
Index
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Technical Textiles Manufacturing
GAO’s Assists Clients with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Technical Textiles Manufacturing
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
Case study of RFID Applications
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Technical Textiles Manufacturing
Overview
Technical textiles manufacturing industry produces specialized textile materials for specific purposes. It utilizes advanced processes like weaving, knitting, and coating to create tailored fabrics. Applications include automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. Growth is driven by demand for high-performance materials, advancements in material science, safety standards, sustainability, and innovation. This industry is vital for providing functional textiles and advancing technology, safety, and performance in diverse sectors.
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in the technical textiles manufacturing industry to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials and operational equipment such as weaving machines, knitting machines, nonwoven formation machines, coating machines, laminating machines, composite manufacturing equipment, cutting machines, sewing machines, printing machines, finishing machines, and packaging machines.
Ranked as a top 10 global RFID supplier and based in New York City and Toronto, GAO RFID Inc offers a wide choice of RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags at ultra-high frequency (UHF), high frequency (HF, including NFC) and low frequency (LF), BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. Such RFID and BLE products and systems, together with its IoT and drone technologies, have been widely used in technical textiles manufacturing.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Technical Textiles Manufacturing
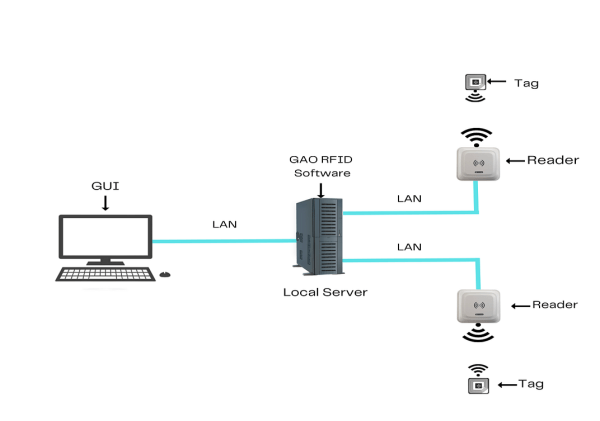
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for technical textiles manufacturing are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server, and another version is that its software runs in the cloud. The above illustrates the GAO system for technical textiles manufacturing with its software running on a local server.
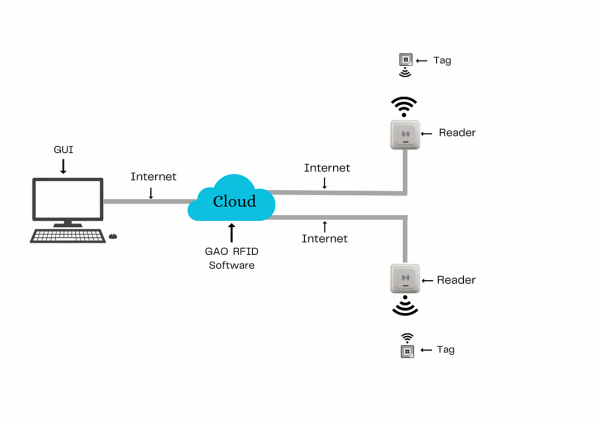
The above illustrates GAO system for technical textiles manufacturing with its software running in cloud.
GAO’s RFID technologies bring the many benefits to technical textiles manufacturing industry:
- Enhanced Supply Chain Visibility: Integrating GAO’s RFID tags enables seamless material tracking, improving visibility and enhancing logistics management. Our RFID solutions track textile components such as fibers, yarns, fabrics, trims, and accessories from suppliers to manufacturers, ensuring timely delivery.
- Streamlined Production Processes: GAO’s RFID technology automates and streamlines production. Tagging textile components such as fibers, yarns, fabrics, trims, and accessories, captures real-time data, optimizes workflows, and identifies bottlenecks.
- Enhanced Quality Control: GAO’s RFID ensures precise quality. Tags on textile samples enable automated identification and inspection, ensuring adherence to standards.
GAO’s BLE technologies offer longer reading range and particularly attractive for applications with larger workspaces within technical textiles manufacturing industry:
- Real-time Tracking: GAO’s BLE technology provide instant visibility of textile materials, including cotton, silk, wool, linen, hemp, jute, and sisal, within the manufacturing facility.
- Preventive Maintenance: GAO’s BLE technology enables proactive maintenance to avoid breakdowns, allowing for timely interventions to optimize performance.
- Optimal Resource Allocation: Our BLE technology optimize resource allocation in the technical textiles manufacturing industry and track materials, including cotton, silk, wool, linen, hemp, jute, and sisal, improving resource planning and cost management.
GAO’s RFID and drone technologies are often combined, and such solutions offer the following benefits to technical textiles manufacturing industry:
- Enhanced Material Tracking: GAO’s RFID technology combined with drones enables real-time tracking of textile components, including fibers, yarns, fabrics, trims, and accessories, throughout the manufacturing process.
- Sustainable Practices: GAO’s RFID technology integrated with drones supports the implementation of sustainable practices in the industry and it can monitor environmental factors, such as energy consumption and waste management.
- Enhanced Collaboration: By leveraging GAO’s RFID technology with drones, we can enhance collaboration among teams and stakeholders, enabling seamless coordination between different departments involved in textile manufacturing processes.
Here are benefits of GAO’s IoT technologies to technical textiles manufacturing industry:
- Data-driven Decision Making: GAO’s IoT technology sensors can gather data on machine performance, environmental conditions such as resource consumption, chemical usage, waste generation, and process parameters.
- Enhanced Process Automation: GAO’s IoT technology automates manual tasks and streamlines processes in the technical textiles manufacturing industry.
- Waste Reduction: GAO’s IoT sensors can measure material usage, detect anomalies, and provide insights to minimize waste generation, resulting in cost savings and improved sustainability.
GAO’s Assists Clients with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Technical Textiles Manufacturing
GAO RFID Inc. has developed its products and systems in compliance with industry standards and mandates. GAO has assisted our customers in the technical textiles manufacturing to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with applicable industry standards, U.S. government regulations and Canadian government regulations such as:
RFID, BLE, IoT, & Drone Standards & Mandates
- CTA-2069: This Consumer Technology Association (CTA) standard offers guidance on ensuring the security of IoT devices used in the technical textiles manufacturing industry, promoting reliable and secure connectivity.
- ASTM F2413-18: The ASTM standard establishes safety requirements for footwear, including the use of RFID tags for tracking and identification in textile manufacturing, enhancing worker safety.
- Industry Canada Spectrum Regulations: These regulations govern the allocation and use of radio frequencies in Canada, including those utilized by RFID, BLE, and IoT devices, ensuring efficient and interference-free communication.
- EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA): This act regulates the use and importation of chemical substances, including those employed in textile manufacturing processes, ensuring environmental protection and safety.
- FDA UDI (Unique Device Identification) System: The UDI system mandates the labeling and tracking of medical devices, including RFID-enabled medical textiles, ensuring traceability and compliance with safety standards in the healthcare sector.
- IEEE 802.15.4: This standard defines the physical and media access control (MAC) layers for low-rate wireless personal area networks (WPANs), including BLE devices used in textile manufacturing for short-range communication.
- Canadian Aviation Regulations: These regulations cover the operation of drones in Canadian airspace, including licensing, flight restrictions, and considerations for privacy.
- CRTC Privacy Regulations: The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) enforces privacy regulations governing the collection and use of personal information by RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies in the industry.
- RoHS Directive: The Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive restricts the use of certain hazardous substances in the manufacturing of RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone devices to safeguard human health and the environment.
- ISED Canada SRSP-514: Regulation by Innovation, Science, and Economic Development Canada on radio equipment, including RFID and BLE devices, ensuring compliance with technical standards and spectrum management.
- S. National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) Voluntary Best Practices for UAS Privacy, Transparency, and Accountability: These guidelines aid drone operators in addressing privacy concerns and promoting responsible drone usage.
- UL 2900: This cybersecurity standard provides guidelines for assessing the security of connected devices, including IoT systems, to protect against cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
U.S. Government Regulations
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations: OSHA ensures workplace safety by establishing and enforcing standards to protect workers in textile manufacturing environments.
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations: The EPA regulates environmental aspects such as air and water quality, waste management, and chemical usage in textile manufacturing processes.
- Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) regulations: CPSC sets safety standards for textiles and textile products, ensuring compliance with safety requirements and labeling guidelines to protect consumers.
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC) regulations: FTC oversees textile labeling, ensuring accurate and transparent information regarding fabric content, country of origin, and care instructions.
- Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act): The FD&C Act governs the safety and labeling of textiles used in medical applications, ensuring adherence to healthcare industry standards and promoting patient safety.
Canadian Government Regulations
- Canadian General Standards Board (CGSB) Standards: CGSB develops standards for various aspects of textile manufacturing, including product performance, testing methods, and quality requirements, promoting consistency and reliability in the industry.
- Competition Bureau Canada: The Competition Bureau enforces fair competition in textile industry, preventing anti-competitive practices and ensuring consumer rights are protected.
- Canada Consumer Product Safety Act: The act establishes safety requirements for textile products to protect Canadian consumers from potential risks and hazards associated with textile materials.
- Health Canada Textile Flammability Regulations: These regulations mandate testing and labeling requirements to address the flammability of textile products, ensuring safety in the event of fire hazards.
- Canadian Competition Act: The act promotes fair competition in textile industry by prohibiting deceptive marketing practices and anti-competitive behavior, ensuring a level playing field for businesses and consumer protection.

Consumer Technology Association

ASTM standard

EPA Toxic Substances Control

IEEE 802.15.4

The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission

RoHS Directive

U.S. National Telecommunications and Information Administrationa

UL 2900

Occupational Safety and Health Administration

Consumer Product Safety Commission

Canadian General Standards Board

Federal Trade Commission
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in technical textiles manufacturing such as:
Personnel Management:
- Employee scheduling and shift management
- Performance evaluation and feedback
- Training and development programs
- Workforce planning and optimization
- Employee onboarding and offboarding processes
Equipment Management:
- Equipment maintenance and repair tracking
- Asset tracking and inventory management
- Equipment utilization and optimization
- Equipment calibration and testing
- Equipment replacement and upgrade planning
Access Control:
- Access control systems for restricted areas
- Employee identification and authentication
- Visitor management and tracking
- Security surveillance and monitoring
- Access logs and audit trails
Warehouse Management:
- Inventory management and stock tracking
- Order fulfillment and picking processes
- Warehouse layout and space optimization
- Receiving and shipping management
- Real-time visibility of stock levels and availability
Supply Chain Management:
- Supplier management and performance tracking
- Demand forecasting and planning
- Order management and tracking
- Logistics and transportation management
- Collaboration with suppliers and partners for seamless supply chain operations
Other Applications:
- Quality control and assurance processes
- Production planning and scheduling
- Compliance management and regulatory adherence
- Product lifecycle management
- Data analytics and business intelligence for decision-making.
GAO has enabled its customers to make use of some of leading software and cloud services in technical textiles manufacturing industry. Below are some of popular software and cloud services in technical textiles manufacturing industry:
- Workday HCM: A cloud-based human capital management platform offering personnel management, workforce planning, talent management, and analytics capabilities.
- Kronos Workforce Ready: A unified cloud-based workforce management solution that includes personnel management, time and attendance tracking, scheduling, and HR analytics.
- Infor CloudSuite HCM: A cloud-based human capital management platform that covers personnel management, payroll, benefits administration, talent management, and workforce planning.
- Blue Yonder: A cloud-based supply chain management platform that integrates planning, execution, and optimization across the entire supply chain.
- Oracle Supply Chain Management Cloud: A comprehensive supply chain management solution that includes modules for demand planning, inventory management, order fulfillment, and logistics.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management: An end-to-end supply chain management solution that covers planning, procurement, inventory management, order fulfillment, and transportation.
- Manhattan Associates Warehouse Management System: A robust warehouse management system that provides advanced capabilities for inventory management, order fulfillment, labor optimization, and automation.
- HighJump Warehouse Management System: A flexible and scalable warehouse management solution that streamlines warehouse operations, improves order accuracy, and optimizes inventory control.
- SAP Extended Warehouse Management: An advanced warehouse management system that offers comprehensive functionalities for warehouse optimization, labor management, inventory tracking, and automation.
- IBM Maximo: An enterprise asset management (EAM) software for equipment management and maintenance.
- Epicor ERP: A comprehensive enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution for managing all aspects of textile manufacturing.
- Netsuite ERP: A cloud-based ERP system for managing various business functions, including supply chain and warehouse management.

Workday HCM

Kronos Workforce Ready

Infor CloudSuite HCM

Blue Yonder

Oracle Supply Chain Management Cloud

Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management

Manhattan Associates Warehouse Management System

HighJump Warehouse Management System

SAP Extended Warehouse Management

IBM Maximo

Epicor ERP

Netsuite ERP
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in technical textiles manufacturing such as:
Personnel Management:
- Employee scheduling and shift management
- Performance evaluation and feedback
- Training and development programs
- Workforce planning and optimization
- Employee onboarding and offboarding processes
Equipment Management:
- Equipment maintenance and repair tracking
- Asset tracking and inventory management
- Equipment utilization and optimization
- Equipment calibration and testing
- Equipment replacement and upgrade planning
Access Control:
- Access control systems for restricted areas
- Employee identification and authentication
- Visitor management and tracking
- Security surveillance and monitoring
- Access logs and audit trails
Warehouse Management:
- Inventory management and stock tracking
- Order fulfillment and picking processes
- Warehouse layout and space optimization
- Receiving and shipping management
- Real-time visibility of stock levels and availability
Supply Chain Management:
- Supplier management and performance tracking
- Demand forecasting and planning
- Order management and tracking
- Logistics and transportation management
- Collaboration with suppliers and partners for seamless supply chain operations
Other Applications:
- Quality control and assurance processes
- Production planning and scheduling
- Compliance management and regulatory adherence
- Product lifecycle management
- Data analytics and business intelligence for decision-making.
GAO has enabled its customers to make use of some of leading software and cloud services in technical textiles manufacturing industry. Below are some of popular software and cloud services in technical textiles manufacturing industry.
- Workday HCM: A cloud-based human capital management platform offering personnel management, workforce planning, talent management, and analytics capabilities.
- Kronos Workforce Ready: A unified cloud-based workforce management solution that includes personnel management, time and attendance tracking, scheduling, and HR analytics.
- Infor CloudSuite HCM: A cloud-based human capital management platform that covers personnel management, payroll, benefits administration, talent management, and workforce planning.
- Blue Yonder: A cloud-based supply chain management platform that integrates planning, execution, and optimization across the entire supply chain.
- Oracle Supply Chain Management Cloud: A comprehensive supply chain management solution that includes modules for demand planning, inventory management, order fulfillment, and logistics.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management: An end-to-end supply chain management solution that covers planning, procurement, inventory management, order fulfillment, and transportation.
- Manhattan Associates Warehouse Management System: A robust warehouse management system that provides advanced capabilities for inventory management, order fulfillment, labor optimization, and automation.
- HighJump Warehouse Management System: A flexible and scalable warehouse management solution that streamlines warehouse operations, improves order accuracy, and optimizes inventory control.
- SAP Extended Warehouse Management: An advanced warehouse management system that offers comprehensive functionalities for warehouse optimization, labor management, inventory tracking, and automation.
- IBM Maximo: An enterprise asset management (EAM) software for equipment management and maintenance.
- Epicor ERP: A comprehensive enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution for managing all aspects of textile manufacturing.
- Netsuite ERP: A cloud-based ERP system for managing various business functions, including supply chain and warehouse management.

IBM

Siemens

Microsoft

Intel

SAP

Oracle

Schneider Electric

Honeywell

Panasonic

Cisco

Siemens Healthineers

Thermo Fisher Scientific
Case study of RFID Applications
Below are some case studies of RFID and UHF RFID application in technical textiles manufacturing industry.
Patagonia Inc., a leading outdoor clothing company, embraced RFID technology to enhance their quality control processes. By attaching RFID tags to fabric rolls, they gained the ability to track and monitor the production stages with precision. This enabled them to ensure adherence to strict quality standards, identify potential issues at early stages, and take prompt corrective actions when necessary. With real-time data provided by RFID, Patagonia Inc. achieved greater visibility and control over their manufacturing operations, resulting in improved product quality, reduced defects, and enhanced customer satisfaction. The implementation of RFID technology empowered them to optimize their quality control procedures, minimize waste, and maintain their reputation as a trusted provider of high-quality textiles.
Nike, Inc., a global leader in athletic footwear and apparel, leveraged UHF RFID technology to transform their asset tracking and management processes. By tagging their textile machinery and equipment with RFID tags, they gained real-time visibility into the utilization, maintenance schedules, and locations of their assets. This allowed them to optimize resource allocation, prevent equipment losses, and schedule timely maintenance interventions, reducing downtime and improving overall operational efficiency. The implementation of UHF RFID technology provided Nike, Inc. with accurate and up-to-date information on their assets, enabling them to make data-driven decisions, enhance productivity, and maximize the lifespan of their machinery and equipment.
Lululemon Athletica, a renowned athletic apparel company, embraced RFID technology to enhance their quality control processes. By attaching RFID tags to fabric rolls, they gained the ability to track and monitor the production stages with precision. This enabled them to ensure adherence to strict quality standards, identify potential issues at early stages, and take prompt corrective actions when necessary. With real-time data provided by RFID, Lululemon Athletica achieved greater visibility and control over their manufacturing operations, resulting in improved product quality, reduced defects, and enhanced customer satisfaction. The implementation of RFID technology empowered them to optimize their quality control procedures, minimize waste, and maintain their reputation as a trusted provider of high-quality textiles.
Levi Strauss & Co., a leading denim and apparel company, leveraged UHF RFID technology to transform their asset tracking and management processes. By tagging their textile machinery and equipment with RFID tags, they gained real-time visibility into the utilization, maintenance schedules, and locations of their assets. This allowed them to optimize resource allocation, prevent equipment losses, and schedule timely maintenance interventions, reducing downtime and improving overall operational efficiency. The implementation of UHF RFID technology provided Levi Strauss & Co. with accurate and up-to-date information on their assets, enabling them to make data-driven decisions, enhance productivity, and maximize the lifespan of their machinery and equipment.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Motion Picture and Sound Recording
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including motion picture and sound recording industries.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including motion picture and sound recording industries.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including t motion picture and sound recording industries
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including motion picture and sound recording industries
and an array of antennas to address different applications
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including motion picture and sound recording industries
- High Frequency 13.56 MHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 134 kHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 125 kHz Passive RFID Readers
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including motion picture and sound recording industries
and antennas
GAO also offers RFID printers
Digital I/O adapters
and relay controllers
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules
- UHF 860 – 960 MHz RFID Modules
- 13.56 MHz High Frequency RFID Modules
- 125 kHz Low Frequency RFID Modules
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in motion picture and sound recording industries
Physical asset or operation equipment tracking system
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include:
- Camera Equipment: High-end digital cameras, film cameras, lenses, and camera support systems.
- Lighting Equipment: Professional lighting fixtures, control systems, and accessories for setting up the desired lighting conditions.
- Sound Recording Equipment: Microphones, mixers, recorders, and boom poles for capturing high-quality audio.
- Editing Software and Hardware: Advanced editing software, workstations, and peripherals for post-production editing and processing.
- Sound Mixing and Dubbing Equipment: Sound consoles, monitors, speakers, and software for mixing and dubbing soundtracks.
- Visual Effects (VFX) Equipment: High-performance computers, rendering servers, and specialized software for creating visual effects.
- Green Screens and Chroma Key Equipment: Backdrops and keying tools for compositing actors and objects into virtual or composited environments.
- Motion Capture Equipment: Optical or inertial systems for capturing the movements of actors or objects for animation purposes.
- Drone Cameras: Remote-controlled aerial cameras for capturing unique perspectives and aerial shots.
People or workers tracking system
Personnel or people access control system
Parking or vehicle control system
GAO Has Served Technical Textiles Manufacturing Extensively
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in the technical textiles manufacturing industry to achieve success in smart textiles, wearable technology, functional fabrics, digital printing, nanotechnology, e-textiles, advanced materials, circular economy, performance enhancement, bio-based textiles, smart garments.
GAO RFID Inc. has served many customers in Technical Textiles Manufacturing, including its various divisions such as:
- Protective Textiles: Manufacturing textiles designed to protect individuals from hazards such as heat, chemicals, flames, or ballistic threats, ensuring safety in various industries.
- Medical Textiles: Producing textiles used in medical applications, including surgical gowns, wound dressings, implants, and healthcare fabrics, contributing to patient comfort and healthcare outcomes.
- Geotextiles: Manufacturing materials used in civil engineering and construction projects to reinforce soil, control erosion, provide drainage, and enhance soil stability and filtration.
- Automotive Textiles: Producing textiles for automotive applications, such as upholstery, seat belts, airbags, carpets, and sound insulation, providing comfort, safety, and aesthetic appeal in vehicles.
- Sports and Outdoor Textiles: Manufacturing textiles for sportswear, outdoor clothing, tents, backpacks, sleeping bags, duffel bags, and travel gear combines functionality, durability, and comfort for outdoor enthusiasts and athletes.
- Agro-Tech Textiles: Producing textiles used in agriculture, horticulture, and aquaculture, including crop covers, shade nets, fishing nets, and geotextiles for soil stabilization and protection.
- Home Textiles: Manufacturing textiles for home furnishing, including curtains, upholstery, bedding, carpets, and towels, enhancing aesthetics, comfort, and functionality in residential spaces.
- Filtration Textiles: Manufacturing textiles used in air and liquid filtration systems, including filter media, filter bags, and membranes, ensuring efficient and reliable filtration in various industries.
- Aerospace Textiles: Producing textiles for the aerospace industry, including aircraft interiors, seat covers, insulation materials such as polyester or polypropylene fibers, and lightweight composites for improved performance and passenger comfort.
- Smart Textiles: Developing textiles embedded with electronic components such as temperature sensors, humidity sensors, or motion sensors, enabling functionalities such as temperature regulation, moisture management, and biometric monitoring.
Here are some of the leading companies in technical textiles manufacturing industry:

Milliken & Company

DuPont de Nemours, Incorporated

International Textile Group

Freudenberg Performance Materials Company

Kimberly-Clark Corporation

Berry Global Group

3M Company

Honeywell International Incorporated

Glen Raven, Incorporated

Eastman Chemical Company

W. L. Gore & Associates, Incorporated

Nan Ya Plastics Corporation

Saint-Gobain Performance Plastics Company

Ahlstrom-Munksjö Company

Ascend Performance Materials Company

Hollingsworth & Vose Company

Trelleborg AB Company

AstenJohnson Company

Groupe PolyAlto

HUESKER Synthetic GmbH Company

Naizil Canada Limited

The Stevens Company Limited

Integrated Textile Solutions Company

North American Textile Company Limited
