
Overview
The Transportation Equipment Manufacturing Industry is a sector of the economy that encompasses the production of vehicles and related components used for transportation purposes. This industry includes the manufacturing of various modes of transportation, such as automobiles, trucks, buses, motorcycles, airplanes, trains, ships, and other vehicles. Additionally, it involves the production of parts, components, and systems that are essential for these modes of transportation to operate efficiently and safely.
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in transportation equipment manufacturing industry to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials and operational equipment such as automated assembly lines, welding robots, stamping presses, and CNC machining centers play crucial roles. Aerospace and aviation manufacturing relies on aircraft assembly jigs, precision machining equipment, and specialized machinery for composite material production. Rail and locomotive manufacturing utilize assembly lines, rail welding equipment, and inspection tools. Shipbuilding requires ship assembly and launching cranes, plate cutting machines, and welding equipment
Ranked as one of the top 10 global RFID suppliers, GAO RFID Inc. is based in New York City, U.S. and Toronto, Canada. GAO offers a comprehensive selection of UHF, HF (including NFC) and LF RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags, BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. RFID and BLE products and systems, as well as its IoT and drone technologies, have been successfully deployed for transportation equipment manufacturing industry. Its sister company, GAO Tek Inc. https://gaotek.com, is a leading supplier of industrial or commercial testers and analyzers, drones, and network products.
The targeted markets of both GAO RFID Inc. and GAO Tek Inc. are North America, particularly the U.S., Canada, Mexico, and Europe. As a result, this website gaorfid.com is offered in English and other major languages of North America and Europe such as Spanish, French, German, Italian, Polish, Ukrainian, Romanian, Russian, Dutch, Turkish, Greek, Hungarian, Swedish, Czech, Portuguese, Serbian, Bulgarian, Croatian, Danish, Finnish, Norwegian, Slovak, Catalan, Lithuanian, Bosnian, Galician, Slovene, Latvian, Estonian, Welsh, Icelandic, and Irish.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for Transportation Equipment Manufacturing Industry
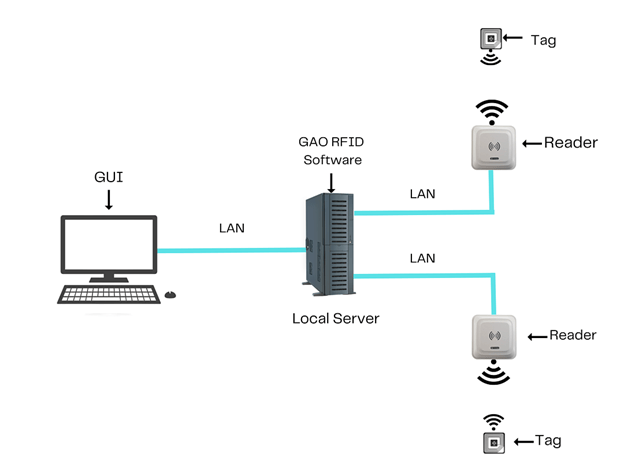
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for sub-industry are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server that normally is on our client’s premises, and another version runs in the cloud. The cloud server could be GAO’s cloud server, client’s own cloud server or a cloud server from one of the leading cloud server providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud (formerly SoftLayer), Oracle Cloud, RedHat, Heroku, Digital Ocean, CloudFlare, Linode and Rackspace. The above illustrates GAO system for transportation equipment manufacturing industry with its software running on a local server.
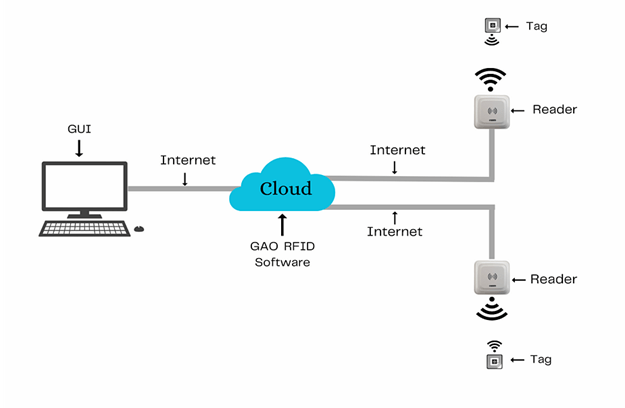 The above illustrates GAO system for transportation equipment manufacturing industry with its software running in cloud.
The above illustrates GAO system for transportation equipment manufacturing industry with its software running in cloud.
GAO’s RFID and BLE technologies, consisting of RFID readers, RFID tags, BLE gateways, BLE beacons, software, cloud services and their systems, have the following applications in transportation equipment manufacturing industry:
- Inventory Management: GAO RFID tags are used to track and manage inventory of parts, components, and materials in manufacturing plants. This ensures accurate stock levels and reduces the risk of production delays due to missing items.
- Work-in-Progress Tracking: GAO RFID tags can be attached to semi-finished products or components as they move through the manufacturing process. This allows manufacturers to monitor the progress of each item and identify any bottlenecks in production.
- Asset Tracking: GAO RFID is used to track the location and status of critical assets such as machinery, tools, and equipment. This helps in preventing loss or theft and ensures that equipment is available when needed.
- Quality Control: GAO RFID tags can be used to associate quality control data with specific components or products. This allows manufacturers to trace defects back to their source and implement corrective measures.
- Maintenance and Repairs: GAO RFID tags on machinery and vehicles enable manufacturers to schedule and track maintenance activities more efficiently. This minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of equipment.
- Supply Chain Visibility: GAO RFID is employed to monitor the movement of materials and products through the supply chain, providing real-time visibility and enabling efficient logistics management.
- Security: GAO RFID access control systems help restrict unauthorized access to sensitive areas within manufacturing facilities, ensuring safety and security.
- Customization and Configuration: GAO RFID tags can store information about a product’s configuration and customization options, helping manufacturers assemble products according to customer specifications.
- Compliance and Documentation: GAO RFID can aid in automating compliance checks and documentation processes, ensuring that products meet regulatory requirements.
- Shipping and Distribution: GAO RFID tags are used in tracking finished products as they are shipped to distributors or customers, providing visibility into the shipping process and enabling efficient delivery.
GAO’s drone technologies find the following applications in the transportation equipment manufacturing industry:
- Inventory Management: GAO drones equipped with cameras and sensors can perform aerial inventory counts of raw materials, components, and finished products in manufacturing facilities. This improves inventory accuracy and reduces manual labor.
- Site Surveys: GAO drones can conduct aerial surveys of manufacturing plant sites to assess terrain, topography, and infrastructure. This data aids in site selection, construction planning, and expansion projects.
- Quality Control Inspections: GAO drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors can inspect vehicles, components, and equipment for defects, ensuring quality standards are met during the manufacturing process.
- Progress Monitoring: GAO drones provide real-time aerial views of ongoing manufacturing projects, allowing managers to monitor progress, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions to keep projects on schedule.
- Maintenance Inspections: GAO drones can access difficult-to-reach areas of machinery and equipment for routine inspections. They capture images and data to identify maintenance needs, reducing downtime.
- Security and Surveillance: GAO drones equipped with cameras and thermal imaging can enhance security by patrolling manufacturing sites, identifying unauthorized access, and monitoring for potential security threats.
- Supply Chain Visibility: GAO drones can be used to track the movement of materials and components within manufacturing facilities and between suppliers and plants, providing real-time visibility into the supply chain.
- Environmental Monitoring: GAO drones equipped with environmental sensors can monitor air and water quality, noise levels, and other environmental factors in and around manufacturing facilities to ensure compliance with regulations.
- Prototype Testing: GAO drones can transport prototypes and experimental components for testing in real-world conditions, allowing engineers and researchers to gather valuable data.
- Transportation: GAO drones can assist in transporting small parts or documents between different areas of a manufacturing plant, reducing the need for manual handling and improving efficiency.
GAO’s IoT technologies, consisting of IoT sensors, sensors networks and systems, find the following applications in the transportation equipment manufacturing industry:
- Inventory Management: GAO drones equipped with cameras and sensors can perform aerial inventory counts of raw materials, components, and finished products in manufacturing facilities. This improves inventory accuracy and reduces manual labor.
- Site Surveys: GAO drones can conduct aerial surveys of manufacturing plant sites to assess terrain, topography, and infrastructure. This data aids in site selection, construction planning, and expansion projects.
- Quality Control Inspections: GAO drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors can inspect vehicles, components, and equipment for defects, ensuring quality standards are met during the manufacturing process.
- Progress Monitoring: GAO drones provide real-time aerial views of ongoing manufacturing projects, allowing managers to monitor progress, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions to keep projects on schedule.
- Maintenance Inspections: GAO drones can access difficult-to-reach areas of machinery and equipment for routine inspections. They capture images and data to identify maintenance needs, reducing downtime.
- Security and Surveillance: GAO drones equipped with cameras and thermal imaging can enhance security by patrolling manufacturing sites, identifying unauthorized access, and monitoring for potential security threats.
- Supply Chain Visibility: GAO drones can be used to track the movement of materials and components within manufacturing facilities and between suppliers and plants, providing real-time visibility into the supply chain.
- Environmental Monitoring: GAO drones equipped with environmental sensors can monitor air and water quality, noise levels, and other environmental factors in and around manufacturing facilities to ensure compliance with regulations.
- Prototype Testing: GAO drones can transport prototypes and experimental components for testing in real-world conditions, allowing engineers and researchers to gather valuable data.
- Transportation: GAO drones can assist in transporting small parts or documents between different areas of a manufacturing plant, reducing the need for manual handling and improving efficiency.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of Transportation Equipment Manufacturing industry
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in transportation equipment manufacturing industry to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates and government regulations:
RFID, BLE, IoT, & Drone Standards & Mandates
- ISO 10374
- ISO 17363
- ISO 18185
- ISO 18186
- ISO 18187
- ISO 18190
- ISO 18191
- ISO 19223
- ISO 19849
- ISO 21093
- BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) Core Specification
- GATT (Generic Attribute Profile)
- ATT (Attribute Protocol)
- Bluetooth Mesh Profile
- Bluetooth 4.0
- Bluetooth 4.1
- Bluetooth 4.2
- Bluetooth 5
- Bluetooth 5.1
- Bluetooth 5.2
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol)
- OPC UA (Unified Architecture)
- DDS (Data Distribution Service)
- Zigbee
- LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network)
- Thread
- Modbus
- BACnet (Building Automation and Control Networks)
- AllJoyn (now part of Project CHIP – Connected Home over IP)
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
- Thread Group Standards
- Industrial IoT (IIoT) Standards
- IoT Security Standards
- ISO 27001
- ISO 21384 (Part 1-3)
- ASTM F3322
- ANSI/UL 3030
- ISO 19684 (Part 1-4)
- AS/NZS 4815
- ANSI/ASSP A10.9
- JARUS (Joint Authorities for Rulemaking on Unmanned Systems)
- FAA (Federal Aviation Administration) Regulations
- EASA (European Union Aviation Safety Agency) Regulations
- Transport Canada Regulations
- CASA (Civil Aviation Safety Authority) Regulations
- DGCA (Directorate General of Civil Aviation) Regulations
- ASTM F3322
- ANSI/UL 3030
- JARUS (Joint Authorities for Rulemaking on Unmanned Systems)
- FAA (Federal Aviation Administration) Regulations
- EASA (European Union Aviation Safety Agency) Regulations
- Transport Canada Regulations
- CASA (Civil Aviation Safety Authority) Regulations
- DGCA (Directorate General of Civil Aviation) Regulations
US Government Regulations
- Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS)
- Federal Aviation Regulations (FARs)
- Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) Regulations
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) Regulations
- Federal Transit Administration (FTA) Regulations
- Federal Maritime Commission (FMC) Regulations
- Federal Highway Administration (FHA) Regulations
- Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Regulations
- Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) Regulations
- Federal Maritime Administration (MARAD) Regulations
- Federal Transit Administration (FTA) Regulations
- Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) Regulations
- Federal Highway Administration (FHA) Regulations
- Federal Transit Administration (FTA) Regulations
- Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Regulations
Canadian Government Regulations
- Motor Vehicle Safety Regulations (MVSR)
- Canadian Aviation Regulations (CARs)
- Canadian Rail Operating Rules (CROR)
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations (TDG)
- Canada Shipping Act, 2001
- Marine Transportation Security Regulations (MTSR)
- Transport Canada Civil Aviation (TCCA) Regulations
- Transportation Appeal Tribunal of Canada (TATC) Regulations
- Canada Labour Code – Part II
- Canadian Transportation Agency (CTA) Regulations
- Railway Safety Management System (SMS) Regulations
- Canada Labour Code – Part III (Occupational Health and Safety)
- Canadian Environmental Assessment Act
- Canada Infrastructure Bank Act
- Canada Transportation Act
GAO’s Software Provides API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in Transportation equipment manufacturing industry such as:
Personnel Management:
- Workforce Scheduling and Optimization
- Employee Training and Certification Tracking
- Health and Safety Compliance
- Labor Union Management
Equipment Management:
- Maintenance and Repairs Tracking
- Asset Tracking and Utilization
- Predictive Maintenance
- Fleet Management
Access Control:
- Facility Security
- Visitor Management
- Restricted Area Access
Warehouse Management:
- Inventory Control
- Order Fulfillment
- Storage Optimization
- Shipping and Receiving
Supply Chain Management:
- Supplier Relationship Management
- Demand Forecasting
- Logistics and Transportation Optimization
- Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI)
Other Applications:
- Quality Control and Assurance
- Regulatory Compliance Monitoring
- Environmental Impact Assessment
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
GAO has enabled its customers to make use of some of the leading software and cloud services in the transportation equipment manufacturing industry. Below are some of the popular software and cloud services in the transportation equipment manufacturing industry.
Oracle Human Capital Management (HCM) provides a comprehensive suite of HR software, encompassing talent management and workforce planning. Workday Human Capital Management is a cloud-based option for HR and talent management. ADP Workforce Now focuses on HR and payroll solutions, while Kronos Workforce Central specializes in workforce management and timekeeping.
In terms of equipment management, several prominent software options cater to the industry’s needs. IBM Maximo stands out with its asset management capabilities, allowing for efficient maintenance and repairs tracking. Infor EAM offers enterprise asset management software for optimizing equipment maintenance and performance. Oracle Maintenance Cloud is a cloud-based solution for maintenance management. Dude Solutions provides a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) designed to manage assets effectively.
Simultaneously, equipment management plays a pivotal role in this industry, and cloud-based services cater to these needs as well. Prominent cloud services for equipment management include IBM Maximo, Infor CloudSuite EAM, Oracle Cloud Maintenance Cloud, Dude Solutions, and eMaint CMMS.
In the Transportation Equipment Manufacturing sector, access control is crucial for ensuring the security and safety of facilities. Prominent access control software solutions include Honeywell Access Control, LenelS2, Genetec Security Center, Brivo, and Avigilon Access Control Manager (ACM). These solutions offer advanced features such as card readers, biometric access, visitor management, and security monitoring to maintain secure facility access.
Efficient warehouse management is another key aspect of this industry. Software options designed to optimize inventory management and distribution operations include SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM), Infor WMS (Warehouse Management System), HighJump WMS, Manhattan Associates Warehouse Management, and Oracle Warehouse Management Cloud.
GAO has worked with some of the leading technology companies in the transportation equipment manufacturing industry to provide integrated RFID, BLE, IoT and drone solutions to customers. Here are some of the technology leaders in transportation equipment manufacturing industry:
IBM, Oracle, SAP, Microsoft, Siemens, Honeywell, Rockwell Automation, Cisco, Accenture, Deloitte, PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC), KPMG, Ernst & Young (EY), Capgemini, Cognizant, Wipro, Infosys, DXC Technology, CGI, Tata Consultancy Services (TCS), Tech Mahindra, HCL Technologies, Atos, NTT Data, and Hitachi
Case Studies of RFID, IoT & Drone Applications
Case Studies of RFID
Below are some RFID application cases in the transportation equipment manufacturing industry.
- Improved Inventory Management: Explore how RFID technology has helped transportation equipment manufacturers in both countries streamline their inventory tracking processes, reduce errors, and optimize stock levels.
- Supply Chain Visibility: Investigate how RFID has been used to enhance supply chain visibility, allowing manufacturers to track the movement of raw materials and components across borders efficiently.
- Asset Tracking: Examine case studies on the use of RFID for tracking high-value assets such as heavy machinery, vehicles, and specialized equipment, contributing to better asset utilization and maintenance.
- Work-in-Progress Tracking: Analyze how RFID systems have been implemented to monitor the production process, ensuring that equipment is assembled correctly and efficiently.
- Quality Control: Investigate how RFID is used for quality control and defect detection during the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet industry standards.
- Maintenance and Servicing: Explore case studies that demonstrate how RFID helps transportation equipment manufacturers schedule preventive maintenance and track servicing needs to extend the lifespan of their products.
- Customization and Personalization: Investigate examples of how RFID technology is used to offer customized or personalized features in transportation equipment, such as vehicle options or onboard systems.
- Regulatory Compliance: Investigate how RFID systems assist manufacturers in complying with safety and environmental regulations in both the USA and Canada.
- Security and Anti-Theft Measures: Analyze cases where RFID technology has been used to enhance security measures and reduce the risk of theft or unauthorized access to transportation equipment.
- Environmental Impact: Explore how RFID applications support sustainability efforts, such as tracking the recyclability of materials or ensuring compliance with emissions standards.
- Optimizing Supply Chain Visibility: Explore how Canadian transportation equipment manufacturers have utilized RFID technology to enhance supply chain visibility, track the movement of components, and streamline the logistics of transporting materials to manufacturing facilities.
- Enhancing Manufacturing Efficiency: Investigate case studies demonstrating how RFID systems have been implemented in Canadian manufacturing plants to monitor and optimize production processes, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
- Inventory Management: Analyze how RFID has been applied in Canadian transportation equipment manufacturing to improve inventory management, reduce stockouts, and ensure the availability of critical components.
- Quality Assurance: Explore examples of how RFID technology is used in Canada to enforce quality control measures, track product defects, and ensure that manufactured equipment meets industry and regulatory standards.
- Asset Tracking and Management: Investigate how Canadian manufacturers use RFID for tracking and managing high-value assets, such as heavy machinery and specialized equipment, to reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
- Customization and Personalization: Examine cases where RFID applications in Canada have been used to offer customization and personalization options to customers, allowing them to tailor transportation equipment to their specific needs.
- Maintenance and Servicing: Analyze how RFID systems help Canadian transportation equipment manufacturers schedule routine maintenance, monitor equipment health, and provide timely servicing to extend the lifespan of their products.
- Compliance with Regulations: Explore how RFID technology assists Canadian manufacturers in ensuring compliance with safety, environmental, and regulatory standards in the transportation equipment industry.
- Security Measures: Investigate cases where RFID applications enhance security measures in Canadian manufacturing facilities, protecting equipment and assets from theft or unauthorized access.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Examine how RFID technology supports sustainability efforts in Canada’s transportation equipment manufacturing sector, including tracking recyclable materials and monitoring emissions to meet environmental goals.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Investigate how Mexican transportation equipment manufacturers have leveraged RFID technology to optimize their supply chains. This could include tracking the movement of raw materials, components, and finished products to ensure timely deliveries and minimize disruptions.
- Inventory Management: Analyze case studies showcasing how RFID systems are used in Mexican manufacturing plants to streamline inventory management processes. This might involve reducing excess inventory, preventing stockouts, and improving overall inventory accuracy.
- Work-in-Progress Tracking: Explore examples of how Mexican manufacturers use RFID to monitor work-in-progress (WIP) on the factory floor. RFID tags can help track the status of different components and assemblies, allowing for more efficient production scheduling.
- Quality Control: Examine how RFID technology has been implemented in Mexican transportation equipment manufacturing to enhance quality control processes. Case studies could focus on how RFID is used to detect defects early in the production cycle and ensure compliance with industry standards.
- Asset Tracking: Investigate cases where Mexican manufacturers use RFID for tracking and managing valuable assets, such as heavy machinery and specialized equipment. RFID can help prevent asset loss or theft and optimize asset utilization.
- Customization and Traceability: Analyze how RFID applications in Mexico’s transportation equipment industry enable customization of products and provide traceability throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring that each unit meets customer specifications.
- Maintenance and Servicing: Explore how Mexican manufacturers utilize RFID technology to schedule preventative maintenance, monitor equipment health, and provide timely servicing to maximize equipment lifespan and minimize downtime.
- Regulatory Compliance: Investigate RFID’s role in helping Mexican manufacturers ensure compliance with safety, environmental, and regulatory standards specific to the transportation equipment sector.
- Security Enhancements: Examine cases where RFID applications enhance security measures within Mexican manufacturing facilities, safeguarding equipment, and assets against theft, unauthorized access, or tampering.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Analyze how RFID technology supports sustainability efforts within Mexico’s transportation equipment manufacturing industry. This could involve tracking recyclable materials, monitoring emissions, or reducing waste.
- Smart Factories: Investigate how European transportation equipment manufacturers have transformed their factories into smart, connected environments using RFID technology. Case studies could highlight improved production efficiency, reduced operational costs, and enhanced quality control.
- Supply Chain Visibility: Analyze how RFID systems enable end-to-end visibility across the supply chain for European manufacturers. Explore how RFID is used to track parts and components from suppliers, through production, and ultimately to the end customer.
- Customization and Personalization: Explore examples of European manufacturers leveraging RFID to offer customized and personalized transportation equipment to customers. Case studies could showcase how RFID-enabled production lines adapt to individual customer preferences.
- Maintenance and Predictive Analytics: Investigate how RFID tags and sensors are used in European transportation equipment manufacturing to monitor the health of vehicles and predict maintenance needs. This proactive approach can reduce downtime and improve safety.
- Quality Assurance: Analyze how RFID technology ensures quality assurance throughout the manufacturing process in Europe. Case studies could focus on how RFID-enabled inspections and testing contribute to meeting stringent industry standards.
- Inventory Optimization: Explore how European manufacturers use RFID for real-time inventory tracking and optimization. Case studies might highlight reduced carrying costs, minimized stockouts, and improved order accuracy.
- Sustainability and Compliance: Investigate RFID’s role in helping European transportation equipment manufacturers achieve sustainability goals and comply with environmental regulations. Explore how RFID is used to track recyclable materials and monitor emissions.
- Asset Management: Analyze how RFID tags are used to track and manage valuable assets, such as machinery, tools, and vehicles, in European manufacturing facilities. Case studies could demonstrate how RFID improves asset utilization and reduces loss.
- Worker Safety: Explore RFID applications for ensuring worker safety in European manufacturing plants. Case studies might focus on how RFID-enabled access control and safety systems prevent accidents and unauthorized access to hazardous areas.
- Traceability and Recall Management: Investigate how European transportation equipment manufacturers use RFID to establish traceability of components and vehicles. Case studies could highlight how RFID simplifies recall management and enhances consumer safety.
Many applications of RFID by GAO can be found here
Case Studies of IoT Applications
Below are some IoT application cases in the transportation equipment manufacturing industry.
- Predictive Maintenance: Explore how IoT sensors and data analytics are used in the manufacturing of transportation equipment in the USA to predict maintenance needs. Case studies could focus on how this approach reduces downtime, extends the lifespan of machinery, and improves overall operational efficiency.
- Connected Vehicles: Analyze how IoT technology is integrated into the production of connected vehicles, such as smart cars and commercial trucks, in the USA. Case studies could demonstrate how IoT enables features like vehicle-to-vehicle communication, autonomous driving, and enhanced safety systems.
- Supply Chain Visibility: Investigate how IoT devices and platforms provide real-time visibility into the supply chain for transportation equipment manufacturers in the USA. Case studies might highlight how IoT improves tracking of parts, components, and finished products as they move through the supply chain.
- Energy Efficiency: Explore IoT-driven initiatives in the USA’s transportation equipment manufacturing sector to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact. Case studies could showcase how IoT sensors optimize energy usage in manufacturing facilities.
- Quality Control: Analyze how IoT sensors and data analytics ensure quality control and adherence to industry standards during the production of transportation equipment in the USA. Case studies might focus on how IoT-driven inspections and testing enhance product quality.
- Worker Safety: Investigate IoT applications for ensuring worker safety in manufacturing plants in the USA. Case studies could highlight how IoT-enabled wearables and safety systems prevent accidents and monitor employee well-being.
- Inventory Management: Explore how IoT technology is used for real-time inventory management in transportation equipment manufacturing in the USA. Case studies could demonstrate how IoT reduces carrying costs, minimizes stockouts, and improves order accuracy.
- Fleet Management: Analyze how IoT solutions are employed in managing and monitoring vehicle fleets, especially in the case of commercial transportation equipment. Case studies could focus on how IoT enhances vehicle tracking, maintenance scheduling, and fuel efficiency.
- Customization and Personalization: Investigate how IoT technologies enable customization and personalization of transportation equipment in the USA. Case studies might highlight how IoT-driven production lines adapt to individual customer preferences.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Explore how IoT enables remote monitoring and control of manufacturing processes and equipment. Case studies could showcase how manufacturers in the USA use IoT for real-time adjustments and troubleshooting.
- Industry Publications: Check industry-specific publications, journals, and magazines related to transportation equipment manufacturing in Canada. These sources may feature case studies or articles on IoT implementations.
- Government Reports: Government agencies, such as Industry Canada, may publish reports on technology adoption and innovation in the transportation sector. These reports may include case studies.
- Academic Research: Explore academic research papers and studies conducted by Canadian universities or research institutions. They often include detailed case studies on specific IoT applications.
- Company Websites: Visit the websites of transportation equipment manufacturing companies in Canada. Some companies may publish case studies or success stories related to their IoT initiatives.
- Consult Industry Associations: Contact industry associations related to transportation equipment manufacturing in Canada, such as the Canadian Association of Railway Suppliers (CARS) or the Canadian Vehicle Manufacturers’ Association (CVMA). They may have resources or case studies.
- Online Databases: Use academic databases, industry-specific search engines, or business research platforms to search for IoT case studies in the Canadian context. Examples include Google Scholar, IEEE Xplore, and industry-specific databases.
- Networking: Attend industry conferences, seminars, and networking events in Canada where experts and professionals share insights and case studies related to IoT applications.
- Industry Publications: Check industry-specific publications, journals, and magazines related to transportation equipment manufacturing in Mexico. These sources may feature case studies or articles on IoT implementations.
- Government Reports: Government agencies in Mexico may publish reports on technology adoption and innovation in the transportation sector. These reports may include case studies.
- Academic Research: Explore academic research papers and studies conducted by Mexican universities or research institutions. They often include detailed case studies on specific IoT applications.
- Company Websites: Visit the websites of transportation equipment manufacturing companies in Mexico. Some companies may publish case studies or success stories related to their IoT initiatives.
- Consult Industry Associations: Contact industry associations related to transportation equipment manufacturing in Mexico, such as the Mexican Association of the Automotive Industry (AMIA) or the Mexican Association of Railroads (AMF). They may have resources or case studies.
- Online Databases: Use academic databases, industry-specific search engines, or business research platforms to search for IoT case studies in the Mexican context. Examples include Google Scholar, IEEE Xplore, and industry-specific databases.
- Networking: Attend industry conferences, seminars, and networking events in Mexico where experts and professionals share insights and case studies related to IoT applications.
- Industry Publications: Check industry-specific publications, journals, and magazines related to transportation equipment manufacturing in Europe. These sources may feature case studies or articles on IoT implementations.
- Government Reports: Government agencies in European countries may publish reports on technology adoption and innovation in the transportation sector. These reports may include case studies.
- Academic Research: Explore academic research papers and studies conducted by European universities or research institutions. They often include detailed case studies on specific IoT applications.
- Company Websites: Visit the websites of transportation equipment manufacturing companies in Europe. Some companies may publish case studies or success stories related to their IoT initiatives.
- Consult Industry Associations: Contact industry associations related to transportation equipment manufacturing in Europe, such as the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA) or the European Rail Industry Association (UNIFE). They may have resources or case studies.
- Online Databases: Use academic databases, industry-specific search engines, or business research platforms to search for IoT case studies in the European context. Examples include Google Scholar, IEEE Xplore, and industry-specific databases.
- Networking: Attend industry conferences, seminars, and networking events in Europe where experts and professionals share insights and case studies related to IoT applications.
Case Studies of Drone Applications
Below are some drone application cases in the transportation equipment manufacturing industry.
- Industry Publications: Check industry-specific publications, journals, and magazines related to transportation equipment manufacturing in the USA. These sources may feature case studies or articles on drone implementations.
- Government Reports: Government agencies in the USA may publish reports on technology adoption and innovation in the transportation sector, including drone applications. Examples include the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and the Department of Transportation (DOT).
- Company Websites: Visit the websites of transportation equipment manufacturing companies in the USA. Some companies may publish case studies or success stories related to their drone initiatives.
- Academic Research: Explore academic research papers and studies conducted by U.S. universities or research institutions. They often include detailed case studies on specific drone applications.
- Industry Associations: Contact industry associations related to transportation equipment manufacturing in the USA, such as the Association of American Railroads (AAR) or the National Association of Manufacturers (NAM). They may have resources or case studies.
- Online Databases: Use academic databases, industry-specific search engines, or business research platforms to search for drone case studies in the U.S. context. Examples include Google Scholar, IEEE Xplore, and industry-specific databases.
- Networking: Attend industry conferences, seminars, and networking events in the USA where experts and professionals share insights and case studies related to drone applications in transportation.
- Industry Publications: Check industry-specific publications, journals, and magazines related to transportation equipment manufacturing in Canada. These sources may feature case studies or articles on drone implementations.
- Government Reports: Government agencies in Canada may publish reports on technology adoption and innovation in the transportation sector, including drone applications. Examples include Transport Canada and Innovation, Science, and Economic Development Canada.
- Company Websites: Visit the websites of transportation equipment manufacturing companies in Canada. Some companies may publish case studies or success stories related to their drone initiatives.
- Academic Research: Explore academic research papers and studies conducted by Canadian universities or research institutions. They often include detailed case studies on specific drone applications.
- Industry Associations: Contact industry associations related to transportation equipment manufacturing in Canada, such as the Canadian Manufacturers & Exporters (CME). They may have resources or case studies.
- Online Databases: Use academic databases, industry-specific search engines, or business research platforms to search for drone case studies in the Canadian context. Examples include Google Scholar, IEEE Xplore, and industry-specific databases.
- Networking: Attend industry conferences, seminars, and networking events in Canada where experts and professionals share insights and case studies related to drone applications in transportation.
- Industry Publications: Check industry-specific publications, journals, and magazines related to transportation equipment manufacturing in Mexico. These sources may feature case studies or articles on drone implementations.
- Government Reports: Government agencies in Mexico may publish reports on technology adoption and innovation in the transportation sector, including drone applications. Examples include the Secretariat of Communications and Transportation (SCT) and the Ministry of Economy.
- Company Websites: Visit the websites of transportation equipment manufacturing companies in Mexico. Some companies may publish case studies or success stories related to their drone initiatives.
- Academic Research: Explore academic research papers and studies conducted by Mexican universities or research institutions. They often include detailed case studies on specific drone applications.
- Industry Associations: Contact industry associations related to transportation equipment manufacturing in Mexico, such as the Mexican Association of the Automotive Industry (AMIA). They may have resources or case studies.
- Online Databases: Use academic databases, industry-specific search engines, or business research platforms to search for drone case studies in the Mexican context. Examples include Google Scholar, IEEE Xplore, and industry-specific databases.
- Networking: Attend industry conferences, seminars, and networking events in Mexico where experts and professionals share insights and case studies related to drone applications in transportation.
- Industry Publications: Check industry-specific publications, journals, and magazines related to transportation equipment manufacturing in Europe. These sources may feature case studies or articles on drone implementations.
- Government Reports: Government agencies in European countries may publish reports on technology adoption and innovation in the transportation sector, including drone applications. Examples include the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and national transportation authorities.
- Company Websites: Visit the websites of transportation equipment manufacturing companies in Europe. Some companies may publish case studies or success stories related to their drone initiatives.
- Academic Research: Explore academic research papers and studies conducted by European universities or research institutions. They often include detailed case studies on specific drone applications.
- Industry Associations: Contact industry associations related to transportation equipment manufacturing in Europe, such as the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA). They may have resources or case studies.
- Online Databases: Use academic databases, industry-specific search engines, or business research platforms to search for drone case studies in the European context. Examples include Google Scholar, IEEE Xplore, and industry-specific databases.
- Networking: Attend industry conferences, seminars, and networking events in Europe where experts and professionals share insights and case studies related to drone applications in transportation.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for Transportation Equipment Manufacturing Industry
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including transportation equipment manufacturing industry.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including the transportation equipment manufacturing industry.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including transportation equipment manufacturing industry:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including transportation equipment manufacturing industry:
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including transportation equipment manufacturing industry:
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including transportation equipment manufacturing industry:
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
Digital I/O adapters:
and relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
In collaboration with its sister company GAO Tek Inc, a wide selection of high quality drones are offered:
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in transportation equipment manufacturing industry:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include welding machines for joining metal components, CNC machining centers for precision machining, metal stamping presses for forming sheet metal, robotic assembly systems for automation, injection molding machines for plastic part production, and painting and coating equipment for vehicle finishing. Material handling equipment like forklifts and conveyors is essential for moving heavy components, while testing and inspection equipment ensures quality control. CNC laser cutting machines are used for precise cutting, and assembly line equipment
People or workers tracking system:
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
Furthermore, GAO provides the customization of RFID tags, RFID readers, BLE beacons and BLE gateways, IoT, drones, and systems and consulting services for transportation equipment manufacturing industry and for various industries in all metropolitans in North America, particularly the U.S., Canada and Mexico, and Europe:
GAO Makes Efforts to Satisfy Customers
Large Choice of Products
To satisfy the diversified needs of their corporate customers, GAO RFID Inc. and its sister company GAO Tek Inc. together offer a wide choice of RFID, BLE, IoT, drones, testing and measurement devices, and network products.
Overnight Delivery
To shorten the delivery to our customers, GAO has maintained a large stock of its products and is able to ship overnight within continental U.S. and Canada, and fast delivery to anywhere in Mexico and Europe from the nearest warehouse.
Local to Our Customers
We are in both the U.S. and Canada. We travel to customers’ premises if necessary. Hence, we provide a very strong local support to our customers in North America, particularly the U.S., Canada and Mexico, and Europe. Furthermore, we have built partnerships with some integrators, consulting firms and other service providers in different cities to further strengthen our services. Here are some of the service providers in transportation equipment manufacturing industry we have worked with to serve our joint customers:
- IBM Global Business Services
- Deloitte
- Accenture
- Capgemini
- Cognizant
- Wipro
- Infosys
- DXC Technology
- CGI
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)
- Tech Mahindra
- HCL Technologies
- IBM Canada
- Deloitte Canada
- Accenture Canada
- Capgemini Canada
- Cognizant Canada
- Wipro Canada
- Infosys Canada
- CGI Canada
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) Canada
- Tech Mahindra Canada
- HCL Technologies Canada
- IBM Mexico
- Deloitte Mexico
- Accenture Mexico
- Capgemini Mexico
- Cognizant Mexico
- WEG Mexico
- Toshiba Mexico
- SolarEdge Mexico
- Schlumberger Mexico
- IBM Europe
- Deloitte Europe
- Accenture Europe
- Capgemini Europe
- Cognizant Europe
- Wipro Europe
- Infosys Europe
- CGI Europe
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) Europe
- Tech Mahindra Europe
- HCL Technologies Europe
GAO Has Served Transportation Equipment Manufacturing Industry Extensively
GAO RFID Inc. and its sister company GAO Tek Inc. together offer a wide choice of RFID, BLE, IoT, drone, testing and measurement devices, and network products.
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in transportation equipment manufacturing industry to achieve success in General Motors (GM), Ford Motor Company, Toyota Motor Corporation, Volkswagen Group, Honda Motor Co., Ltd., Daimler AG, BMW Group, Hyundai Motor Group, Nissan Motor Co., Ltd., Fiat Chrysler Automobiles (FCA), Kia Corporation, Volvo Group, Subaru Corporation, Mazda Motor Corporation, Jaguar Land Rover (JLR), Tesla, Inc., Navistar International Corporation, PACCAR Inc., Harley-Davidson, Inc., Caterpillar Inc., Bombardier Inc., Deere & Company, The Boeing Company, Textron Inc., Harley-Davidson, Inc.
GAO RFID Inc. has deployed RFID, BLE and IoT projects for many companies in transportation equipment manufacturing industry, including many in its various divisions such as
- Automotive Manufacturing: This division focuses on the production of automobiles, including passenger cars, trucks, and commercial vehicles.
- Aerospace Manufacturing: It involves the design and manufacture of aircraft, spacecraft, and related components.
- Motorcycle Manufacturing: This sub-industry specializes in the production of motorcycles and related two-wheeled vehicles.
- Railroad Rolling Stock Manufacturing: It involves the production of locomotives, passenger and freight railcars, and other railway-related equipment.
- Ship and Boat Building: This division includes the construction of ships, boats, and other waterborne vessels, such as cruise ships, cargo vessels, and naval vessels.
- Electric Vehicle Manufacturing: With the rise of electric vehicles, this sub-industry focuses on producing electric cars, buses, and related components.
- Bicycle Manufacturing: This sub-industry involves the production of bicycles and related accessories.
- Spacecraft and Satellite Manufacturing: It focuses on the construction of spacecraft, satellites, and other space-related equipment.
- Commercial and Military Vehicle Manufacturing: This includes the production of commercial trucks, military vehicles, and armored vehicles.
- Other Transportation Equipment Manufacturing: This category encompasses various other transportation-related products, such as trailers, recreational vehicles (RVs), and specialty vehicles.
GAO’s technologies enable its customers in transportation equipment manufacturing to effectively track their workforces such as Assembly Line, Chassis, Welding, Fabrication, CNC Machining, Robotics, Injection Molding, OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer), Lean Manufacturing, Quality Control (QC), Safety Protocols, Materials Handling, Testing and Inspection, Supply Chain Management, CAD (Computer-Aided Design), Machinist, Technician, Welder, Painter, Engineer, and many more and effectively track operational assets such as conveyor belts, hydraulic presses, CNC machines, robotic arms, welding machines, assembly lines, paint booths, injection molding machines, stamping presses, CNC routers, 3D printers, material handling equipment, tube bending machines, laser cutting machines, plasma cutters, shearing machines, roll forming machines, powder coating ovens, sandblasting cabinets, and lathe machines. These tools and machines play a crucial role in manufacturing automobiles, trucks, aircraft, and trains, ensuring the efficient production of transportation equipment.
Here are some of the leading companies in sub-industry industry GAO has served:
- Ford Motor Company
- General Motors Company
- The Boeing Company
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Harley-Davidson, Inc.
- Tesla, Inc.
- Bombardier Inc.
- Magna International Inc.
- BRP Inc. (Bombardier Recreational Products)
- Linamar Corporation
- Wescast Industries Inc.
- New Flyer Industries Inc.
- Autoliv Mexico
- Delphi Technologies (Mexico)
- Lear Corporation (Mexico)
- Faurecia Mexico
- Grupo Bimbo (manufactures delivery vehicles)
- Volaris (manufactures some aircraft components)
- Volkswagen Group
- Daimler AG (Mercedes-Benz)
- BMW Group
- Airbus SE
- Rolls-Royce Holdings plc
- Safran S.A.








![]()















You Are Invited to Contact Us!
If you are interested in our products, services or partnering with us, please feel free to contact us by filling out this form:
or email us at sales@gaorfid.com
