacturers: This division focuses on producing equipment for voice and data communication systems, including PBX (Private Branch Exchange) systems, VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) equipment, video conferencing systems, and unified communication solutions.
- Satellite Communication Equipment Manufacturers: These companies specialize in manufacturing equipment used for satellite communication, including satellite dishes, transceivers, ground stations, and satellite-based communication systems.
- Component and Semiconductor Manufacturers: This division produces electronic components, semiconductors, integrated circuits (ICs), and other specialized components used in various communication equipment and devices.
Some of the leading companies in the communications equipment manufacturing industry: