Index for Contents on This Page:
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for the medical and diagnostic laboratories
Case studies of RFID applications
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for the medical and diagnostic laboratories
GAO has served the medical and diagnostic laboratories extensively
Related Products & Systems on Other Pages on This Website
GAO RFID Medical Diagnostic Laboratories Asset Management System
GAO RFID Diagnostic Imaging Services Asset Management System
Hands Free Access Control For Institutions & Manufacturing
BLE | Bluetooth Low Energy | BLE Gateways & Beacons – GAO RFID
RFID Readers | Buy RFID Readers | RFID Reader Writers – GAO RFID
RFID Tags | Buy RFID Tags – GAO RFID
Temperature RFID Tags | Temperature Sensing RFID Tags- GAO RFID
High-Temperature Tolerant RFID Tags
Overview
The medical and diagnostic laboratories industry analyzes patient samples to diagnose diseases, monitor health, and support medical treatment and research. These labs conduct tests on blood, urine, tissue, and body fluids, providing timely diagnostic information. They play a vital role in disease detection, prevention, and management. Regulatory oversight ensures quality and safety. Technological advancements and automation enhance efficiency and accuracy, leading to improved patient care and outcomes.
GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone technologies have helped its customers in the Medical and diagnostic laboratories industry to improve their work processes, their operations and productivity by better management of their staff, materials and operational equipment such as centrifuges, microscopes, spectrophotometers, autoclaves, incubators, refrigerators, freezers, pipettes, PCR machines, DNA sequencers, blood analyzers, hematology analyzers, chemistry analyzers, coagulation analyzers, urine analyzers, microbiological culture systems, flow cytometers, tissue processors, cryostats, immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining systems, ELISA readers, electrophoresis systems, imaging systems (X-ray, MRI, CT scan), ultrasound machines, endoscopes, surgical instruments, laboratory information management systems (LIMS), and safety equipment (gloves, lab coats and goggles).
Ranked as one of the top 10 global RFID suppliers, GAO RFID Inc. is based in New York City, U.S. and Toronto, Canada. GAO offers a comprehensive selection of UHF, HF (including NFC) and LF RFID (radio frequency identification) readers and tags, BLE (Low Energy Bluetooth) gateways and beacons, and various RFID and BLE systems such as people tracking, asset tracking, access control, parking control, fleet management, WIP (work in progress), traceability. Such RFID and BLE products and systems, as well as its IoT and drone technologies, have been successfully deployed for the Medical and diagnostic laboratories industry.
Applications & Benefits of GAO’s RFID, BLE, IoT & Drones for the Medical and Diagnostic Laboratories
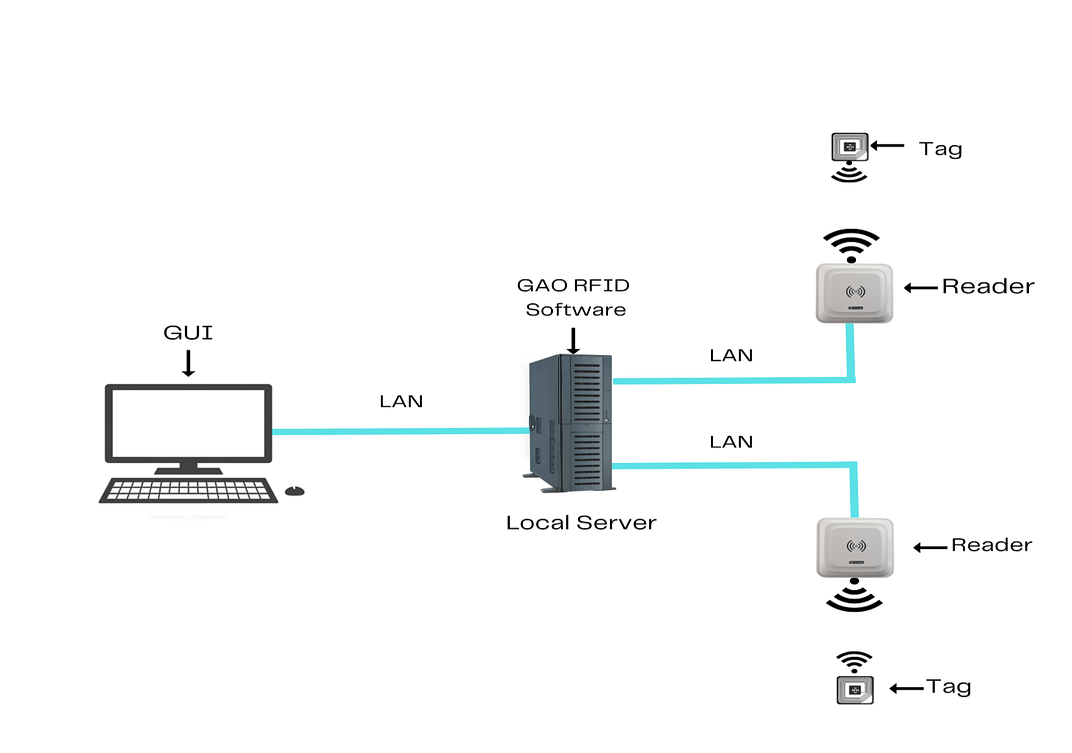
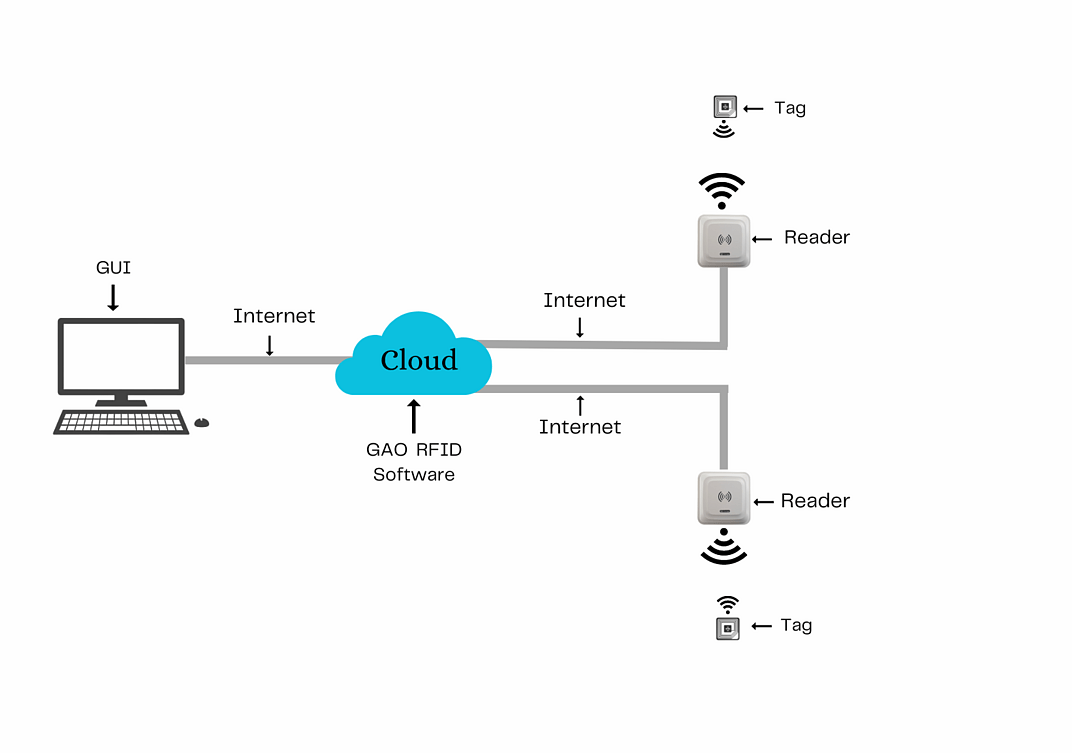
To satisfy its customers, GAO’s RFID or RFID systems for the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry are offered in 2 versions. One version is that its software is running on a local server, and another version is that its software runs in the cloud. The above illustrates GAO system for the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry with its software running on a local server.
GAO’s RFID technologies bring the many benefits to the medical and diagnostic laboratories:
- Enhanced Inventory Management: GAO’s RFID enables real-time tracking of medical supplies, equipment, and reagents, minimizing stockouts, optimizing storage, and improving overall inventory management efficiency.
- Streamlined Workflow: With our RFID technology, medical and diagnostic laboratories experience streamlined processes, as RFID tags facilitate automated data capture, reducing manual errors and enabling seamless workflow management.
- Improved Patient Safety: GAO RFID ensures accurate patient identification, reducing the risk of errors in sample collection, testing, and medication administration, thereby enhancing patient safety and preventing potential medical errors.
- Increased Traceability and Compliance: Leveraging our RFID solutions, medical laboratories can effortlessly track and trace samples, medications, and instruments, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and enhancing quality control measures.
- Efficient Asset Tracking: By utilizing GAO’s RFID technology, laboratories can monitor and locate critical assets, such as lab equipment, specimens, and consumables, optimizing resource allocation and reducing operational costs.
- Enhanced Data Integrity: Our RFID solutions provide reliable and secure data capture, preserving the integrity of vital information throughout the laboratory processes, promoting accurate results, and facilitating data-driven decision-making.
GAO’s BLE technologies offer longer reading range and particularly attractive for applications with larger workspaces within the medical and diagnostic laboratories:
- Proximity-Based Tracking: GAO’s BLE technology enables precise tracking of medical equipment, ensuring efficient inventory management and minimizing the time spent searching for essential tools.
- Patient Monitoring: With our BLE solutions, healthcare professionals can remotely monitor patients’ vital signs and receive real-time alerts, facilitating timely interventions and personalized care.
- Asset Security: GAO BLE provides robust asset security by alerting staff if valuable equipment or supplies move beyond designated areas, preventing theft or loss.
- Improved Workflow Efficiency: Utilizing our BLE technology streamlines workflows by automating tasks such as patient check-ins, specimen tracking, and equipment maintenance, leading to increased operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Patient Experience: GAO BLE enables seamless patient navigation within medical facilities, guiding them to the right departments, reducing wait times, and improving overall satisfaction.
- Location-based Services: With GAO’s BLE, hospitals and clinics can offer location-based services such as indoor navigation, wayfinding, and personalized patient assistance, enhancing the overall healthcare experience.
GAO’s RFID and drone technologies are often combined and such solutions offer the following benefits to the medical and diagnostic laboratories:
- Rapid Sample Transportation: By integrating GAO’s RFID with drones, we enable swift and secure delivery of medical samples, reducing transportation time and ensuring timely diagnostics.
- Remote Area Access: Our RFID-equipped drones provide access to remote areas, facilitating the collection of samples from hard-to-reach locations, enhancing healthcare accessibility, especially in rural or disaster-stricken regions.
- Temperature Monitoring: GAO RFID integrated with drones allows continuous temperature monitoring during sample transportation, ensuring the integrity of sensitive specimens and medications.
- Emergency Response: With our RFID-enabled drones, we expedite the delivery of critical medical supplies and equipment to emergency sites, bolstering the efficiency and effectiveness of emergency response efforts.
- Cost Savings: Utilizing GAO’s RFID with drones optimizes logistics, reducing the need for manual transportation and minimizing operational costs associated with sample delivery and inventory management.
- Enhanced Tracking and Tracing: Integrating GAO RFID with drones enables real-time tracking and tracing of samples, providing end-to-end visibility throughout the transportation process, improving sample management, and reducing the risk of loss or misplacement.
Here are benefits of GAO’s IoT technologies to the medical and diagnostic laboratories:
- Real-time Monitoring: IoT empowers medical laboratories to monitor critical parameters such as temperature, humidity, and equipment performance in real time, ensuring optimal conditions for sample integrity.
- Predictive Maintenance: Leveraging our IoT solutions, laboratories can proactively monitor equipment health and receive alerts for maintenance, minimizing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: With IoT, healthcare providers can remotely monitor patients’ vital signs and health data, enabling timely interventions and personalized care, even from a distance.
- Data-driven Decision Making: IoT solutions collect and analyze vast amounts of data, enabling laboratories to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and improve overall performance and patient outcomes.
- Enhanced Security: IoT incorporates robust security measures, safeguarding sensitive patient information, protecting against unauthorized access, and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Seamless Integration: Integrating IoT seamlessly connects disparate systems, allowing for smooth data flow and interoperability among various devices and platforms within the laboratory environment.
GAO’s Assists Clients with Standards, Mandates & Regulations of the Medical and Diagnostic Laboratories
GAO RFID Inc. has developed its products and systems in compliance with industry standards and mandates. GAO has assisted our customers in the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry to deploy RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems and to ensure such deployments complying with applicable industry standards, U.S. government regulations and Canadian government regulations such as:
RFID, BLE, IoT, & Drone Standards & Mandates
- FDA UDI (Unique Device Identification): The U.S. FDA mandates RFID for tracking and identifying medical devices, ensuring traceability and enhancing patient safety.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): HIPAA sets privacy and security standards for patient data, including RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone usage in healthcare.
- Health Canada MDSAP (Medical Device Single Audit Program): MDSAP requires adherence to quality management systems, including RFID, BLE, IoT, and drone usage for medical devices.
- ISO 18000-6C: This global RFID standard ensures interoperability and compatibility of RFID tags and readers, promoting efficient data capture and tracking in healthcare settings.
- IEC 62304: This international standard governs the software lifecycle of medical device software systems, including those integrated with BLE, IoT, and drone technologies.
- NIST SP 800-53: NIST provides security and privacy controls for federal information systems in the U.S., covering IoT, RFID, BLE, and drone usage in healthcare.
- CSA Z317.10: This Canadian standard focuses on infection control during healthcare facility design and operations, including considerations for IoT, RFID, BLE, and drones.
- FAA Part 107: In the U.S., this regulation governs commercial drone operations, including drone usage for medical purposes, ensuring safety and compliance.
- ANSI (American National Standards Institute): ANSI is a U.S.-based non-profit organization that coordinates voluntary consensus standards development, accreditation, and conformity assessment services across various industries, promoting competitiveness and global harmonization.
- UL 2900: UL 2900 is a cybersecurity certification standard applicable to IoT devices and systems, ensuring secure implementation and protection against cyber threats.
- FCC Part 15: This regulation by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission governs radio frequency devices, including RFID and BLE, to ensure proper operation and interference prevention.
US.Government Regulations
- Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA): CLIA establishes quality standards for laboratory testing to ensure accurate and reliable results, safeguarding patient health and safety.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA protects patient privacy by setting standards for the secure handling and transmission of personal health information.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Conditions of Participation: CMS sets requirements for laboratories to participate in Medicare and Medicaid programs, ensuring compliance with quality standards and reimbursement criteria.
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Regulations: FDA regulates medical devices and diagnostic tests, ensuring their safety, effectiveness, and proper labeling for use in laboratories.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Standards: OSHA sets workplace safety regulations, including guidelines for handling hazardous materials and ensuring the well-being of laboratory personnel.
Canadian Government Regulations
- Medical Device Regulations (MDR): MDR ensures the safety and effectiveness of medical devices used in Canadian laboratories, including diagnostic equipment and testing reagents.
- Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA): PIPEDA governs the collection, use, and disclosure of personal health information, protecting patient privacy and promoting data security in healthcare.
- Food and Drugs Act and Regulations: These regulations provide oversight for medical devices, drugs, and natural health products used in Canadian laboratories, ensuring their safety and efficacy.
- Canadian Standards Association (CSA) Group’s Z902-15: Z902-15 sets standards for the handling, transportation, and storage of medical laboratory specimens, promoting safety and quality in specimen management.
- Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS): WHMIS ensures the safe handling, storage, and disposal of hazardous materials used in Canadian laboratories, protecting the health and safety of workers.
GAO Software Provides Easy Integration with API
GAO’s RFID and BLE software offers a free trial for both the server-based and cloud versions, and offers an API to the important systems in the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry such as:
Personnel Management:
- Employee Scheduling and Shift Management
- Training and Certification Tracking
- Performance Evaluation and Appraisal
- Staff Attendance and Time Tracking
- Skills and Competency Management
Equipment Management:
- Asset Tracking and Inventory Management
- Maintenance and Calibration Scheduling
- Equipment Utilization and Efficiency Monitoring
- Asset Lifecycle Management
- Equipment Service and Repair History Tracking
Access Control:
- Secure Access to Laboratory Facilities and Restricted Areas
- Visitor Management and Registration
- Biometric Identification for Authorized Personnel
- Access Logging and Audit Trail
- Integration with Security Systems (CCTV, Alarm Systems)
Warehouse Management:
- Storage Optimization and Space Utilization
- Inventory Tracking and Replenishment
- Barcode or RFID-based Item Identification
- Order Fulfillment and Pick-and-Pack Operations
- Automated Stock Reordering and Notifications
Supply Chain Management:
- Vendor Management and Procurement
- Supplier Evaluation and Performance Tracking
- Order Processing and Tracking
- Inventory Forecasting and Demand Planning
- Logistics and Distribution Management
Other Applications:
- Sample Tracking and Chain of Custody
- Quality Control and Compliance Management
- Lab Data Management and Integration with LIMS (Laboratory Information Management System)
- Research Project Management
- Document Control and Regulatory Compliance
GAO has integrated its RFID, BLE, IoT and drone systems with some of leading software and cloud services in the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry. Below are some of popular software and cloud services in the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry.
- Oracle PeopleSoft: A comprehensive human capital management software that streamlines personnel management, including recruitment, performance evaluation, and employee self-service.
- IBM Maximo: An enterprise asset management system that enables efficient equipment management, including maintenance scheduling, asset tracking, and inventory optimization.
- SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM): A cloud-based solution for warehouse management, offering real-time visibility, inventory control, and streamlined order fulfillment.
- JDA Software: A leading provider of supply chain management solutions, offering end-to-end visibility, demand planning, inventory optimization, and logistics management.
- Workday: A cloud-based human capital management platform that covers personnel management, including HR, payroll, talent management, and workforce planning.
- Infor CloudSuite WMS: A cloud-based warehouse management system that provides robust inventory control, order processing, and efficient warehouse operations.
- Epicor ERP: An enterprise resource planning solution with modules for supply chain management, inventory control, and order management.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management: A cloud-based solution for supply chain management, offering features like inventory control, demand planning, and supplier collaboration.
- Kronos Workforce Central: A workforce management system that enables personnel management, including time and attendance tracking, labor scheduling, and absence management.
- Netsuite: A cloud-based ERP system that integrates various modules, including supply chain management, warehouse management, and financial management.
- Salesforce: A leading customer relationship management (CRM) platform that offers solutions for supply chain management, inventory tracking, and order management.
- Zoho Inventory: A cloud-based inventory management software that provides features for inventory tracking, order management, and procurement.
GAO has worked with some of the leading technology companies in the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry in to provide integrated its RFID, BLE, IoT and drone solutions to customers. Here are some of the technology leaders in the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry:
- Roche Diagnostics: A leading information and technology company offering a wide range of diagnostic solutions, including laboratory instruments, reagents, and software for medical laboratories.
- Siemens Healthineers: A global medical technology company providing diagnostic imaging systems, laboratory diagnostics, and digital healthcare solutions for medical and diagnostic laboratories.
- Abbott Laboratories: A diversified healthcare company offering diagnostic solutions, including point-of-care testing devices, laboratory instruments, and informatics solutions.
- Bruker Corporation: A scientific research company and leading provider of scientific instruments and solutions for research, analysis, and diagnostics in life sciences and healthcare industries.
- Philips Healthcare: A leading electronic company offering advanced medical imaging systems, patient monitoring solutions, and healthcare informatics for diagnostic laboratories.
- BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company): A global medical technology company specializing in diagnostic systems, including specimen collection devices, laboratory instruments, and informatics solutions.
- Sysmex Corporation: A manufacturer of in vitro diagnostic equipment, including automated hematology analyzers, flow cytometry systems, and laboratory information systems.
- Beckman Coulter: A provider of biomedical testing instruments and systems, including clinical chemistry analyzers, immunoassay systems, and laboratory automation solutions.
- Cerner Corporation: A leading healthcare information technology company offering electronic health record systems, laboratory information systems, and data analytics solutions.
- Danaher Corporation: A manufacturer which offers a wide range of products and services specifically tailored for healthcare professionals, including diagnostic equipment, laboratory instruments, and innovative diagnostic solutions
- Olympus Corporation: A technology company specializing in medical and surgical equipment, including endoscopes, microscopes, and digital imaging systems used in diagnostic laboratories.
- PerkinElmer: A provider of analytical instruments, reagents, and informatics solutions for diagnostics, including genetic testing, environmental analysis, and drug discovery research.
Case Studies of RFID Applications
Below are some RFID application cases in the medical and diagnostic laboratories:
- Asset Tracking and Inventory Management: UPMC implemented an RFID-based asset tracking system to manage medical equipment in their laboratories. RFID tags were attached to equipment such as centrifuges, microscopes, and analyzers, allowing real-time tracking of their location and status. The system improved inventory management, reduced equipment loss, and streamlined workflow efficiency.
- Blood and Specimen Tracking: Toronto General Hospital implemented an RFID-enabled tracking system for blood and specimen samples. RFID tags were attached to sample containers, and RFID readers were placed at various points in the laboratory workflow. The system automated sample tracking, reduced errors, improved turnaround times, and enhanced patient safety.
- Laboratory Supply Chain Management: Mayo Clinic implemented an RFID-based supply chain management system for their laboratories. RFID tags were affixed to laboratory supplies and consumables, and RFID readers were installed at different supply chain points. The system enabled real-time inventory monitoring, streamlined procurement processes, reduced stockouts, and improved cost efficiency.
- Patient Flow and Asset Tracking: Mount Sinai Hospital deployed an RFID system to track patient flow and monitor high-value assets. RFID tags were embedded in patient wristbands, enabling real-time tracking of their location within the hospital. Additionally, RFID tags were attached to critical assets like infusion pumps and wheelchairs, facilitating their efficient allocation and reducing equipment search times.
- University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (USA): The University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) implemented UHF RFID technology to enhance laboratory operations. The RFID system facilitated automated sample tracking, inventory management, and improved efficiency in the laboratory setting.
- Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre (Canada): Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, located in Toronto, Canada, utilized UHF RFID to improve the accuracy and efficiency of specimen identification and tracking within their pathology laboratory. The RFID-enabled system enhanced patient safety and reduced the risk of misdiagnosis or errors.
GAO RFID Systems & Hardware for the medical and diagnostic laboratories
GAO RFID Inc. offers the largest selection of BLE gateways, BLE beacons, RFID readers, tags, antenna, printers, and integrated RFID systems for various industries, including the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
GAO offers advanced BLE gateways:
as well as versatile beacons with such important functions as temperature, humility, vibration and panic button:
GAO’s BLE technology is suitable for many industries, including the Medical and diagnostic laboratories industry.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of UHF RFID readers for various industries, including the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry:
GAO RFID offers the widest choice of UHF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry:
and an array of antennas to address different applications:
HF (High Frequency), NFC (Near Field Communications) and LF (Low Frequency) RFID
GAO offers the largest selection of HF, NFC, and LF RFID readers for various industries, including the Medical and diagnostic laboratories industry:
- High Frequency 13.56 MHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 134 kHz Passive RFID Readers
- Low Frequency 125 kHz Passive RFID Readers
HF, NFC and LF RFID tags, labels, badges, wristbands for various industries, including the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry:
and antennas:
GAO also offers RFID printers:
Digital I/O adapters:
and relay controllers:
For embedded applications, GAO offers UHF, HF and LF RFID reader modules:
- UHF 860 – 960 MHz RFID Modules
- 13.56 MHz High Frequency RFID Modules
- 125 kHz Low Frequency RFID Modules
The RFID systems by GAO are highly popular for clients in the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry:
Physical asset or operational equipment tracking system:
Assets that can be effectively tracked using GAO’s technologies include
- Microscopes: Used for examining cells, tissues, and microorganisms at high magnification.
- Centrifuges: Used to separate components of a liquid sample based on their density, such as blood components or cell cultures.
- Spectrophotometers: Instruments used to measure the absorption or emission of light by a sample, allowing analysis of chemical compounds, proteins, and nucleic acids.
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) machines: Used for DNA amplification and analysis, critical for various genetic tests and research.
- Flow cytometers: Instruments used to analyze and sort cells or particles based on their physical and chemical properties, often used in immunology and hematology.
- Incubators: Provide controlled temperature and environmental conditions for the growth and maintenance of cell cultures or microorganisms.
- Autoclaves: Used to sterilize equipment, media, and other laboratory materials using high-pressure steam.
- Electrophoresis equipment: Used to separate and analyze molecules, such as DNA or proteins, based on their size, charge, or other physical properties.
- Liquid chromatography systems: Instruments that separate, identify, and quantify components in a mixture, commonly used for drug analysis and biochemical research.
- Mass spectrometers: Instruments that measure the mass and composition of molecules, often used for analyzing complex biological samples, identifying biomarkers, and drug testing.
- Incubators: Provide controlled temperature and environmental conditions for the growth and maintenance of cell cultures or microorganisms.
- HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) systems: Used for separating, identifying, and quantifying compounds in a liquid sample, commonly used in pharmaceutical and clinical analysis.
People or workers tracking system:
Personnel or people access control system:
Parking or vehicle control system:
GAO Has Served the Medical and diagnostic laboratories Extensively
GAO’s products and technologies have helped its customers in the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry to achieve success in precision medicine, telehealth, big data analytics, AI and machine learning, digital pathology, genomic sequencing, point-of-care testing, wearable healthcare devices, blockchain technology, interoperability, data privacy and security, remote monitoring, patient-centric care, personalized diagnostics, virtual reality in healthcare, lab automation.
GAO RFID Inc. has deployed RFID, BLE and IoT projects for many companies in the medical and diagnostic laboratories industry, including many in its various divisions such as:
- Clinical Laboratories: These labs perform diagnostic testing on patient samples, including blood, urine, tissue, and genetic material, to aid in disease diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment.
- Pathology Laboratories: Pathology labs specialize in examining tissues, cells, and bodily fluids to diagnose diseases, determine the nature of tumors, and provide insights into the progression of diseases.
- Medical Imaging Centers: These facilities house diagnostic imaging equipment, such as X-ray, CT scan, MRI, ultrasound, and PET-CT scanners, to visualize internal structures and diagnose conditions.
- Reference Laboratories: Reference labs provide specialized testing services to support clinical laboratories and healthcare providers in diagnosing complex or rare conditions.
- Molecular Diagnostic Laboratories: These labs focus on genetic testing and molecular analysis to detect genetic disorders, identify specific genetic variations, and guide targeted treatments.
- Blood and Plasma Banks: These facilities collect, process, and store blood and plasma donations for transfusion or further manufacturing into blood products.
- Toxicology Laboratories: Toxicology labs specialize in analyzing samples to detect and quantify the presence of drugs, medications, or toxins in the body, often for forensic or occupational health purposes.
- Research and Development Laboratories: These labs conduct scientific research, develop new diagnostic techniques, explore innovative therapies, and contribute to advancements in medical knowledge and technology.
- Point-of-Care Testing Centers: These settings provide rapid diagnostic tests and immediate results at the patient’s bedside or in outpatient clinics, enabling quick decision-making and treatment.
- Forensic Laboratories: Forensic labs analyze evidence collected from crime scenes or accidents, applying scientific techniques to assist in criminal investigations and legal proceedings.
Here are some of the leading companies in the medical and diagnostic laboratories: