
Overview
Museums, historical sites, and similar institutions industry is a part of the arts, entertainment, and recreation sector. Industries in this subsector engage in the preservation and exhibition of objects, sites, and natural wonders of historical, cultural, and/or educational value. The industry includes museums, historical sites, zoos, aquariums, arboretums, botanical gardens, planetariums, and other similar institutions.
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in Farm Product Raw Material Merchant Wholesalers Industry to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials and operational equipment such as: Staff, Material, Security equipment, Cleaning equipment, Moving equipment, Exhibit maintenance equipment, Audiovisual equipment, Computer equipment, Storage equipment, First aid equipment, Fire extinguishers.
Ranked as one of the top 10 global RFID suppliers, GAO RFID Inc. is based in New York City, U.S. and Toronto, Canada. GAO offers a comprehensive selection of UHF, HF (including NFC) and LF RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags, BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. Such RFID and BLE products and systems, as well as its IoT and drone technologies, have been successfully deployed for Museums, Historical Sites, and Similar Institutions Industry.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Museums, Historical Sites, and Similar Institutions
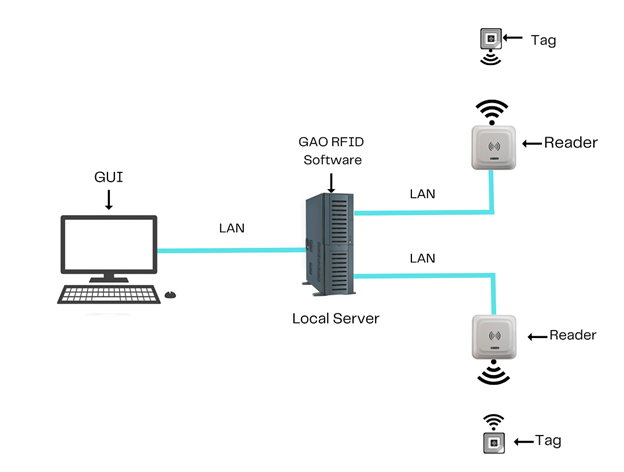
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for Museums, Historical Sites, and Similar Institutions Industry are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server that normally is on our client’s premises, and another version runs in the cloud. The cloud server could be GAO’s cloud server, client’s own cloud server or a cloud server from one of the leading cloud server providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud (formerly SoftLayer), Oracle Cloud, RedHat, Heroku, Digital Ocean, Cloudflare, Linode and Rackspace. The above illustrates GAO system for Museums, Historical Sites, and Similar Institutions Industry with its software running on a local server.
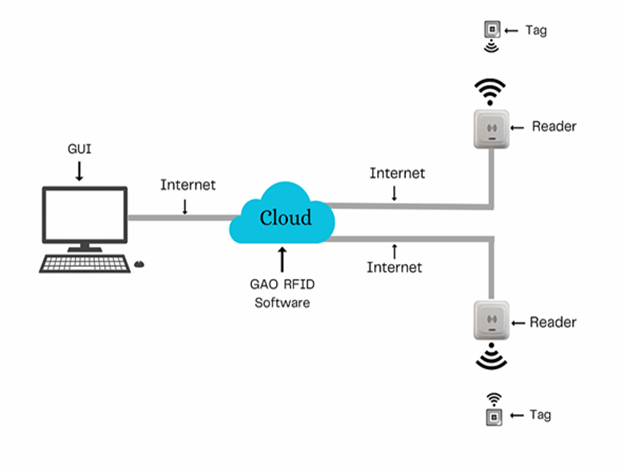
The above illustrates GAO system for museums, historical sites, and similar institutions with its software running in cloud.
GAO’s RFID and BLE technologies, consisting of RFID readers, RFID tags, BLE gateways, BLE beacons, software, cloud services and their systems, have the following applications in Museums, Historical Sites, and Similar Institutions Industry:
- Artifact and Exhibit Tracking: GAO RFID readers and tags enable precise tracking and monitoring of artifacts and exhibits throughout the institution. This ensures accurate inventory management, reduces the risk of loss or theft, and provides valuable insights into the movement of valuable items.
- Visitor Management: GAO RFID systems help streamline visitor check-in processes by utilizing RFID badges or tickets. This allows for efficient access control, personalized experiences, and data collection for visitor analytics.
- Audio Guide Systems: GAO RFID tags can be integrated into audio guide devices, providing visitors with an interactive and informative experience. As visitors approach exhibits, the RFID system triggers relevant audio content, enhancing their engagement and understanding.
- Conservation and Climate Monitoring: GAO’s RFID sensors are employed to monitor environmental conditions in sensitive areas, such as storage rooms and exhibit spaces. This data aids in maintaining proper climate conditions to preserve delicate artifacts and historical objects.
- Maintenance and Asset Tracking: RFID tags can be attached to maintenance equipment, ensuring timely and proactive maintenance of facilities and exhibits. Additionally, GAO RFID systems facilitate tracking and locating essential assets, such as AV equipment and exhibit components.
- Crowd Management: RFID technology helps monitor visitor flow and manage crowd congestion during peak hours or special events. This allows institutions to optimize space utilization and ensure a smooth visitor experience.
- Interactive Exhibits: GAO’s RFID solutions enable interactive exhibits where visitors can engage with digital content or participate in educational activities by tapping RFID-enabled objects or displays.
- Security and Access Control: RFID access control systems restrict access to authorized personnel only, safeguarding restricted areas and valuable collections. GAO RFID readers and tags are utilized to monitor entry and exit points efficiently.
- Historical Reenactments: RFID technology can enhance historical reenactments by automating specific actions, activating audiovisual displays, or triggering special effects as actors move through designated areas.
- Collection Management: GAO’s RFID systems aid in cataloging and tracking historical artifacts and documents in the institution’s collection, providing accurate records and facilitating efficient loan processes.
GAO’s drone technologies find the following applications in the Museums, Historical Sites, and Similar Institutions Industry:
- Aerial Surveys and Documentation: GAO’s drones can conduct aerial surveys of historical sites and museums, capturing high-resolution images and videos for documentation, preservation, and research purposes.
- Site Inspection and Maintenance: Drones equipped with cameras and sensors can be used to inspect hard-to-reach areas of historical structures, enabling efficient maintenance and identifying potential issues.
- Virtual Tours: GAO’s drones can capture immersive aerial footage of museums and historical sites, creating virtual tours that allow visitors to explore these locations from unique perspectives.
- Crowd Monitoring: Drones can be deployed to monitor visitor flow and crowd density during events or busy periods, helping museums and historical sites manage visitor safety and comfort.
- Security and Surveillance: GAO’s drone technologies can enhance security measures by providing real-time aerial surveillance of museum grounds and historical sites, helping to deter potential threats and ensuring the safety of visitors and staff.
- Environmental Monitoring: Drones equipped with environmental sensors can monitor air quality, temperature, and humidity in and around museums and historical sites, aiding in conservation efforts and ensuring proper environmental conditions for artifacts and exhibits.
- Archaeological Exploration: Drones equipped with specialized sensors and cameras can assist in archaeological surveys and explorations, providing valuable insights into historical sites and landscapes.
- Public Events Coverage: GAO’s drones can capture aerial footage of public events and activities held at museums and historical sites, enhancing marketing efforts and providing unique content for promotional purposes.
- Emergency Response: In case of emergencies or natural disasters, drones can be deployed for rapid assessment and situational analysis, aiding in decision-making and response coordination.
- Educational Content Creation: Drones can be used to film educational videos and documentaries about the history and significance of museums and historical sites, enriching educational programs and outreach initiatives.
GAO’s IoT technologies, consisting of IoT sensors, sensors networks and systems, find the following applications in the Museums, Historical Sites, and Similar Institutions Industry:
- Environmental Monitoring: GAO’s IoT sensors can be deployed throughout museums and historical sites to monitor temperature, humidity, light exposure, and air quality. This data helps in preserving artifacts and exhibits by maintaining optimal environmental conditions.
- Energy Management: GAO’s IoT systems enable efficient energy management by monitoring and controlling lighting, heating, and cooling systems in museums and historical buildings. This contributes to energy conservation and cost reduction.
- Exhibit Interaction and Engagement: GAO’s IoT technologies can be integrated into exhibits, allowing visitors to interact with displays and artifacts through touch-sensitive sensors or mobile applications, enriching the visitor experience.
- Asset Tracking: GAO’s IoT sensor networks enable tracking and monitoring of valuable artifacts and equipment within museums and historical sites, reducing the risk of loss and improving inventory management.
- Visitor Analytics: GAO’s IoT systems collect data on visitor movements and interactions within museums and historical sites. This data aids in understanding visitor behavior, preferences, and interests, facilitating better exhibit curation and visitor engagement strategies.
- Security and Surveillance: GAO’s IoT sensors and systems contribute to enhanced security measures by monitoring access points, detecting anomalies, and providing real-time alerts in case of security breaches.
- Predictive Maintenance: GAO’s IoT technologies enable predictive maintenance of museum equipment and facilities by continuously monitoring equipment health and detecting potential issues before they escalate.
- Conservation and Restoration: GAO’s IoT sensors can be utilized to monitor the condition of historical artifacts and structures, providing insights for conservation and restoration efforts.
- Audio and Visual Enhancements: GAO’s IoT systems can control audiovisual components within museums and historical sites, creating immersive experiences through synchronized audio guides or interactive displays.
- Disaster Preparedness: GAO’s IoT technologies aid in disaster preparedness by monitoring for potential hazards, such as fire or water leaks, and providing early warning systems for immediate response.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Museums, Historical Sites, and Similar Institutions Industry
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in Museums, Historical Sites, and Similar Institutions Industry to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates and government regulations:
RFID, BLE, IoT, & Drone Standards & Mandates
- EPCglobal UHF Gen2 (ISO/IEC 18000-63)
- ISO/IEC 18000-6C
- ISO 11784/11785
- Bluetooth 4.0 (Bluetooth Low Energy)
- Bluetooth 5.0
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol)
- OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture)
- ASTM F38
- ISO 21384-3
- DoD-STD-2010
- FAA
- FCC
US Government Regulations
- The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA
- The Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA)
- The Archaeological Resources Protection Act (ARPA)
- The National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA)
Canadian Government Regulations
- The Canadian Museums Association Code of Ethics
- The Canadian Cultural Property Export and Import Act
- The Ontario Heritage Act
- The Alberta Historical Resources Act
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in museums, historical sites, and similar institutions such as:
Personnel Management:
- Staff attendance tracking and time management
- Employee scheduling and shift planning
- Staff training and certification management
- Performance evaluation and appraisals
- HR data and records management
Equipment Management:
- Inventory tracking of exhibits, artifacts, and equipment
- Maintenance and repair scheduling for audiovisual, lighting, and display equipment
- Asset tracking and lifecycle management
- Equipment maintenance history and documentation
- Preventive maintenance planning
Access Control:
- Visitor access and ticketing management
- Member and VIP access privileges
- Access control for restricted areas and exhibits
- Real-time monitoring of entry and exit points
- Integration with visitor management systems
Warehouse Management:
- Inventory management of archival materials and historical documents
- Artifact and exhibit storage tracking
- Warehouse organization and shelving management
- Temperature and humidity monitoring for storage preservation
- Item retrieval and retrieval history tracking
Supply Chain Management:
- Procurement and vendor management for museum supplies
- Supply chain visibility for tracking shipments of artifacts and exhibits
- Logistics and transportation management for traveling exhibits
- Supplier performance evaluation and contract management
- Inventory optimization and demand forecasting for gift shop merchandise
Other Applications:
- Exhibit interaction and engagement through audio guides and interactive displays
- Visitor analytics and behavior tracking for exhibit and layout optimization
- Environmental monitoring for conservation and preservation efforts
- Crowd management during events and peak visiting times
- Disaster preparedness and emergency response planning
- Conservation and restoration project management
- Virtual tours and digital exhibit experiences for remote access
- Research and curation collaboration tools for historians and curators
- Educational programs and content creation for public outreach
GAO has enabled its customers to make use of some of the leading software and cloud services in museums, historical sites, and similar institutions industry. Below are some of popular software and cloud services in museums, historical sites, and similar institutions industry: Workday, SAP SuccessFactors, Oracle Cloud HCM, PeopleSoft HCM Cloud, Avigilon Control Center, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management, LenelS2 Identity Manager Cloud, HID Global Access Control Station Cloud, Collection management software, Visitor management software, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Amazon Web Services (AWS).
GAO has worked with some of the leading technology companies in museums, historical sites, and similar institutions to provide integrated RFID, BLE, IoT and drone solutions to customers. Here are some of the technology leaders in museums, historical sites, and similar institutions industry: Google Arts & Culture, Aventis Systems, MuseumNext, TechSoup, AVer Information Systems, Epson, Intelisys, NEC Display Solutions, Crestron, Leica Geosystems, Planon, Siemens.
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Below are some RFID application cases in museums, historical sites, and similar institutions industry.
In the United States, several prominent museums and historical institutions have embraced RFID technology to optimize their operations and improve the visitor experience. One such institution is the Smithsonian Institution, which utilizes RFID to meticulously track and manage its vast collection of artifacts, ensuring efficient inventory management and bolstering security measures. Similarly, the Metropolitan Museum of Art has implemented RFID tags to create interactive experiences for visitors, enabling them to access detailed information about exhibits and artworks with a simple scan. The Museum of Modern Art (MoMA) also leverages RFID technology to enhance visitor engagement by offering supplementary information about artworks and artists, enriching the overall museum experience. Through these RFID applications, these institutions are elevating their efficiency and fostering a deeper connection between visitors and their treasured exhibits.
In Canada, various museums, historical sites, and similar institutions have embraced RFID technology to enhance their operations and provide immersive experiences for visitors. The Royal Ontario Museum utilizes RFID to optimize collection management, enabling efficient tracking of artifact movement and mitigating the risk of loss or damage. At the Canadian Museum for Human Rights, RFID tags are employed to offer personalized visitor experiences, tailoring exhibit content based on individual preferences, and creating a more engaging and relevant journey through the museum. Similarly, the Glenbow Museum leverages RFID technology to design interactive exhibits, allowing visitors to engage directly with artifacts through RFID-enabled touchpoints, fostering a deeper connection and understanding of the exhibits on display. These RFID applications in Canadian institutions showcase a commitment to leveraging technology for improved visitor engagement and management of valuable collections.
In the USA, UHF RFID technology has found valuable applications in various museums, historical sites, and similar institutions, facilitating efficient operations and ensuring the preservation of exhibits. The Field Museum in Chicago employs UHF RFID to track the movement of large exhibits, including dinosaur skeletons, ensuring proper management and protection of these valuable artifacts. Similarly, the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum utilizes UHF RFID to track the movement of its collection items, enhancing their security during transport and safeguarding against potential loss or damage. At the California Academy of Sciences, UHF RFID is employed to monitor and track the movement of animal specimens, promoting their safety and well-being, thereby contributing to the responsible care of the museum’s living collections. These UHF RFID applications exemplify how advanced technology benefits the preservation and management of invaluable artifacts and exhibits in prominent cultural institutions across the United States.
In Canada, UHF RFID technology has been effectively utilized in museums, historical sites, and similar institutions to enhance various aspects of their operations. The Royal Tyrrell Museum of Paleontology employs UHF RFID to track the movement of precious dinosaur bones, ensuring their proper management and preservation, which is crucial for maintaining their historical and scientific significance. At the Museum of Nature in Ottawa, UHF RFID is used to monitor the movement of animals in their exhibits, ensuring their safety and well-being, and providing a conducive environment for their care and study. Meanwhile, at Fort George National Historic Site in Ontario, UHF RFID technology is implemented to track the movement of cannons and artifacts, optimizing inventory management and enhancing protection measures for these valuable historical pieces. These UHF RFID applications exemplify how advanced technology contributes to the responsible stewardship and preservation of valuable collections in Canadian cultural institutions.
Many applications of RFID by GAO can be found here.
Case Studies of IoT Applications
Below are some IoT application cases in Museums, Historical Sites, and Similar Institutions Industry.
Franklin Institute implemented IoT sensors to monitor environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and light levels, to ensure the preservation of delicate artifacts and artworks. The data collected is used to maintain optimal conditions for exhibits and reduce the risk of damage due to improper environmental conditions.
Tenement Museum adopted IoT-enabled smart audio guides for visitors. These guides provide interactive and personalized tours, offering real-time information about exhibits and the historical significance of each area within the museum.
Getty Center uses IoT technology to optimize energy consumption and environmental sustainability. IoT sensors monitor and control lighting, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to reduce energy waste and operational costs.
Canadian Museum of History utilizes IoT devices for visitor analytics and crowd management. IoT sensors track visitor movements, identify popular exhibits, and provide valuable data for improving visitor flow and overall museum experience.
Royal BC Museum integrates IoT technology to enhance the visitor experience in their outdoor exhibits. IoT-based interactive displays provide contextual information and multimedia content, enriching the understanding of historical artifacts and natural specimens.
Canadian Museum for Human Rights implemented IoT sensors to monitor and control environmental conditions within exhibits. This ensures that sensitive artifacts are preserved in optimal conditions and protected from environmental harm.
Case Studies of Drone Applications
Below are some drone application cases in Museums, Historical Sites, and Similar Institutions Industry.
The Alamo (San Antonio, Texas) drones have been used to conduct aerial surveys and 3D mapping of the Alamo, a historic site of great significance. The data collected from these drone flights helps with preservation efforts, architectural analysis, and ongoing maintenance of the site.
Getty Museum (Los Angeles, California) drones have been employed to capture stunning aerial footage of the museum and its surroundings. These aerial shots are used for promotional purposes, providing captivating views of the museum’s architecture and exhibitions.
Historic Sites and Monuments Board of Canada drones have been used by the board to conduct aerial surveys of historical sites and monuments. This data aids in documentation, conservation, and assessing the condition of these national heritage sites.
Fort Henry National Historic Site (Kingston, Ontario) drones have been utilized to capture aerial images and videos of Fort Henry, a historical site and UNESCO World Heritage Site. The footage obtained from drones offers unique perspectives for educational and promotional purposes.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Museums, Historical Sites, and Similar Institutions
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including museums, historical sites, and similar institutions.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration, and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including museums, historical sites, and similar institutions.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including museums, historical sites, and similar institutions:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including museums, historical sites, and similar institutions:
- Gen 2 UHF 902-928 MHz RFID Tags
- Find Your Gen 2 UHF 865-868 MHz RFID Tags
- Semi Passive UHF Gen2 RFID Tags
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including museums, historical sites, and similar institutions:
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including museums, historical sites, and similar institutions:
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
Digital I/O adapters:
and relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
- Find Your 860-960 MHz RFID Module
- Find Your 13.56 MHz High Frequency RFID Module
- Find Your 125 kHz RFID Reader Modules
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in museums, historical sites, and similar institutions:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include.
- Art handling equipment: This includes dollies, carts, and lifts that are used to move large or heavy objects.
- Environmental monitoring equipment: This includes temperature and humidity sensors that are used to ensure that the environment is safe for the collection.
- Security equipment: This includes cameras, alarms, and motion detectors that are used to protect the collection from theft and vandalism.
- Audiovisual equipment: This includes projectors, screens, and sound systems that are used to create interactive exhibits and presentations.
- Computer software: This includes inventory management software, conservation software, and educational software that is used to manage the collection, conserve objects, and educate visitors.
People or workers tracking system:
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
GAO Has Served Museums, Historical Sites, and Similar Institutions Extensively
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in museums, historical sites, and similar institutions industry to achieve success in digitalization, interactivity, STEAM (science, technology, engineering, arts, and math) education, community engagement, and sustainability.
GAO RFID Inc. has deployed RFID, BLE and IoT projects for many companies in museums, historical sites, and similar institutions, including many in its various divisions such as
- Art museums: These museums focus on the visual arts, such as painting, sculpture, and photography.
- Natural history museums: These museums focus on the natural world, such as plants, animals, and geology.
- Science museums: These museums focus on science and technology, such as astronomy, physics, and engineering.
- History museums: These museums focus on human history, such as wars, cultures, and civilizations.
- Children’s museums: These museums are designed for children, and they often feature interactive exhibits and programs.
- Military museums: These museums focus on military history, such as wars, battles, and weapons.
- Archaeological museums: These museums focus on archaeological artifacts, such as fossils, pottery, and jewelry.
- Memorial museums: These museums are dedicated to remembering and honoring people or events.
- Smithsonian Institution (USA): World’s largest museum and research complex in Washington, D.C., with 19 museums, 21 libraries, and the National Zoo.
- Metropolitan Museum of Art (USA): Iconic art museum in NYC with a vast collection spanning over 5,000 years of art history.
- Museum of Modern Art (USA): Prominent NYC Museum dedicated to modern and contemporary art, featuring works by famous artists.
- American Museum of Natural History (USA): NYC museum showcasing the wonders of the natural world, including astronomy, paleontology, and anthropology.
- Los Angeles County Museum of Art (USA): Largest art museum in the western U.S. with a diverse collection from various regions and time periods.
- National Geographic Society (USA): Non-profit organization exploring and protecting the planet through research, publications, and documentaries.
- Guggenheim Museum (USA): NYC museum with unique spiral architecture, focusing on modern and contemporary art.
- Whitney Museum of American Art (USA): NYC museum dedicated to American art from the 20th and 21st centuries.
- Museum Hack (USA): Company offering unconventional and interactive museum tours for engaging experiences.
- Canadian Museum of Nature (Canada): Ottawa museum focusing on Canada’s natural history, wildlife, and ecosystems.
- Royal Ontario Museum (Canada): Toronto Museum with a diverse collection of art, culture, and natural history artifacts.
- Vancouver Museum (Canada): Now part of the Museum of Vancouver, formerly focusing on Vancouver’s history and culture.
- Canadian War Museum (Canada): Ottawa museum dedicated to Canada’s military history and armed conflicts.
- Maritime Museum of the Atlantic (Canada): Halifax Museum exploring the maritime heritage and history of Atlantic Canada.
- Canada Science and Technology Museum (Canada): Ottawa museum showcasing Canada’s science and technology history through interactive exhibits.
Here are some of the leading companies in museums, historical sites, and similar institutions industry:

Smithsonian Institution

Metropolitan Museum of Art

Museum of Modern Art

American Museum of Natural History

Los Angeles County Museum of Art

National Geographic Society

Guggenheim Museum

Whitney Museum of American Art

Museum Hack

Thinc Design

Glaserworks

RSM Visuals

ESI Design

LD Products

Artechouse

The Tech Interactive

Exhibit Technologies

Museum Store Association

Canadian Museum of Nature

Royal Ontario Museum

Vancouver Museum

Canadian War Museum

Maritime Museum of the Atlantic

Canada Science and Technology Museum
