
Index
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Foundries
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Foundries
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
Case Studies of RFID Applications
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Foundries
Related Products & Systems on Other Pages on This Website
Related Products & Systems on Other Pages on This Website
Tool & Industrial Equipment Tracking System
WIP RFID Tracking System | RFID WIP Software – GAO (gaorfid.com)
Employee Access Control | Office Access Control (gaorfid.com)
BLE | Bluetooth Low Energy | BLE Gateways & Beacons – GAO RFID
RFID Readers | Buy RFID Readers | RFID Reader Writers – GAO RFID
RFID Tags | Buy RFID Tags – GAO RFID
Rugged RFID Tags | GAO RFID Inc.
On Metal RFID Tags – All Types
High Temperature RFID Tags – GAO RFID
Hazardous Environment RFID Tags | ATEX RFID Tags (gaorfid.com)
Overview
The foundries industry represents a dynamic and innovative sector at the intersection of healthcare and advanced manufacturing. In medical robotics, cutting-edge technologies are employed to create robotic systems that assist in surgeries, diagnostics, and rehabilitation, enhancing precision and minimizing invasiveness. Meanwhile, foundries within this industry are responsible for producing specialized components and materials crucial for medical device manufacturing, including implants and prosthetics. Together, these sectors play a pivotal role in advancing medical care, improving patient outcomes, and driving technological advancements in the healthcare field.
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in foundries Industry to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials and operational equipment such as the key equipment categories include furnaces for melting metals, molding equipment for creating molds, core making equipment, casting equipment like ladles and shakeout machines, melting equipment accessories such as crucibles, cleaning and finishing equipment including grinding machines, material handling equipment like overhead cranes, dust collection and ventilation systems, environmental control equipment for emissions management, quality control equipment like NDT tools, safety equipment, laboratory equipment for testing, foundry tools and accessories, automation and robotics for tasks like pouring, waste management equipment, energy management systems, and computerized systems for process control and management.
Ranked as one of the top 10 global RFID suppliers, GAO RFID Inc. is based in New York City, U.S. and Toronto, Canada. GAO offers a comprehensive selection of UHF, HF (including NFC) and LF RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags, BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. RFID and BLE products and systems, as well as its IoT and drone technologies, have been successfully deployed for foundries. Its sister company, GAO Tek Inc. https://gaotek.com, is a leading supplier of industrial or commercial testers and analyzers, drones, and network products.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Foundries
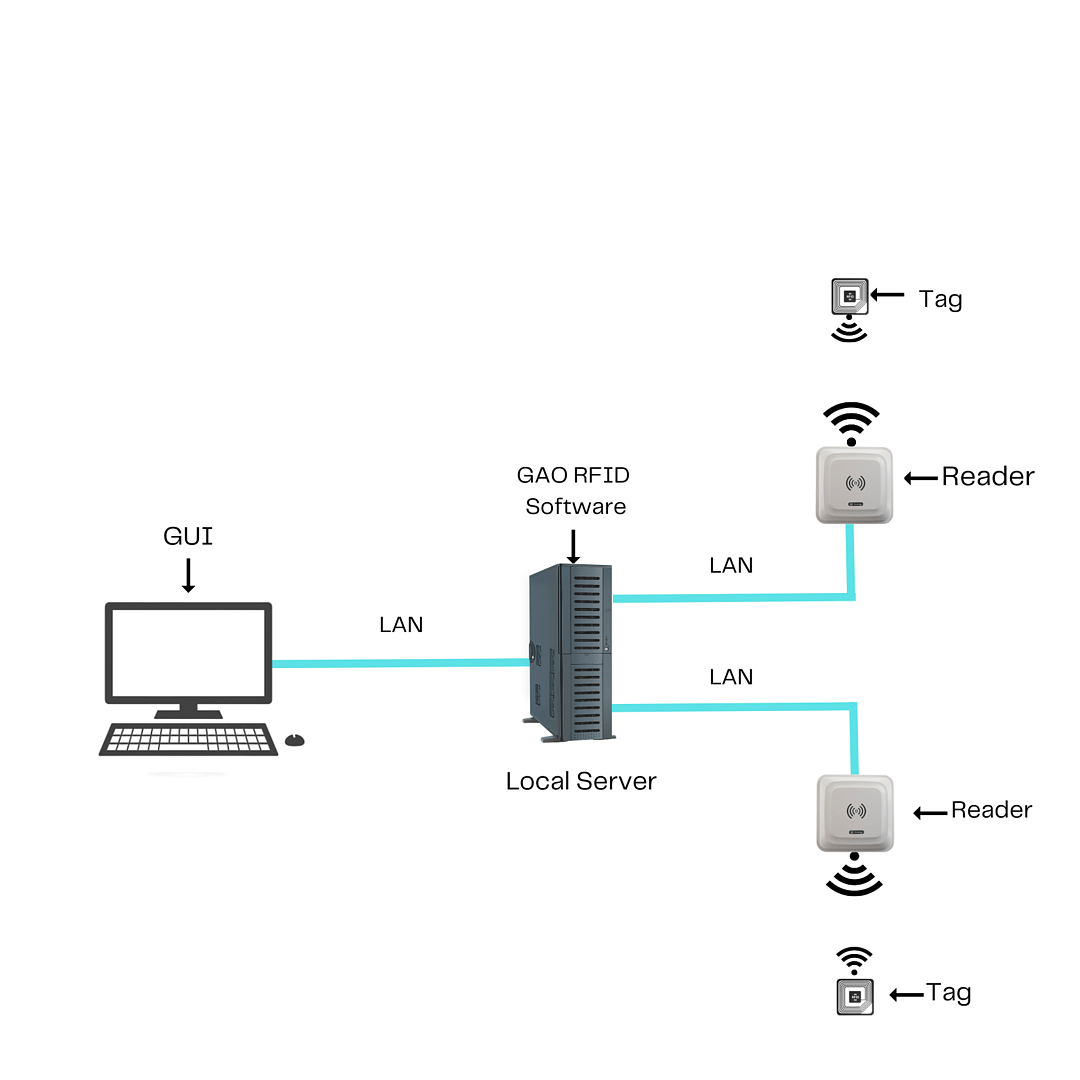 To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for foundries are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server that normally is on our client’s premises, and another version runs in the cloud. The cloud server could be GAO’s cloud server, client’s own cloud server or a cloud server from one of the leading cloud server providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud (formerly SoftLayer), Oracle Cloud, RedHat, Heroku, Digital Ocean, CloudFlare, Linode and Rackspace. The above illustrates GAO system for foundries with its software running on a local server.
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for foundries are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server that normally is on our client’s premises, and another version runs in the cloud. The cloud server could be GAO’s cloud server, client’s own cloud server or a cloud server from one of the leading cloud server providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud (formerly SoftLayer), Oracle Cloud, RedHat, Heroku, Digital Ocean, CloudFlare, Linode and Rackspace. The above illustrates GAO system for foundries with its software running on a local server.
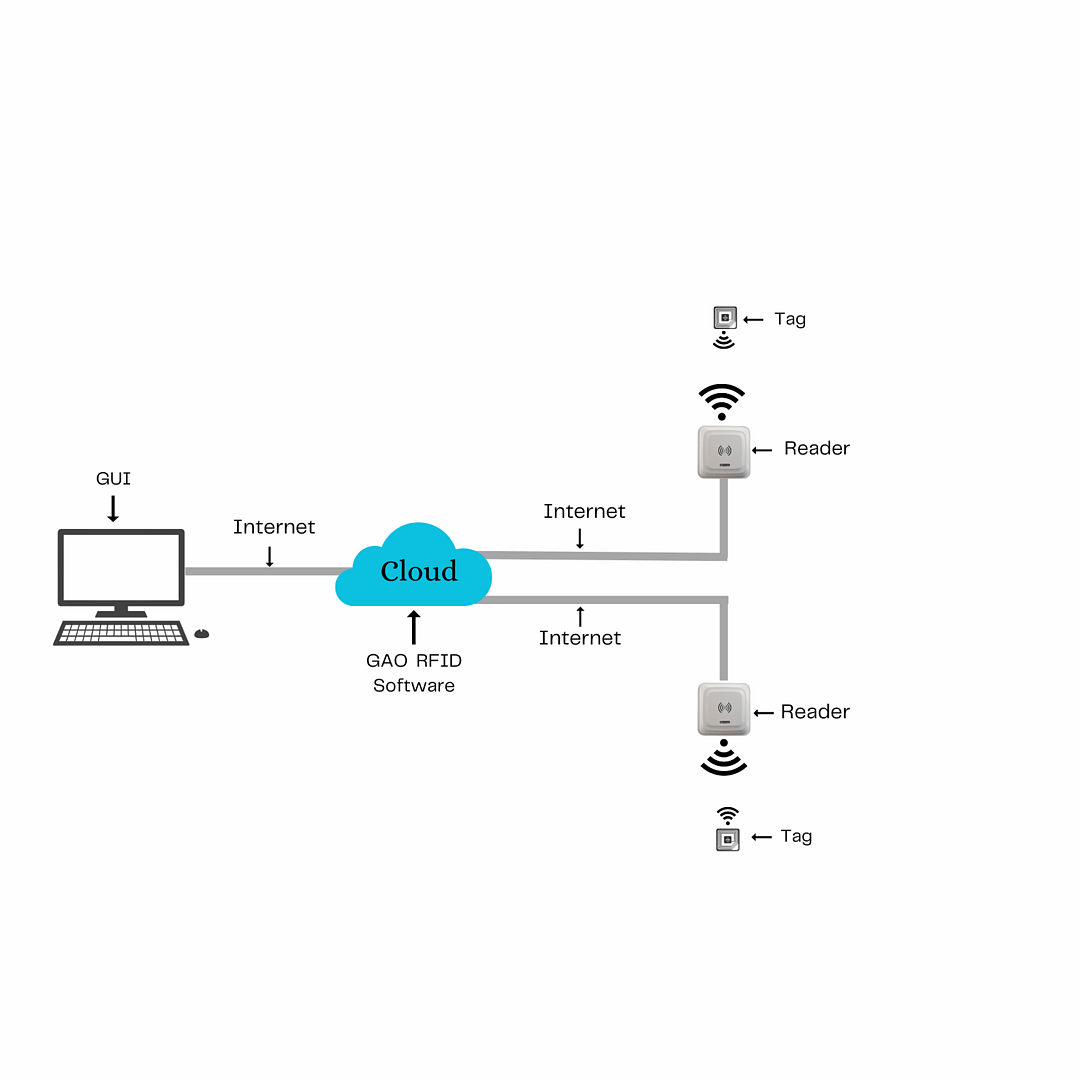 The above illustrates GAO system for foundries industry with its software running in cloud.
The above illustrates GAO system for foundries industry with its software running in cloud.
GAO’s RFID and BLE technologies, consisting of RFID readers, RFID tags, BLE gateways, BLE beacons, software, cloud services and their systems, have the following applications in foundries industry:
- Inventory Tracking: GAO’s RFID tags can be attached to raw materials, castings, and finished products to monitor their movement throughout the foundry. This helps maintain accurate inventory levels and reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
- Tool and Equipment Management: GAO’s RFID tags can be affixed to tools and equipment, allowing for real-time tracking of their location and usage. This minimizes the risk of loss or theft and ensures that the right tools are available when needed.
- Work-in-Progress (WIP) Tracking: GAO’s RFID technology can be used to monitor the progress of casting production. By attaching RFID tags to molds and castings, foundries can track each casting’s status, from pouring to finishing, facilitating better production planning and quality control.
- Asset Tracking: GAO’s Foundries often have a wide range of assets, such as molds, ladles, and crucibles. RFID tags enable efficient tracking and management of these assets, reducing the risk of misplacement or loss.
- Quality Control: GAO’s RFID can be employed to link product information and quality control data to individual castings. This allows for easy traceability and retrieval of quality records during inspections and audits.
- Maintenance Management: GAO’s RFID can be used to schedule and track maintenance activities on machinery and equipment. Maintenance history, service schedules, and equipment specifications can all be linked to RFID tags for quick reference.
- Access Control and Security: GAO’s RFID-based access control systems can enhance security by restricting unauthorized personnel from entering sensitive areas within the foundry.
- Workforce Management: GAO’s RFID badges or cards can be used to monitor employee attendance and time tracking, ensuring accurate records for payroll and shift management.
- Environmental and Safety Compliance: GAO’s RFID can help monitor and control environmental conditions within the foundry, ensuring compliance with safety regulations and minimizing health risks for workers.
- Real-time Process Monitoring: GAO’s RFID sensors can be employed to collect real-time data on various parameters like temperature, pressure, and humidity, allowing for better process control and optimization.
- Supply Chain Integration: GAO’s RFID enables seamless integration with suppliers and customers, allowing for efficient tracking of raw materials and finished products as they move in and out of the foundry.
- Batch Tracking: GAO’s Foundries can use RFID technology to track batches of castings, making it easier to trace the source of any defects or quality issues.
- Energy Management: GAO’s RFID systems can be used to monitor energy consumption within the foundry, helping to identify areas for energy savings and sustainability improvements.
GAO’s drone technologies find the following applications in the foundries industry:
- Site Inspection and Monitoring: GAO’s Drones can be used for routine inspections of the entire foundry site, including buildings, equipment, and infrastructure. This helps identify maintenance needs, safety hazards, or structural issues.
- Inventory Management: GAO’s Drones equipped with cameras and sensors can provide real-time inventory counts of raw materials, finished products, and equipment, helping optimize inventory levels and prevent shortages.
- Safety Inspections: GAO’s Drones can access high-risk or difficult-to-reach areas to perform safety inspections, identifying potential hazards such as leaks, cracks, or structural weaknesses.
- Environmental Compliance: GAO’s Drones equipped with environmental sensors can monitor emissions, air quality, and water quality to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Heat and Temperature Monitoring: In foundries, where extreme temperatures are common, GAO’s drones can be equipped with thermal imaging cameras to monitor temperature variations in equipment and processes, helping to detect overheating or equipment malfunctions.
- Mapping and Surveying: GAO’s Drones can create high-resolution maps and 3D models of the foundry site, aiding in layout planning, expansion, and optimizing workflow.
- Quality Control: GAO’s Drones can capture detailed images and videos of castings and molds to identify defects, imperfections, or dimensional variations, facilitating quality control inspections.
- Emergency Response: In the event of accidents or fires, drones can provide real-time aerial views to assist emergency responders in assessing the situation and planning rescue efforts.
- Maintenance and Repairs: GAO’s Drones equipped with tools like robotic arms or spray nozzles can perform routine maintenance tasks or apply coatings to equipment, reducing downtime and the need for manual labor in hazardous environments.
- Security Surveillance: GAO’s Drones can be used for security purposes by patrolling the perimeter of the foundry, monitoring for unauthorized access, and providing surveillance footage.
- Training and Simulations: GAO’s Drones can simulate complex foundry operations and help train personnel in a safe and controlled environment.
- Material Handling: GAO’s Drones equipped with lifting mechanisms can transport small materials or tools within the foundry, reducing the need for manual labor in material handling.
- Data Collection and Analysis: GAO’s Drones can collect a wide range of data, such as images, videos, and sensor readings, which can be analyzed to improve operational efficiency and decision-making.
- Aerial Advertising: Some foundries use drones for marketing and promotional purposes by capturing aerial footage of their facilities and products.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: GAO’s Drones can be used to assess the environmental impact of foundry operations and identify areas for improvement in sustainability and resource management.
GAO’s IoT technologies, consisting of IoT sensors, sensors networks and systems, find the following applications in the foundries industry:
- Predictive Maintenance: GAO’s IoT sensors can monitor the condition of equipment and machinery in real-time, predicting when maintenance is needed to prevent breakdowns and optimize maintenance schedules.
- Energy Management: GAO’s IoT systems can monitor and control energy usage within the foundry, identifying opportunities for energy savings and efficiency improvements.
- Asset Tracking: GAO’s IoT tags and sensors can be attached to equipment, molds, and other assets, providing real-time location data and usage information, reducing the risk of loss or theft.
- Environmental Monitoring: GAO’s IoT sensors can measure emissions, air quality, temperature, and humidity, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and providing data for sustainability initiatives.
- Process Automation: GAO’s IoT can automate various processes in the foundry, such as controlling furnaces, molding machines, and conveyor systems based on real-time data and demand.
- Quality Control: GAO’s IoT sensors can monitor casting processes and collect data on temperature, pressure, and other variables, allowing for real-time quality control and defect detection.
- Inventory Management: GAO’s IoT systems can track the movement and levels of raw materials, finished products, and consumables, ensuring accurate inventory management and reducing waste.
- Worker Safety: Wearable GAO’s IoT devices can monitor workers’ health and safety in real-time, providing alerts in case of emergencies or unsafe conditions.
- Supply Chain Visibility: GAO’s IoT can provide real-time visibility into the movement of materials and products throughout the supply chain, improving logistics and reducing delays.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Foundry managers can remotely monitor and control equipment and processes using GAO’s IoT-enabled dashboards and mobile apps, improving operational oversight.
- Data Analytics: GAO’s IoT generates vast amounts of data that can be analyzed to identify patterns, optimize processes, and make data-driven decisions for continuous improvement.
- Inventory Reordering: GAO’s IoT sensors can trigger automatic reordering of materials and supplies when stock levels fall below a predefined threshold, reducing manual intervention.
- Production Planning: GAO’s IoT data can be used for demand forecasting and production planning, ensuring that the right products are produced at the right time.
- Error Reduction: By automating processes and providing real-time feedback, GAO’s IoT can help reduce human errors in data entry and production tasks.
- Security and Access Control: GAO’s IoT can enhance security through access control systems, surveillance cameras, and alarms, ensuring that only authorized personnel enter restricted areas.
- Customer Service: GAO’s IoT-enabled products can provide data on product performance and usage to offer better customer support and service.
- Sustainability Initiatives: GAO’s IoT can help monitor and reduce waste, energy consumption, and emissions, contributing to sustainable foundry practices.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Foundries
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in foundries to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates and government regulations:
RFID, BLE, IoT, & Drone Standards & Mandates
- ISO 18000
- ISO 15693
- ISO 14443
- EPC Gen2
- ISO 17367
- ISO 28560
- ISO 29143
- ISO 18013
- ISO 14223
- ISO 10374
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol)
- OPC UA (OPC Unified Architecture)
- BACnet (Building Automation and Control Networks)
- Modbus
- LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network)
- Zigbee
- Thread
- AllJoyn
- OCF (Open Connectivity Foundation)
- DDS (Data Distribution Service)
- AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol)
- RESTful APIs (Representational State Transfer)
- WebSockets
- 6LoWPAN (IPv6 over Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Networks)
- OneM2M
- Sigfox
- NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT)
- Cellular IoT (e.g., LTE-M)
- TSN (Time-Sensitive Networking)
- Bluetooth 4.0
- Bluetooth 4.1
- Bluetooth 4.2
- Bluetooth 5.0
- Bluetooth 5.1
- Bluetooth 5.2
- ASTM F2910
- ASTM F3224
- ISO 21384-3
- ISO 21384-4
- ISO 21384-5
- ISO 21384-6
- ISO 23627-1
- ISO 23627-2
- ISO 23627-3
- ISO 23627-4
- ISO 23627-5
- ISO 23627-6
- ISO 23627-7
US. Government Regulations
- Clean Air Act (CAA)
- Clean Water Act (CWA)
- Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA)
- Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA)
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Regulations
- National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP)
- National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS)
- Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA)
- Hazardous Waste Generator Regulations
- National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) Standards
- Foundry Rule (40 CFR Part 464)
- Hazard Communication Standard (HazCom)
- National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) Permitting
- Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (EPCRA)
- Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) Regulations
- Department of Transportation (DOT) Hazardous Materials Regulations
- Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA)
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program (GHGRP)
- Noise Control Act
- Clean Energy Standard (CES) Regulations
Canadian Government Regulations
- Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999 (CEPA)
- Canadian Environmental Assessment Act (CEAA)
- Canadian Environmental Assessment Agency (CEAA) Regulations
- Fisheries Act
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods Act (TDGA)
- Occupational Health and Safety Regulations
- Hazardous Products Regulations
- Canadian Standards Association (CSA) Standards
- Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety (CCOHS) Guidelines
- Environmental Emergency Regulations
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods (TDG) Regulations
- Canadian Environmental Assessment Agency (CEAA) Guidelines
- Federal Water Pollution Control Act (FWPCA) Regulations
- Canadian Air Quality Management System (AQMS) Regulations
- National Emission Guidelines for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NEGHAP)
- Canada Labour Code, Part II
- Pest Control Products Act (PCPA) Regulations
- Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) Regulations
- Explosives Act and Regulations
- Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) Requirements
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in foundries industry such as:
Personnel Management:
- Workforce Scheduling and Shift Management
- Employee Training and Certification Tracking
- Health and Safety Compliance Monitoring
- Performance Evaluation and Skill Assessment
- Employee Attendance and Time Tracking
Equipment Management:
- Predictive Maintenance and Equipment Health Monitoring
- Asset Tracking and Inventory Management
- Equipment Utilization and Downtime Analysis
- Calibration and Maintenance Records
- Energy Consumption Monitoring for Equipment
Access Control:
- Restricted Area Access Control
- Visitor Management and Authentication
- CCTV Surveillance and Intrusion Detection
- Biometric Access Control Systems
- Electronic Locking Systems
Warehouse Management:
- Raw Material Inventory Tracking
- Finished Product Inventory Management
- Material Handling and Transportation Optimization
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
- Warehouse Layout and Space Utilization
Supply Chain Management:
- Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
- Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization
- Supplier Quality Assurance and Compliance
- Order Processing and Tracking
- Logistics and Transportation Management
Other Applications:
- Environmental Compliance and Emission Monitoring
- Energy Management and Sustainability Initiatives
- Quality Control and Defect Detection
- Remote Monitoring of Critical Processes
- Process Automation and Robotics Integration
- Data Analytics for Process Optimization
- Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Research and Development (R&D) and Innovation Initiatives
- Product Traceability and Serialization
GAO has enabled its customers to make use of some of the leading software and cloud services in the foundries industry. Below are some of the popular software and cloud services in foundries industry.
Leading commercial software for personnel management in foundries includes SAP SuccessFactors, ADP Workforce Now, Oracle HCM Cloud, Kronos Workforce Ready, and Ultimate Software UltiPro, offering comprehensive HR, recruitment, and talent management solutions. For equipment management, foundries rely on Maintenance Connection, eMaint CMMS, IBM Maximo, Fiix, and Infor EAM, which provide robust asset tracking, maintenance, and performance optimization tools. These software options cater to the diverse needs of foundries, enhancing personnel and equipment management efficiency.
GAO has worked with some of the leading technology companies in foundries to provide integrated RFID, BLE, IoT and drone solutions to customers. Here are some of the technology leaders in foundries industry such Foundries include Siemens, SAP, Rockwell Automation, IBM, Schneider Electric, Honeywell, GE Digital, PTC, AVEVA, Wonderware (Schneider Electric), Siemon, Cisco Systems, and Dassault Systèmes. These companies offer a spectrum of digital solutions encompassing automation, industrial software, IoT, and data management to optimize processes, enhance efficiency, and improve overall performance in foundry operations. The choice of IT partner depends on the specific requirements and objectives of the foundry.
Case Studies of RFID, IoT & Drone Applications
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Below are some RFID application cases in foundries industry.
An aerospace foundry in the USA implemented RFID technology to track and manage the movement of molds and patterns used in their casting processes. RFID tags were attached to each mold, and RFID readers were strategically placed throughout the facility. This system allowed real-time tracking of mold location and usage, reducing the chances of misplaced or lost molds. As a result, the foundry experienced a significant reduction in production delays and improved overall efficiency.
A steel foundry in Canada utilized RFID technology to monitor the temperature and condition of molds during the casting process. RFID temperature sensors were embedded in the molds, and RFID readers were integrated into the production line. This implementation enabled real-time temperature monitoring and quality control, reducing the number of defective castings and ensuring consistent product quality.
An automotive foundry in Mexico adopted RFID technology to streamline its inventory management and reduce material handling errors. RFID tags were attached to raw materials, such as metal ingots and alloys, and RFID readers were placed at various checkpoints throughout the facility. By automating the tracking of materials, the foundry reduced inventory discrepancies, minimized stockouts, and optimized material flow, leading to cost savings and improved production efficiency.
A non-ferrous foundry in Europe implemented RFID technology to enhance the traceability of its finished products. RFID tags were affixed to each casting, and RFID readers were installed at key points in the production and shipping process. This allowed the foundry to provide customers with detailed product information, including material composition, production date, and quality certifications, improving customer satisfaction and compliance with industry regulations.
In Europe, a consortium of foundries collaborated to implement RFID technology across their supply chain. RFID tags were used to track the movement of raw materials, components, and finished products among multiple foundries and distribution centers. This collaborative RFID system improved supply chain visibility, reduced lead times, and enabled better demand forecasting, benefiting all participating foundries.
Many applications of RFID by GAO can be found here
Case Studies of IoT Applications
Below are some IoT application cases in foundries industry.
A steel foundry in the USA implemented an IoT-based system to improve overall efficiency. Sensors were deployed throughout the facility to collect data on temperature, humidity, machine performance, and energy consumption. This real-time data was integrated into a centralized IoT platform. By analyzing this data, the foundry was able to optimize furnace operation, reduce energy wastage during idle periods, and schedule maintenance based on actual machine performance. This resulted in a 15% reduction in energy costs and a 20% increase in production efficiency.
A Canadian foundry focused on improving its casting process using IoT technology. Temperature and pressure sensors were embedded in the casting molds, and IoT devices were placed on the production line. The data collected from these sensors allowed for precise monitoring of the casting process in real-time. By analyzing this data, the foundry could detect and address issues such as air bubbles or temperature fluctuations immediately. This reduced the rejection rate of castings by 30%, leading to substantial cost savings.
A foundry in Mexico prioritized safety by implementing an IoT-based system. Wearable devices with environmental sensors were provided to workers. These devices monitored factors such as temperature, air quality, and noise levels. In the event of hazardous conditions, workers receive immediate alerts and instructions on their devices. This proactive safety approach reduced workplace accidents by 40% and improved employee morale.
An aluminum foundry in Europe adopted IoT technology for predictive maintenance. Sensors were installed on critical machinery to continuously monitor vibrations, temperature, and other performance metrics. Data from these sensors was transmitted to a cloud-based analytics platform that used machine learning algorithms to predict equipment failures. As a result, the foundry reduced unplanned downtime by 25%, extended the lifespan of machinery, and saved approximately 15% on maintenance costs.
In Europe, a consortium of foundries collaborated to implement IoT solutions across their supply chain. IoT-enabled tracking devices were attached to raw materials, molds, and finished products. This provided real-time visibility into the movement and location of materials and products. By optimizing logistics and supply chain operations, the consortium reduced lead times, improved on-time delivery rates, and reduced excess inventory, resulting in cost savings for all member foundries
Case Studies of Drone Applications
Below are some drone application cases in foundries industry.
A foundry in the USA implemented drone technology to enhance safety and inspection processes. Drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras and gas sensors were deployed to inspect the condition of furnaces and identify potential gas leaks or overheating issues. By using drones for these hazardous inspections, the foundry improved safety for its workers while also reducing downtime and maintenance costs. The real-time data collected by drones allowed for quicker responses to potential safety concerns.
A Canadian foundry situated in a sensitive environmental area used drones for environmental compliance monitoring. Drones equipped with air quality sensors and cameras were flown regularly to monitor emissions, smokestacks, and any potential environmental impacts. This proactive approach to compliance not only helped the foundry meet stringent environmental regulations but also improved its reputation as a responsible and environmentally conscious organization.
In Europe, a foundry implemented drone technology for asset management and inventory control. Drones with high-resolution cameras and RFID scanners were used to conduct regular aerial surveys of the facility. These surveys helped track the location and condition of molds, equipment, and other valuable assets. By automating this process, the foundry improved asset utilization and reduced the risk of misplacing or losing critical equipment.
A foundry in Mexico used drones for site surveying and expansion planning. Drones equipped with LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology were deployed to create highly detailed 3D maps of the facility and the surrounding area. These maps provided valuable data for optimizing the layout of the foundry, identifying potential expansion areas, and improving workflow efficiency. The drone-generated maps were also used for better disaster preparedness and response.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Foundries
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including foundries.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including foundries.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including foundries:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including foundries:
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including foundries:
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including foundries
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
Digital I/O adapters:
and relay Controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
- UHF 860-960 MHz RFID Module
- 13.56 MHz High Frequency RFID Module
- 125 kHz Low Frequency RFID Reader Modules
In collaboration with its sister company GAO Tek Inc, a wide selection of high-quality drones is offered:
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in foundries
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include
Foundries employ a diverse array of specialized equipment to facilitate the casting process. This includes furnaces like cupola, induction, and electric arc furnaces, various molding equipment, pattern and core making machinery, equipment for melting and pouring metal, casting cleaning and finishing tools, quality control instruments such as X-ray and ultrasonic testing machines, environmental control systems, material handling equipment, safety gear, automation and robotics, instrumentation and sensors, sand preparation and coating machinery, foundry ladles and crucibles, patternless casting and molding technologies, handling equipment for molds and cores, refractory materials and equipment, and specialized software and control systems. The selection of equipment depends on the casting method, materials used, production capacity, and technological capabilities of the foundry.
People or workers tracking system:
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
Furthermore, GAO provides the customization of RFID tags, RFID readers, BLE beacons and BLE gateways, IoT, drones, and systems and consulting services for foundries and for various industries in all metropolitans in the U.S. and Canada:
GAO Makes Efforts to Satisfy Customers
Large Choice of Products
In order to satisfy the diversified needs of their corporate customers, GAO RFID Inc. and its sister company GAO Tek Inc. together offer a wide choice of RFID, BLE, IoT, drones, testing and measurement devices, and network products.
Overnight Delivery
In order to shorten the delivery to our customers, GAO has maintained a large stock of its products and is able to ship overnight within continental U.S. and Canada.
Local to Our Customers
We are located in both the U.S. and Canada. We travel to customers’ premises if necessary. Hence, we provide a very strong local support to our customers in the U.S. and Canada. Furthermore, we have built partnerships with some integrators, consulting firms and other service providers in different cities to further strengthen our services. Here are some of the service providers in foundries we have worked with to serve our joint customers:
- Industry Associations
- Online Business Directories
- Consultation
- Trade Shows and Events
- Request for Proposals (RFPs)
- Online Search
- Consult with Industry Experts
- Accenture
- Deloitte
- Capgemini
- IBM Global Business Services
- PwC (PricewaterhouseCoopers)
- KPMG
- Cognizant
- Infosys
- Wipro
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)
- Ernst & Young (EY)
- CGI
- HCL Technologies
- Tech Mahindra
- Atos
GAO Has Served Foundries Extensively
GAO RFID Inc. and its sister company GAO Tek Inc. together offer a wide choice of RFID, BLE, IoT, drone, testing and measurement devices, and network products.
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in foundries Industry to achieve success in the foundries industry, several notable trends and buzzwords have emerged in recent years. These include Industry 4.0, characterized by the integration of digital technologies and automation; the Internet of Things (IoT) for real-time data collection; the concept of digital twins to simulate and optimize processes; additive manufacturing for 3D printing of patterns and cores; the adoption of smart foundries with data-driven decision-making; the application of artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive maintenance and quality control; robotic automation for enhanced efficiency and safety; a focus on energy efficiency and sustainability; reshoring to mitigate supply chain risks; big data analytics and predictive maintenance; lean manufacturing principles; advanced quality control techniques; adherence to environmental compliance and emissions standards; innovation in metal alloys; supply chain digitalization and blockchain for traceability; the pursuit of zero-defect manufacturing; and the vision of a “Foundry of the Future” characterized by automation, data-driven operations, and environmental responsibility. These trends collectively reflect the industry’s commitment to technological advancement, sustainability, and meeting evolving market demands.
GAO RFID Inc. has served many customers in foundries, including its various divisions such as
- Iron Foundries: Specializing in casting iron components, including gray iron, ductile iron, and malleable iron.
- Steel Foundries: Focused on casting steel alloys, both carbon steel and alloy steel, for various industrial applications.
- Aluminum Foundries: Specializing in the production of aluminum castings, often used in aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods.
- Non-Ferrous Foundries: Casting metals other than iron and steel, such as copper, brass, bronze, and zinc.
- Sand Casting Foundries: Using sand molds to create complex shapes and a wide range of sizes.
- Die Casting Foundries: Employing reusable dies to produce high-precision, intricate parts, often in aluminum, zinc, or magnesium.
- Investment Casting Foundries: Utilizing wax patterns and ceramic molds to achieve high-detail and near-net-shape components.
- Permanent Mold Casting Foundries: Employing reusable molds made of materials like steel or graphite to produce consistent, durable parts.
- Aerospace Foundries: Focusing on the production of high-strength and precision components for the aerospace sector.
- Automotive Foundries: Supplying cast parts for the automotive industry, including engine blocks, cylinder heads, and transmission components.
- Foundries for Art and Sculpture: Catering to artistic and creative applications, producing metal sculptures, artwork, and decorative pieces.
- Foundries for Electronics: Casting components for the electronics industry, including heat sinks and housing for electronic devices.
- Sand Foundries: Specializing in sand casting processes, which are versatile and commonly used for a wide range of metals.
- Gray Iron Foundries: Focusing on gray iron casting, which has excellent machinability and damping properties.
- Ductile Iron Foundries: Concentrating on ductile iron casting, known for its high strength and ductility.
- Steel Investment Casting Foundries: Primarily producing steel castings using the investment casting process.
- Aluminum Die Casting Foundries: Specializing in high-pressure die casting of aluminum alloys.
- Foundry Pattern Making: Specializing in the design and creation of casting patterns and core boxes.
- Foundry Tooling and Machining: Providing machining and finishing services for cast components.
- Foundry Quality Assurance and Testing: Concentrating on quality control, inspection, and non-destructive testing of castings.
- Foundry Research and Development: Engaging in R&D activities to improve casting processes and materials.
GAO’s technologies enable its customers in “foundries” to effectively track their workforces such as workers use a range of specialized terms and job titles to describe their roles and responsibilities. Commonly used terms include molder, who prepares molds; caster, responsible for pouring molten metal; coremaker, producing internal cores; furnaceman, operating melting furnaces; finisher, performing post-casting operations; casting inspector, checking for defects; patternmaker, crafting or repairing patterns; foundry supervisor, overseeing operations; casting engineer, with technical expertise; safety officer, ensuring safety protocols, foundry laborer, assisting skilled workers; fettler, removing rough edges, shakeout worker, extracting castings; knockout worker, breaking molds; runner and riser cutter, trimming excess metal; and heat treater, enhancing casting properties. These terms reflect the diverse roles within a foundry, with workers specializing in their respective areas and effectively track operational assets such as furnace, mold, pattern, core box, ladle, crucible, shakeout machine, knockout machine, sand mixer, foundry flask, sand reclaimer, casting cleaning equipment, core shooting machine, fettling tools, mold cooling system, mold handling equipment, sand testing equipment, pouring equipment, tundish, crane and hoist systems, safety gear and equipment, environmental control systems, foundry sand conveyor, foundry ladle and skimmer, and mold coating equipment, all vital in the casting process.
Here are some of the leading companies in foundries industry GAO has served:
- American Axle & Manufacturing Inc.
- Waupaca Foundry, Inc.
- Grede Holdings LLC
- Neenah Foundry Company
- Badger Foundry Company
- McWane, Inc.
- East Jordan Iron Works, Inc.
- Columbia Steel Casting Co., Inc.
- Charlotte Pipe and Foundry Company
- Intermet Corporation
- Ferralloy Inc.
- Bremen Castings, Inc.
- Plymouth Foundry, Inc.
- Interstate Castings
- Sioux City Foundry Co.
- Aarrowcast, Inc.
- Bodine Aluminum, Inc.
- State Line Foundries, Inc.
- Castcon Corporation
- Francis Manufacturing Company Limited
- Chapman’s Foundry Ltd.
- Coulée Mécanique Drummondville (CMD)
- Wabi Iron & Steel Corp.
- Pacific Alloy Casting Co. Ltd.












You Are Invited to Contact Us!
If you interested in our products, services or partnering with us, please feel free to contact us by filling out this form:
or email us at sales@gaorfid.com












