
Index
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for utility construction
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of utility construction
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
Case Studies of RFID, IoT & Drone Applications
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for utility construction
Overview
The utility construction industry focuses on designing, installing, and maintaining crucial infrastructure systems like water, electricity, gas, telecommunications, and transportation networks. It involves specialized equipment, compliance with strict regulations, and a commitment to safety and environmental considerations. This industry plays a pivotal role in providing essential services, supporting economic growth, and adapting to technological advancements while addressing the needs of both public and private projects.
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in utility construction Industry to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials and operational equipment such as specialized equipment to efficiently and safely complete projects. Common equipment includes excavators, backhoes, bulldozers, trenchers, and directional drills for groundwork, while utility trucks, bucket trucks, and cranes assist in transporting materials and working at height. Pipe fusion equipment, compactors, and hydraulic jacks aid in utility installation and foundation preparation. Surveying tools, trenchless technology equipment, and safety gear are crucial for precision, safety, and compliance. Additionally, generators, communication devices, utility locators, and environmental monitoring instruments play vital roles in ensuring smooth operations and minimizing disruptions during the construction of essential utility infrastructure.
Ranked as one of the top 10 global RFID suppliers, GAO RFID Inc. is based in New York City, U.S. and Toronto, Canada. GAO offers a comprehensive selection of UHF, HF (including NFC) and LF RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags, BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. Such RFID and BLE products and systems, as well as its IoT and drone technologies, have been successfully deployed for utility construction. Its sister company, GAO Tek Inc. https://gaotek.com, is a leading supplier of industrial or commercial testers and analyzers, drones, and network products.
The targeted markets of both GAO RFID Inc. and GAO Tek Inc. are North America, particularly the U.S., Canada, Mexico, and Europe. As a result, this website gaorfid.com is offered in English and other major languages of North America and Europe such as Spanish, French, German, Italian, Polish, Ukrainian, Romanian, Russian, Dutch, Turkish, Greek, Hungarian, Swedish, Czech, Portuguese, Serbian, Bulgarian, Croatian, Danish, Finnish, Norwegian, Slovak, Catalan, Lithuanian, Bosnian, Galician, Slovene, Latvian, Estonian, Welsh, Icelandic, and Irish.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for utility construction
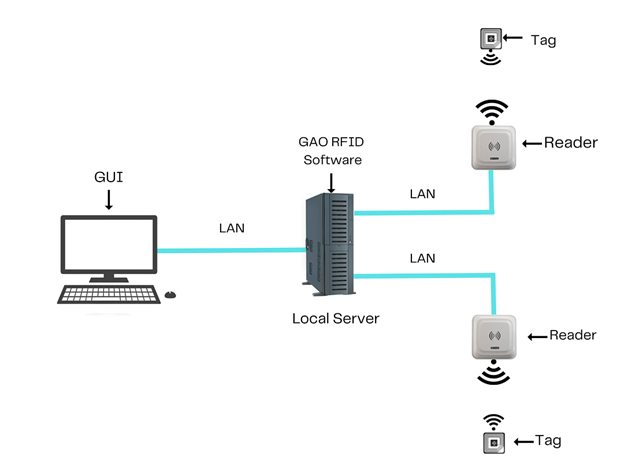
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID Systems for utility construction are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server that normally is on our client’s premises, and another version runs in the cloud. The cloud server could be GAO’s cloud server, client’s own cloud server or a cloud server from one of the leading cloud server providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud (formerly SoftLayer), Oracle Cloud, RedHat, Heroku, Digital Ocean, CloudFlare, Linode and Rackspace. The above illustrates GAO system for utility construction software running on a local server
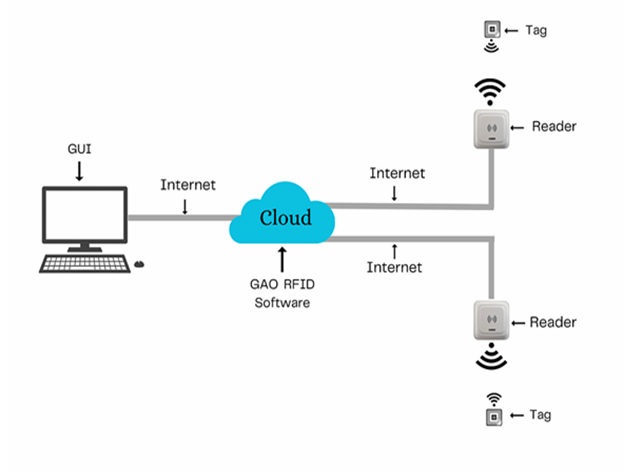
The above illustrates GAO system for utility construction with its software running in cloud.
GAO’s RFID and BLE technologies, consisting of RFID readers, RFID tags, BLE gateways, BLE beacons, software, cloud services and their systems, have the following applications in utility construction industry:
- Asset Tracking: Utilizing our RFID tags can be attached to construction equipment, tools, and materials, allowing companies to monitor their location and usage in real-time. This helps prevent loss or theft and ensures that assets are deployed effectively.
- Inventory Management: Utilizing our RFID enables automated inventory control by tracking the quantities and status of materials and supplies on construction sites. This reduces the risk of running out of essential resources and streamlines procurement processes.
- Personnel Tracking: Utilizing our RFID badges or wearable tags can be issued to workers, enabling real-time monitoring of their presence on job sites. This enhances safety by ensuring that the right personnel are in the correct location, and it can assist in emergency evacuation procedures.
- Access Control: Utilizing our RFID-based access control systems can restrict entry to specific areas of a construction site, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive or hazardous zones. This enhances security and safety.
- Tool Management: Utilizing our RFID tags on tools enable easy tracking and monitoring of tool usage. This helps prevent tool loss, reduces downtime, and ensures that tools are properly maintained.
- Equipment Maintenance: Utilizing our RFID technology can be used to schedule and track equipment maintenance. Maintenance history and service schedules can be easily accessed, leading to improved equipment reliability and reduced downtime.
- Material Authentication: Our RFID tags can be used to authenticate construction materials, ensuring that only approved and high-quality materials are used in projects. This helps maintain construction quality and safety standards.
- Workforce Safety: Our RFID-enabled personal protective equipment (PPE) can monitor workers’ safety gear usage. Alerts can be triggered if workers are not wearing required safety gear, promoting a safer work environment.
- Site Access Records: Our RFID systems can automatically log the entry and exit of vehicles and personnel on a construction site, creating an accurate record of site activities. This can be valuable for project management and compliance reporting.
- Tool and Equipment Security: Our RFID technology can be integrated into anti-theft systems for tools and equipment. Stolen items can be easily tracked and identified, aiding in recovery efforts.
- Supply Chain Visibility: Our RFID tags can be used to monitor the movement of construction materials and equipment through the supply chain, from suppliers to construction sites, enhancing logistics and reducing delays.
- Construction Site Efficiency: Our RFID can be used to optimize workflows and logistics on construction sites, helping project managers make informed decisions based on real-time data.
- Quality Control: Our RFID tags can be used to track and verify the quality of construction components and materials, ensuring that they meet project specifications and regulatory standards.
GAO’s drone technologies find the following applications in utility construction industry:
- Surveying and Mapping: GAO’s Drones equipped with LiDAR, photogrammetry, or GPS technology can quickly survey construction sites and create accurate topographic maps, helping with site planning and design.
- Site Inspection: GAO’s Drones enable close-up inspections of construction sites, structures, and utility assets, identifying potential issues, such as equipment damage or safety hazards, without the need for manual inspection.
- Progress Monitoring: GAO’s Aerial imagery captured by drones provides a visual record of construction progress, allowing project managers to assess work completion and identify any delays or discrepancies.
- Safety Inspections: GAO’s Drones can access challenging or hazardous areas, such as tall structures or remote locations, to conduct safety inspections and identify potential risks.
- Asset Inventory: GAO’s Drones can be used to create inventories of utility assets, such as power lines, transformers, and substations, ensuring accurate record-keeping and maintenance planning.
- Environmental Monitoring: Utilizing Our Drones can collect data on environmental conditions in and around construction sites, helping with compliance and mitigating potential environmental impacts.
- Security Surveillance: Drones equipped with our cameras and sensors can monitor construction sites for unauthorized access, theft, and vandalism, enhancing security.
- Communication Infrastructure: Utilizing Our Drones can inspect and maintain cell towers, antennas, and other communication infrastructure, ensuring optimal performance and reducing downtime.
- Power Line Inspection: Our Drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras can detect hotspots and potential issues in power lines, helping prevent electrical failures and fires.
- Vegetation Management: Our Drones can assess vegetation encroachment near utility lines and help plan and execute vegetation management strategies.
- Emergency Response: Our Drones can rapidly assess damage and access disaster-stricken areas following natural disasters, facilitating quicker response and recovery efforts.
- Material Transport: Our Some specialized drones can transport lightweight materials, tools, or equipment to remote or inaccessible locations on construction sites.
- Quality Control: Our Drones can capture high-resolution images and videos for quality control purposes, helping ensure that construction work meets specifications and standards.
- Documentation and Reporting: Our Drones can automatically generate reports, including visual documentation of construction phases, which can be useful for compliance, audits, and reporting to stakeholders.
- Training and Simulation: Our Drones can be used in training simulations for operators of heavy machinery or utility equipment, providing a safe and controlled learning environment.
- Data Analysis: The data collected by our drones can be processed and analyzed to extract valuable insights, such as 3D models, volumetric measurements, and trends in construction progress.
GAO’s IoT technologies, consisting of IoT sensors, sensors networks and systems, find the following applications in the utility construction industry:
- Equipment Monitoring: GAO’s IoT sensors can be placed on construction equipment and machinery to monitor their status, performance, and usage in real-time. This data helps schedule maintenance, prevent breakdowns, and optimize equipment utilization.
- Asset Tracking: GAO’s IoT-enabled tracking devices are used to monitor the location and condition of construction assets, including tools, materials, and equipment. This reduces loss, theft, and inefficiencies in asset management.
- Safety Management: GAO’s Wearable IoT devices, such as smart helmets and vests, can track worker movements and vital signs, providing real-time safety alerts and ensuring compliance with safety protocols.
- Environmental Monitoring: GAO’s IoT sensors can measure and report environmental conditions on construction sites, such as temperature, humidity, air quality, and noise levels, helping ensure compliance with regulations and worker safety.
- Energy Management: GAO’s IoT can optimize energy consumption on construction sites by controlling lighting, heating, and cooling systems based on occupancy and usage patterns, reducing energy costs and environmental impact.
- Site Security: GAO’s IoT cameras, motion detectors, and access control systems enhance security by monitoring construction sites 24/7 and sending alerts in case of unauthorized access or suspicious activity.
- Fleet Management: Our IoT devices on vehicles and construction machinery provide real-time location data, fuel consumption, and maintenance alerts, allowing for efficient fleet management and route optimization.
- Remote Equipment Control: Our IoT allows remote monitoring and control of construction equipment, enabling operators to start, stop, or adjust machinery settings from a centralized location.
- Supply Chain Management: Our IoT sensors on shipments and materials enable real-time tracking of deliveries, helping manage inventory, reduce theft, and ensure materials arrive on time.
- Predictive Maintenance: Our IoT analytics can predict equipment failures based on sensor data, allowing proactive maintenance to prevent costly breakdowns and downtime.
- Inventory Management: Our RFID and IoT technologies can track and manage construction materials and supplies, automating inventory control and reducing waste.
- Drone Integration: Our IoT can facilitate communication between drones and ground-based equipment, enabling autonomous flight for tasks like surveying, inspection, and site monitoring.
- Communication Infrastructure: Our IoT sensors can monitor the condition and performance of communication infrastructure, such as cell towers and fiber-optic networks, ensuring uptime and quality of service.
- Quality Control: Our IoT devices can capture data related to construction quality, such as temperature, humidity, and material properties, ensuring compliance with project specifications.
- Data Analytics: Our IoT-generated data can be analyzed to identify trends, optimize workflows, and make informed decisions for project management and resource allocation.
- Emergency Response: Our IoT sensors can detect hazardous conditions or incidents on construction sites and automatically trigger emergency response protocols.
- Smart Building Integration: In utility construction, Our IoT devices can be integrated into the final utility structures (e.g., substations) to monitor performance, detect faults, and remotely control systems.
GAO Helps Customers Comply with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of utility construction
GAO RFID Inc. has helped many companies in utility construction to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with the applicable industry standards, mandates and government regulations:
RFID, BLE, IoT, & Drone Standards & Mandates
- ISO 18000
- EPC Gen2
- ISO 15693
- ISO 14443
- ISO 17367
- ISO 18046
- ASTM E-53
- IEC 62690
- IEEE 1902.1
- Bluetooth 4.0
- Bluetooth 4.1
- Bluetooth 4.2
- Bluetooth 5
- Bluetooth 5.1
- Bluetooth 5.2
- Bluetooth Mesh
- Bluetooth SIG (Special Interest Group)
- Bluetooth Profiles
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol)
- OPC UA (Unified Architecture)
- LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network)
- Sigfox
- 6LoWPAN (IPv6 over Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Networks)
- Thread
- Z-Wave
- BACnet (Building Automation and Control Networks)
- Modbus
- IEEE 802.15.4
- IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi)
- OGC (Open Geospatial Consortium) SensorThings API
- OMA LWM2M
- AllJoyn
- UPnP (Universal Plug and Play)
- Bluetooth Mesh
- KNX
- DNP3
- IEC 61850
- ASTM F2910
- ASTM F3002
- ASTM F3178
- ASTM F3266
- ASTM F3322
- ISO 21384-3
- ISO 21384-2
- ISO 21384-1
- ISO 23665
- RTCA DO-362
- RTCA DO-375
- RTCA DO-389
- RTCA DO-328
US. Government Regulations
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Regulations
- Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) Regulations
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Regulations
- Department of Transportation (DOT) Regulations
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Regulations
- National Electrical Safety Code (NESC)
- Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) Regulations
- S. Army Corps of Engineers Regulations
- Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) Regulations
- Bureau of Land Management (BLM) Regulations
- Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) Regulations
- Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Regulations
- Department of the Interior (DOI) Regulations
- Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) Regulations
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Regulations
Canadian Government Regulations
- Canadian Occupational Health and Safety Regulations
- Canadian Environmental Protection Act (CEPA) Regulations
- Canadian Energy Regulator Act (CERA) Regulations
- Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) Regulations
- Canadian Transportation Agency (CTA) Regulations
- National Energy Board (NEB) Regulations
- Canadian Electrical Code (CEC)
- Canadian Standards Association (CSA) Regulations
- Canada Labour Code Regulations
- Canada Infrastructure Bank (CIB) Regulations
- Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) Regulations
- Transport Canada Regulations
- Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO) Regulations
- Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC) Regulations
- Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) Regulations
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in utility construction such as:
Personnel Management:
- Workforce scheduling and resource allocation.
- Safety training and certification tracking.
- Employee performance monitoring and evaluation.
- Payroll and timekeeping systems.
- Health and wellness programs for workers.
Equipment Management:
- Preventive maintenance scheduling and tracking.
- Equipment utilization and downtime monitoring.
- Equipment location tracking (GPS and RFID).
- Fuel consumption tracking.
- Inventory management for spare parts and components.
- Telematics for real-time monitoring of machinery.
Access Control:
- Secure access to construction sites and facilities.
- Visitor and contractor management systems.
- Biometric authentication for workers.
- Surveillance systems and intrusion detection.
- Mobile access control using smartphones.
Warehouse Management:
- Inventory tracking and management.
- Automated picking and packing systems.
- Demand forecasting and order optimization.
- Material handling and storage solutions.
- RFID technology for real-time inventory updates.
Supply Chain Management:
- Supplier relationship management.
- Procurement and vendor management.
- Transportation and logistics optimization.
- Demand planning and forecasting.
- Track and trace solutions for materials and equipment.
- Supplier diversity and sustainability programs.
Other Applications:
- Project management and scheduling software.
- Drone technology for site inspections and surveying.
- Environmental monitoring and compliance management.
- GIS (Geographic Information Systems) for mapping and geospatial analysis.
- Data analytics for project performance and decision-making.
- Mobile apps for field data collection and reporting.
- IoT sensors for monitoring environmental conditions, equipment, and materials.
GAO has enabled its customers to make use of some of the leading software and cloud services in the utility construction industry. Below are some of the popular software and cloud services in the utility construction industry.
Leading commercial software for personnel management in the utility construction industry includes SAP SuccessFactors, Oracle HCM Cloud, Workday HCM, BambooHR, and ADP Workforce Now, offering various HR and workforce management features. For equipment management, utility construction companies can choose from solutions like Trimble Viewpoint, B2W Maintain, e-Builder, Infor EAM, Hippo CMMS, Asset Panda, and Samsara, each designed to streamline equipment maintenance, tracking, and utilization, contributing to efficient project operations. The choice of software depends on the specific needs and scale of the construction operations.
GAO has worked with some of the leading technology companies in utility construction to provide integrated RFID, BLE, IoT and drone solutions to customers. Here are some of the technology leaders in utility construction Trimble Inc., Bentley Systems, Autodesk, Aconex (Oracle Construction and Engineering Cloud), Procore, e-Builder (by Trimble), Hilti, Topcon Positioning Systems, Samsara, In Eight, Oracle Utilities, IBM, Esri, GE Digital, and Siemens Digital Industries Software, providing a range of software, hardware, and IoT solutions for project management, equipment tracking, asset management, and geospatial analysis tailored to the unique needs of utility construction projects.
Case Studies of RFID, IoT & Drone Applications
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Below are some RFID application cases in the utility construction industry.
Industry Associations Check with industry associations related to utility construction, such as the National Utility Contractors Association (NUCA) or the American Public Power Association (APPA). They may have published case studies or reports on RFID applications.
Government Agencies Explore websites of government agencies like the Department of Energy (DOE) or the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). They often provide case studies and reports related to utility construction and technology adoption.
Consult Industry Publications Look into industry-specific magazines, journals, and websites like Utility Contractor Magazine or Construction Executive. They often feature case studies and articles on technology implementations.
RFID technology providers, such as RFID manufacturers and solution providers, may have case studies on their websites showcasing how their RFID solutions have been used in utility construction projects.
Academic Institutions: Universities and research institutions may publish case studies or research papers related to RFID applications in construction, including utility construction.
Online Databases Utilize online databases like Google Scholar, ResearchGate, or academic journals’ websites to search for relevant case studies and research papers.
Government Agencies Check the websites of Canadian government agencies responsible for utility regulation and infrastructure development, such as Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) and provincial energy and utility authorities. They often publish case studies and reports related to technology implementations.
Industry Associations Explore websites and publications of industry associations like the Canadian Construction Association (CCA) and the Canadian Electricity Association (CEA). These organizations may feature case studies and articles on RFID applications in utility construction.
Utility Companies Visit the websites of Canadian utility companies, such as Hydro-Québec, BC Hydro, or Toronto Hydro. They may share case studies or success stories related to RFID technology adoption in their construction and maintenance projects.
Academic Institutions Canadian universities and research institutions may have conducted studies or published research papers on RFID applications in utility construction. Search academic databases and institutional websites.
RFID Solution Providers RFID technology vendors and solution providers often showcase case studies on their websites, demonstrating how their solutions have been used in utility construction projects in Canada
Trade Publications Look into industry-specific magazines, journals, and websites dedicated to construction, utilities, and technology in Canada. They may feature case studies and articles on RFID applications.
Online Databases Utilize online databases, academic search engines, and research platforms like Google Scholar, ResearchGate, or databases provided by academic institutions to search for relevant case studies and research papers.
Many applications of RFID by GAO can be found here
GAO RFID Commercial Construction Asset Management System| GAO RFID
Case Studies of IoT Applications
Below are some IoT application cases in the utility construction industry.
PG&E implemented IoT solutions to monitor and manage its electrical grid, reducing outage times and improving overall grid reliability.
Duke Energy used IoT devices to track the location and condition of utility poles and other assets, optimizing maintenance schedules and reducing costs.
SFPUC deployed IoT sensors to monitor water quality and distribution in its water utility system, improving water resource management and reducing leaks.
IoT sensors were used to monitor environmental factors such as air quality and weather conditions to support construction projects while minimizing environmental impacts.
BGE implemented IoT-based predictive maintenance for its gas pipelines to detect leaks and other issues before they became critical, enhancing safety and reducing repair costs.
SCE employed IoT cameras and sensors to remotely monitor construction sites, ensuring safety compliance and project progress tracking.
Various building owners and property management companies across the USA have adopted IoT-based REM systems to optimize energy consumption in commercial and residential buildings.
LADOT implemented IoT solutions to manage traffic flow, reduce congestion, and monitor road infrastructure for maintenance.
Numerous waste management companies have adopted IoT sensors in their dumpsters and collection vehicles to optimize waste collection routes and schedules.
Companies in the oil and gas sector have deployed IoT sensors to monitor pipelines for leaks, corrosion, and operational efficiency.
Utility companies like Hydro-Québec and BC Hydro may have implemented IoT solutions for grid management, including monitoring and optimizing the distribution of electricity.
Municipalities like the City of Toronto or City of Vancouver may have used IoT sensors to monitor water quality, detect leaks, and optimize water distribution systems.
Companies involved in the energy sector, such as Enbridge or TransCanada (now TC Energy), might have deployed IoT sensors to monitor the condition and safety of pipelines.
Utility construction companies and municipalities across Canada could have implemented IoT-based asset tracking systems to manage and maintain infrastructure like utility poles, transformers, and sewage systems.
Organizations responsible for environmental conservation may use IoT sensors to monitor air and water quality, as well as other environmental factors.
Municipalities like Montreal and Calgary could have adopted IoT technology to manage and optimize street lighting systems, reducing energy consumption and maintenance costs.
Construction companies in Canada may have used IoT cameras and sensors to remotely monitor construction sites, enhancing safety and project management.
Building owners, property managers, and government agencies may have implemented IoT systems to improve energy efficiency in residential and commercial buildings.
Companies involved in renewable energy projects, such as wind farms or solar installations, could have used IoT technology to monitor and optimize energy generation.
Municipalities and waste management companies may have adopted IoT solutions to optimize waste collection and recycling programs.
Case Studies of Drone Applications
Below are some drone application cases in the utility construction industry.
Southern Company, one of the largest utility holding companies in the USA, utilized drones to inspect power transmission lines. Drones equipped with cameras and sensors were employed to identify issues such as damaged insulators and vegetation encroachment.
Duke Energy used drones to inspect substations, enabling the assessment of equipment conditions, detecting defects, and improving worker safety.
Con Edison explored the use of drones for monitoring its vast network of infrastructure in New York City, including gas pipelines and electrical systems. Drones were employed to assess the condition of assets in hard-to-reach or hazardous locations.
Several wind energy companies across the USA have adopted drones to inspect wind turbines for damage and wear, increasing operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
Drones have been used to inspect solar panels in large solar farms, enabling early detection of issues such as panel damage and soiling.
Companies in the oil and gas sector have employed drones to inspect pipelines for leaks, corrosion, and structural integrity, enhancing safety and reducing maintenance costs.
PG&E used drones to assess the damage caused by wildfires, hurricanes, or other natural disasters, aiding in quick response and recovery efforts.
Drones were used for collecting geospatial data, creating 3D models, and mapping utility assets, aiding in planning and maintenance.
National Grid explored the use of drones for vegetation management around power lines, reducing the risk of outages caused by tree interference.
Dominion Energy has used drones to enhance worker safety by remotely inspecting areas that may pose risks to personnel.
Hydro-Québec, one of Canada’s largest electric utilities, has utilized drones to inspect transmission lines, assess equipment condition, and identify vegetation encroachment issues.
BC Hydro, the electricity distribution company in British Columbia, has explored drone technology for inspecting substations and other critical infrastructure, improving worker safety and efficiency.
Toronto Hydro has considered the use of drones for monitoring and inspecting its extensive electrical infrastructure, including power poles, transformers, and distribution lines.
OPG, which operates hydroelectric power stations, has used drones to inspect dam structures, ensuring their integrity and safety.
Wind energy companies across Canada have employed drones to inspect wind turbines, reducing operational downtime and maintenance costs.
Drones have been used to inspect solar panel arrays in large solar farms, detecting issues such as panel damage and soiling.
Enbridge, a major energy transportation company, has employed drones for pipeline inspections, detecting leaks and assessing pipeline conditions.
Various government agencies and environmental organizations in Canada have used drones to monitor and assess natural habitats, water quality, and environmental changes near utility construction sites.
Drones have been used in emergency response scenarios, including assessing damage caused by natural disasters or accidents in utility infrastructure.
Engineering and construction firms have employed drones for data collection, mapping, and creating 3D models to aid in utility construction and maintenance projects.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for utility construction
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including utility construction.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including utility construction.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including utility construction:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including utility construction:
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including utility construction:
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including residential building construction:
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
Digital I/O adapters:
and relay Controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
- UHF 860-960 MHz RFID Modules
- 13.56 MHz High Frequency RFID Modules
- 125 kHz Low Frequency RFID Reader Modules
In collaboration with its sister company GAO Tek Inc, a wide selection of high-quality drones is offered:
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in utility construction:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include
Utility construction relies on a range of specialized equipment to install, maintain, and repair vital infrastructure components like electricity, water, gas, and telecommunications. This equipment includes backhoes, excavators, trenchers, directional drills, utility trucks, hydro excavators, bucket trucks, cranes, towers, concrete mixers, cable reel trailers, pipe benders, fusion welding equipment, surveying tools, duct rodders, line locators, ground-penetrating radar, pavement cutters, and various safety gear. These tools and machines facilitate safe and efficient utility line installations, excavation, maintenance, and repair, ensuring the reliability of essential services.
People or workers tracking system:
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
Furthermore, GAO provides the customization of RFID tags, RFID readers, BLE beacons and BLE gateways, IoT, drones, and systems and consulting services for utility construction and for various industries in all metropolitans in North America, particularly the U.S., Canada and Mexico, and Europe:
GAO Makes Efforts to Satisfy Customers
Large Choice of Products
In order to satisfy the diversified needs of their corporate customers, GAO RFID Inc. and its sister company GAO Tek Inc. together offer a wide choice of RFID, BLE, IoT, drones, testing and measurement devices, and network products.
Overnight Delivery
In order to shorten the delivery to our customers, GAO has maintained a large stock of its products and is able to ship overnight within continental U.S. and Canada, and fast delivery to anywhere in Mexico and Europe from the nearest warehouse.
Local to Our Customers
We are located in both the U.S. and Canada. We travel to customers’ premises if necessary. Hence, we provide a very strong local support to our customers in North America, particularly the U.S., Canada and Mexico, and Europe. Furthermore, we have built partnerships with some integrators, consulting firms and other service providers in different cities to further strengthen our services. Here are some of the service providers in utility construction we have worked with to serve our joint customers:
- IBM
- Siemens
- GE Digital
- Schneider Electric
- ABB
- Oracle Utilities
- SAP
- Trimble
- Bentley Systems
- Black & Veatch
- Wipro
- Capgemini
- Cognizant
- Eaton
- HCL Technologies
GAO Has Served utility construction Extensively
GAO RFID Inc. and its sister company GAO Tek Inc. together offer a wide choice of RFID, BLE, IoT, drone, testing and measurement devices, and network products.
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in utility construction Industry to achieve success in the utility construction industry, several trends and buzzwords have been prominent as of my last update in September 2021. Key trends include the adoption of smart grid technology, integration of renewable energy sources, digital twins for asset management, IoT and sensor utilization, predictive maintenance through data analytics, grid resilience enhancement, grid modernization initiatives, energy storage solutions, microgrid development, and the expansion of electric vehicle infrastructure. Buzzwords encompass concepts like smart cities, digital transformation, grid edge, decentralized energy, distributed energy resources (DERs), resilience, demand response, 5G connectivity, blockchain, cybersecurity, big data analytics, edge computing, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), circular economy, hydrogen economy, and climate resilience, all reflecting the industry’s evolution toward digitalization, sustainability, and adaptability to changing energy landscapes.
GAO RFID Inc. has deployed RFID, BLE and IoT projects for many companies in utility construction, including many in its various divisions such as
- Electrical Utility Construction: This division focuses on the installation, maintenance, and repair of electrical infrastructure, including power generation, transmission, and distribution systems.
- Gas Utility Construction: Gas utility construction companies specialize in the installation and maintenance of natural gas distribution systems, pipelines, and related facilities.
- Water and Wastewater Utility Construction: These companies are involved in the construction and maintenance of water supply systems, sewage treatment plants, water mains, and wastewater collection systems.
- Telecommunications Utility Construction: This division deals with the installation of telecommunications infrastructure, including fiber-optic networks, cell towers, and broadband connectivity.
- Renewable Energy Construction: Renewable energy construction focuses on the development of clean energy sources such as wind farms, solar installations, and hydroelectric projects.
- Cable and Internet Infrastructure Construction: Companies in this sector specialize in laying cable and internet infrastructure, including coaxial and fiber-optic cable networks.
- Utility Line Clearance: This sub-industry involves tree trimming and vegetation management along utility lines to prevent outages and ensure safety.
- Underground Utility Construction: Underground utility construction companies specialize in the installation of utility lines, conduits, and pipes below ground, reducing visual impact and enhancing safety.
- Utility Facility Maintenance: These companies provide ongoing maintenance and repair services for utility infrastructure, ensuring its continued reliability and safety.
- Utility Asset Management: Asset management firms focus on monitoring and optimizing the performance and lifespan of utility assets through data-driven strategies.
- Environmental Remediation: This division deals with the cleanup and restoration of contaminated sites, often related to past utility operations.
- Smart Grid and Grid Modernization: Companies in this sub-industry work on modernizing electrical grids and implementing smart grid technologies for improved efficiency and reliability.
- Emergency Response and Disaster Recovery: These organizations specialize in rapid response and recovery efforts during emergencies, such as natural disasters or system failures.
- Drone and Technology Services: This sector provides technological solutions, including drone services, GIS (Geographic Information Systems), and IT integration, to enhance utility construction and operations.
- Energy Efficiency and Conservation: Companies in this field focus on initiatives to reduce energy consumption and enhance sustainability, often through infrastructure upgrades.
- Safety and Training Services: Organizations specializing in safety training and consulting for utility construction workers to ensure adherence to safety regulations.
GAO’s technologies enable its customers in “utility construction” to effectively track their workforces such as workers assume various roles crucial to the planning, installation, and maintenance of utility infrastructure. Lineworkers oversee electrical lines, pipefitters manage pipes and pipelines, while utility technicians handle inspections and maintenance. Heavy equipment operators operate machinery, surveyors ensure precise placements, and project managers coordinate projects. Civil engineers design infrastructure, environmental specialists address regulations, and safety coordinators enforce safety protocols. Equipment mechanics maintain machinery, drone operators gather aerial data, and GIS technicians manage spatial information. Cable installers handle telecommunications infrastructure, concrete finishers work with concrete, and welders join metal components. Traffic control technicians manage site traffic, and emergency response specialists deal with crises. Quality control inspectors assess project compliance, utility arborists manage vegetation, and laborers provide general support, all contributing to the industry’s success respectively track operational assets such as Operational equipment in utility construction includes backhoes, excavators, trenchers, directional drills, utility trucks, hydro excavators, bucket trucks, cranes, cable plows, concrete mixers, cable reel trailers, pipe benders, fusion welding equipment, duct rodders, line locators, ground penetrating radar (GPR), pavement cutters, surveying equipment, utility pole setters, jackhammers, compactors, bulldozers, aerial lifts, graders, air compressors, and various specialized tools, all crucial for tasks ranging from excavation and trenching to installation and maintenance of utility infrastructure.
Here are some of the leading companies in utility construction industry GAO has served:
- Aecon Group Inc.
- SNC-Lavalin Group Inc.
- EPCOR Utilities Inc.
- Valard Construction LP
- Black & McDonald
- Alectra Utilities
- Ledcor Group
- Hydro-Québec
- Northland Utilities
- EllisDon Corporation
- Graham Construction
- Stantec
- Siemens Canada
- TELUS Communications
- Enbridge Inc.
- SaskPower
- Horizon Utilities
- Fortis Inc.
- Emera Inc.
- FortisAlberta Inc
- AECOM
- Black & Veatch
- Michels Corporation
- Burns & McDonnell
- Power Engineers
- ABB
- Quanta Services
- GZA GeoEnvironmental, Inc.
- Bechtel Corporation
- MasTec
- HDR
- Henkels & McCoy Group
- TRC Companies, Inc.
- NPL Construction Co.
- Atlantic Engineering Group
- American Infrastructure
- Kiewit Corporation
- The Middlesex Corporation
- New York Power Authority (NYPA)
- National Grid
- Verizon Communications
- Eversource Energy
- PSEG (Public Service Enterprise Group)
- Consolidated Edison (Con Edison)
- Cianbro Corporation
- Eversource Communications
- Stantec
- Avalon Building Systems
- Parsons Corporation
- CCMSI (Central Claims Management Services)






























You Are Invited to Contact Us!
If you are interested in our products, services or partnering with us, please feel free to contact us by filling out this form:
or email us at sales@gaorfid.com
